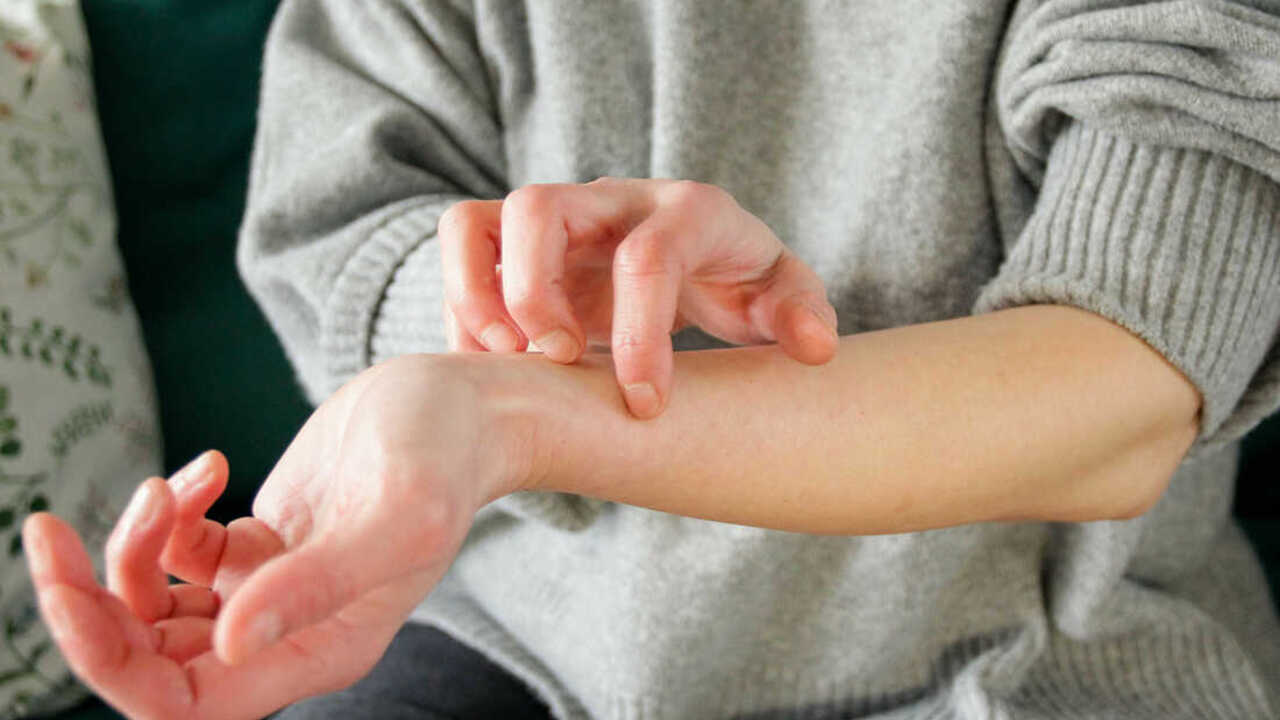
An article published in the journal Cell states that Staphylococcus aureus secretes a chemical that activates human nerve cells. After this, a signal is sent to the brain, which our brain perceives as itching.
In general, many beneficial bacteria live on human skin. And thanks to the balance of these microorganisms, health is maintained. When the balance is disrupted, the S. aureus bacteria can go on a rampage.
Scientists reached all these results through experiments conducted on mice and human cells. First, they exposed the skin of mice to S. aureus, which caused the animals to become increasingly itchy. The researchers then isolated S. aureus, the only enzyme they knew of that was released when this microbe came into contact with the skin. They tested the enzyme in mice and measured the enzyme levels in the skin of different people. It turned out to be the culprit of the itching. Additionally, in people with dermatitis, the levels of this enzyme called Proteaste V8, which activates the PAR1 protein in the nerves, are higher than in people with healthy skin.
This discovery explains why eczema and atopic dermatitis patients itch so much.
News materials cannot be equated with a doctor’s prescription. Consult an expert before making a decision.
Source: Ferra
I am a professional journalist and content creator with extensive experience writing for news websites. I currently work as an author at Gadget Onus, where I specialize in covering hot news topics. My written pieces have been published on some of the biggest media outlets around the world, including The Guardian and BBC News.