Yes, it is an event full of cosmological and astrophysical evidence that emerges on the horizon thanks to technological advances in the fields of observation and data reading both in the sky and on earth.
Recently, two studies on arXiv that are still in preprint discuss new clues about theories including: gravitational lensing, wrinkles in space, age and expansion rate of the universe. Learn more about studies and news about the universe.
Gravitational Lenses
At the heart of both studies is a discussion of an optical effect you’ve probably heard of: gravitational lensing. Light can be deflected when it passes near large celestial objects or gravitational fields.
This deviation of light can cause some anomalies for those observing from a distance. Likewise as Lenses commonly used in our daily lives can enlarge, reduce or even multiply an image, the same phenomenon occurs in space.
The existence of these lenses directly affects how we observe the universe because they can produce noise in the captured image and prevent ambitious analysis. Images of stars, galaxies, and other light sources may be distorted or distorted.
What we do not see, or see very little of, cannot be considered complete evidence of a theory. However, new developments emerge when we can observe more clearly or develop methods to mitigate these deviations.
‘Wrinkles’ in the Universe?
A very interesting pair of galaxies were discovered in the research conducted by the Indian Institute of Astrophysics. For the team, this duo is a candidate for the “cosmic rope” category.
According to theory, cosmic strings are one-dimensional defects in space-timeIt forms a fold, a crack that formed during the formation of the universe and remains frozen in time.
The pair “SDSSJ110429” is not the first candidate identified, but even if there are other examples there are some obstacles to proving the existence of strings. One of these is gravitational lenses, which can transform a single galaxy into a mirror system by copying images.
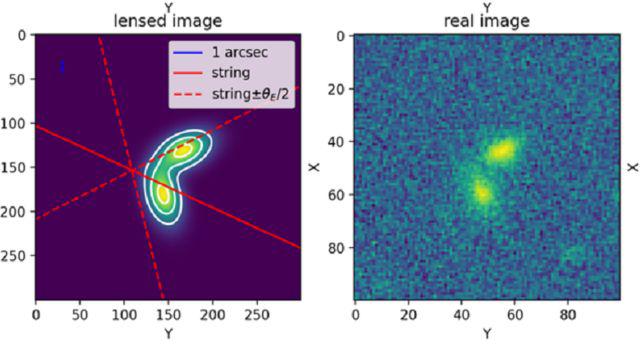
Other events may also produce data similar to those observed. Therefore it is still difficult to distinguish. between a real example of a cosmic string or another cosmic phenomenon.
However, if the theory is proven, it will be a new advance for astrophysics and much more can be discovered about the formation of the universe, how it expands, and whether it has boundaries.
Supernovae and the age of the universe
The James Webb Super Telescope (JWST) continues to make a splash in the field of physics. In one data set, a supernova called SN H0pe could give cosmology a new lease on life. SN H0pe is the second most distant supernova ever observed.
By comparing data from JWST with DDT (Director’s Discretionary Period) from the Space Telescope Science Institute, researchers from the University of Arizona discovered a supernova that may have exploded 10 billion years ago.

Due to its distance and the effect of gravitational lensing, the supernova has a triple appearance. In this way, it will be possible to create a measurement between the time differences in which the images are formed.
If this is possible, a more accurate calculation of the Hubble finding, which determines the expansion rate of the universe, can be achieved. Knowing how fast the universe is expanding, it becomes “simpler” to determine the approximate age of formation of the cosmos.
New lenses for new times
Although the studies require peer review and more data to fill existing gaps, these are good examples of how theories gain evidence to remain in research focus.

With the development of technological equipment on the ground and in the sky, we are increasing the limits of observing and understanding what is around us. Thus, cosmology, astrophysics, astronomy and many other fields of physics have advanced at great speed.
Knowing how stars, planets, and entire galaxies are formed helps us understand how our own neighborhood was formed and how it maintains its unique way of existence.
Want to learn more about the universe out there? So, find out what the universe would be like without dark matter. Stay tuned to TecMundo for more content about astronomy and physics!
Source: Tec Mundo
I’m Blaine Morgan, an experienced journalist and writer with over 8 years of experience in the tech industry. My expertise lies in writing about technology news and trends, covering everything from cutting-edge gadgets to emerging software developments. I’ve written for several leading publications including Gadget Onus where I am an author.













