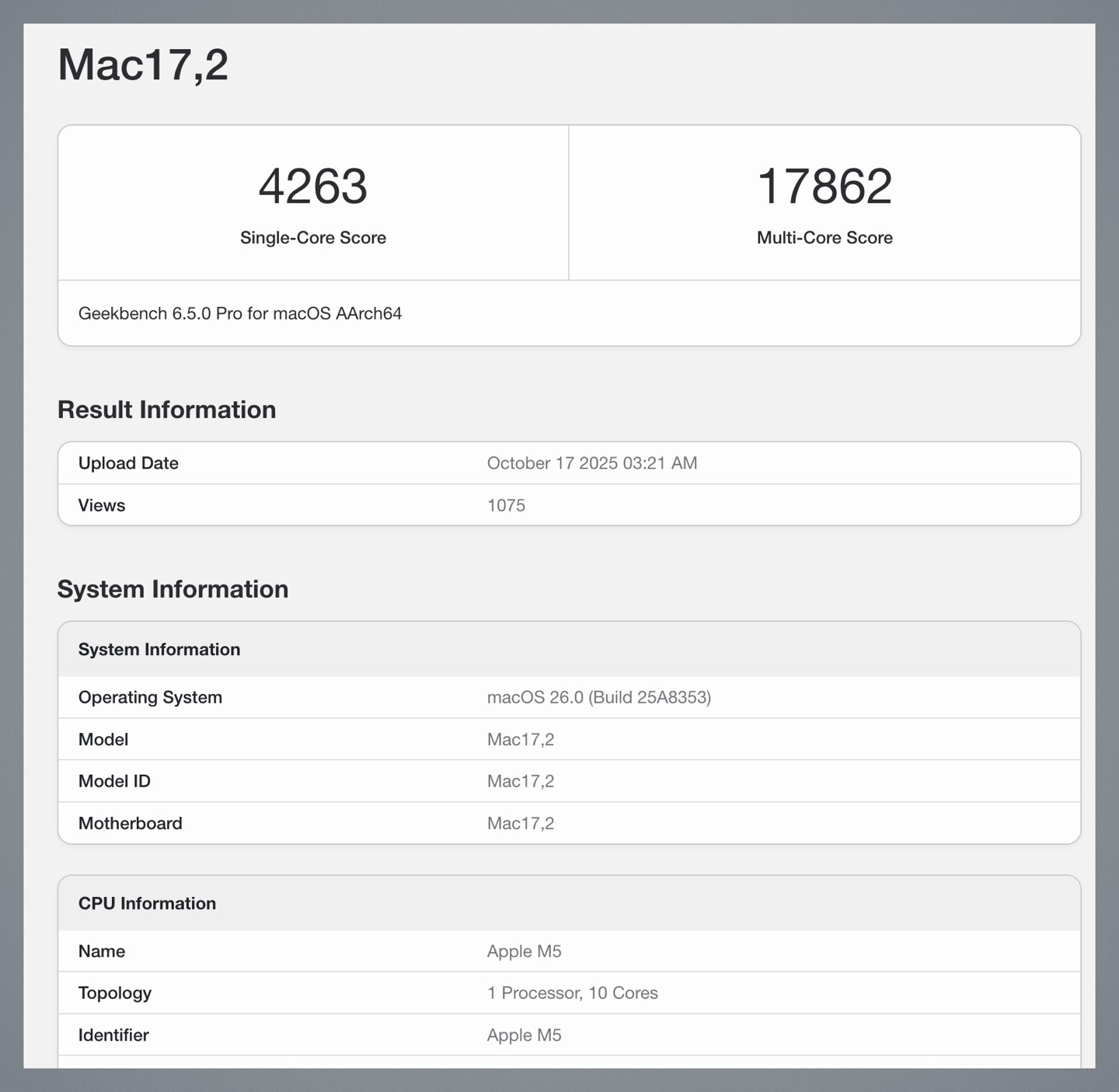
This Wednesday (22), processors Intel pentium turn 30. Released on March 22, 1993, the fifth-generation x86 CPUs were the most popular processor series for decades, available in nearly all home computers until the mid-2000s.
However, Intel has confirmed that 2023 will no longer produce new Pentium processor models. Thus, in addition to completing thirty years, this It will probably be the last year for the company’s best-known CPU family even today..
Thinking about it, Technology World It has crafted the history of Intel CPUs, from the first models to the “warrior” that shaped generations and is part of not only the history of the company but the foundations of the current digitized global economy.
Intel processors over the years
A Integrated Electronics It was established in the state of California in 1968. Created by Gordon Moore and Robert Noyce, identical to Moore’s Law, Intel began designing and manufacturing orbital integrated circuits. It was only in 1971 that the company released its first commercial microprocessor.
pre x86 era
The 4004 was a 4-bit CPU running between 108 and 740 kHz and 2,300 transistors. The processor created the UniCom 141P, the first programmable calculators with printers. Although innovative, the price of $695, equivalent to $5,000 in 2023, made the product a commercial failure.
In 1972, Intel replaced the 4004 with 8008, 8 bits and frequencies approaching 1 MHz. The release of his successor took a little longer. The Intel 8080, which equipped the Altair 8080, only reached the market in 1974.
Intel 8086 to x486
The arrival of the 8086 processor in 1978, early x86 architecture. Also known as the iAPX 86, these processors were Intel’s first commercial 16-bit CPUs designed to work as embedded system controllers.
Over the years, most of Intel’s releases were variations of the 8086, often targeting specific projects. One of the clones was the 8088 found in the 1981 IBM PC 5150, a model that had already defined the main standard for domestic computers with Microsoft’s DOS 1.0.
The first successors of the 8086 arrived only in 1982, with the 80186 and 80286, both operating up to 25 MHz. While the i186 was still aimed at embedded systems, the i268 was available on the next two generations of IBM computers, PC/AT and PS/2.
Launched in 1985 i386 introduced the 32-bit busand can perform up to 11 million instructions per second (MIPS). With the introduction of the i486 in 1989 this performance jumped to 50 MIPS at 50 MHz frequencies, delivering more than double the instruction per cycle.
Already in the CPU market in the early 1990s, AMD used the x86 architecture for its products. For stand out from the competition and bring a less technical and more user-friendly appealin 1993 Intel named its 5th generation x86 CPU Pentium – and precisely because it was the fifth, the chosen name was “Pentium” from “penta”. — created the label that has dominated the market for nearly two decades.
Intel Pentium (i586)
In terms of performance, the main competitors in the CPU segment were RISC processors. A The original architecture of ARM chips used reduced instruction sets, which simplifies operators and speeds up software development and execution.
First Pentium i586 or P5 processors Not much improvement over the 486 and even less improvement over RISC models. However, much of this was due to Intel’s efforts. Maintain backward compatibility with x86 applicationsThis is exactly what provided the initial success of the new brand.
Subsequent generations continued to bring small increments and new embedded technologies. Notable among them, instructions for multimedia extensions (MMX)parallel lines xeonfor workstations support for two physical processors on the same motherboard, and Celeron designed as low-power CPUsoriginally for laptops.
However, the most notable change to the general public is frequency scaling is in direct dispute with AMD. The first Pentium was released at 200 MHz, in the next generation it was increased to 266 MHz and repeatedly increased to 200 MHz. Impressive 1.4 GHz to 2.2 GHz Pentium 4.
Hyper-Threading and Dual Core policy
However, increased frequencies have resulted in higher-than-usual thermal designs. To date, power and heat dissipation are the main barriers to faster processors. However, Intel chose to focus on other aspects and seek a solution to improve performance.
In 2002, the company released the first chips with its technology. hyper threading (HT) implements the ability to handle two simultaneous streams of instructions. Even at lower clocks, 3 GHz CPUs with HT performed better than models with frequencies higher than 3.6 GHz.
In 2005, AMD released the Athlon 64 X2, a processor with two physical cores on the same chip. Also, the new CPUs brought multi-threading technology, forcing Intel to act quickly to avoid losing ground in the market.
A the answer came with Core 2 Duoin 2006. Although it also launched the Pentium Dual Core, the company was already trying to put the brand aside for the arrival of what would be its successor. Intel core.
The arrival of Intel Cores and the end of an era
In 2008, Intel launched the first Intel Core i3, i5 and i7, offering three parallel product lines for different segments. Starting from this point, Pentium has become a simpler family of processors with far less technology than Intel Core..
Pentium Gold 8505, the last model of the brand, was launched in 2022. It even uses the hybrid Alder Lake architecture but is limited to 5 cores, only one of which is performance oriented with hyper-thread support.
Since 2019, the Intel Core lineup has even added the very high-performance Core i9, but it’s redundant. products in the lower segment created redundant models with similar applications. Therefore, Intel’s strategy is to consolidate all CPUs in this niche under the Intel Processors brand and leave the current portfolio as:
- Intel Xeon — servers and workstations;
- Intel Core i3, i5, i7, and i9 — entry-level to high-end desktops;
- Intel Processors — Low-power CPUs primarily focused on embedded systems;
- Intel Atom — Low-power CPUs for secure systems and working in harsh conditions.
After 30 years on the market, this move ends the Pentium series as a special model. In practice the essence would still exist, but commercially it made no sense to keep different products under different labels.
Source: Tec Mundo
I am a passionate and hardworking journalist with an eye for detail. I specialize in the field of news reporting, and have been writing for Gadget Onus, a renowned online news site, since 2019. As the author of their Hot News section, I’m proud to be at the forefront of today’s headlines and current affairs.