hour galaxies It is one of the most fascinating structures of the whole. Universe. These are huge clumps of gravitationally bound celestial bodies. But how are they formed? This is a question that still intrigues astrophysicists around the world.
Estimates suggest that there are at least 200 billion of them in the universe. But there are those who think that this number is modest, it can go up to 10 times. We don’t know the exact amount, but we already know millions of them.
This is because they are relatively easy to observe. The amount of energy emitted by these systems is so great that it reaches us even from the farthest distances. one of them object astronomical farther than we know. It’s called GN-z11 and it’s 32 billion light-years away.
When you look at the night sky, you may be seeing many of them. Viewed only from here, they may appear as a single bright spot, and we confuse them with stars. But it is possible to look better, to see beyond appearances, for example, with a telescope.
The origin of galaxies may be linked to the universe itself. After the Big Bang, space consisted only of hydrogen and helium atoms. Observations made by Hubble indicate that after only 1 billion years there is already a mass of celestial bodies.
How did galaxies arise?
There are two main theories about their formation. According to the first, galaxies They were born after primordial stars emerged from the two original chemical elements and collapsed under the influence of their own gravity.
The second, which has attracted a lot of attention recently, is Universe the young already had small “clumps” of agglomerated matter that gained mass over time and evolved to form. galaxies.
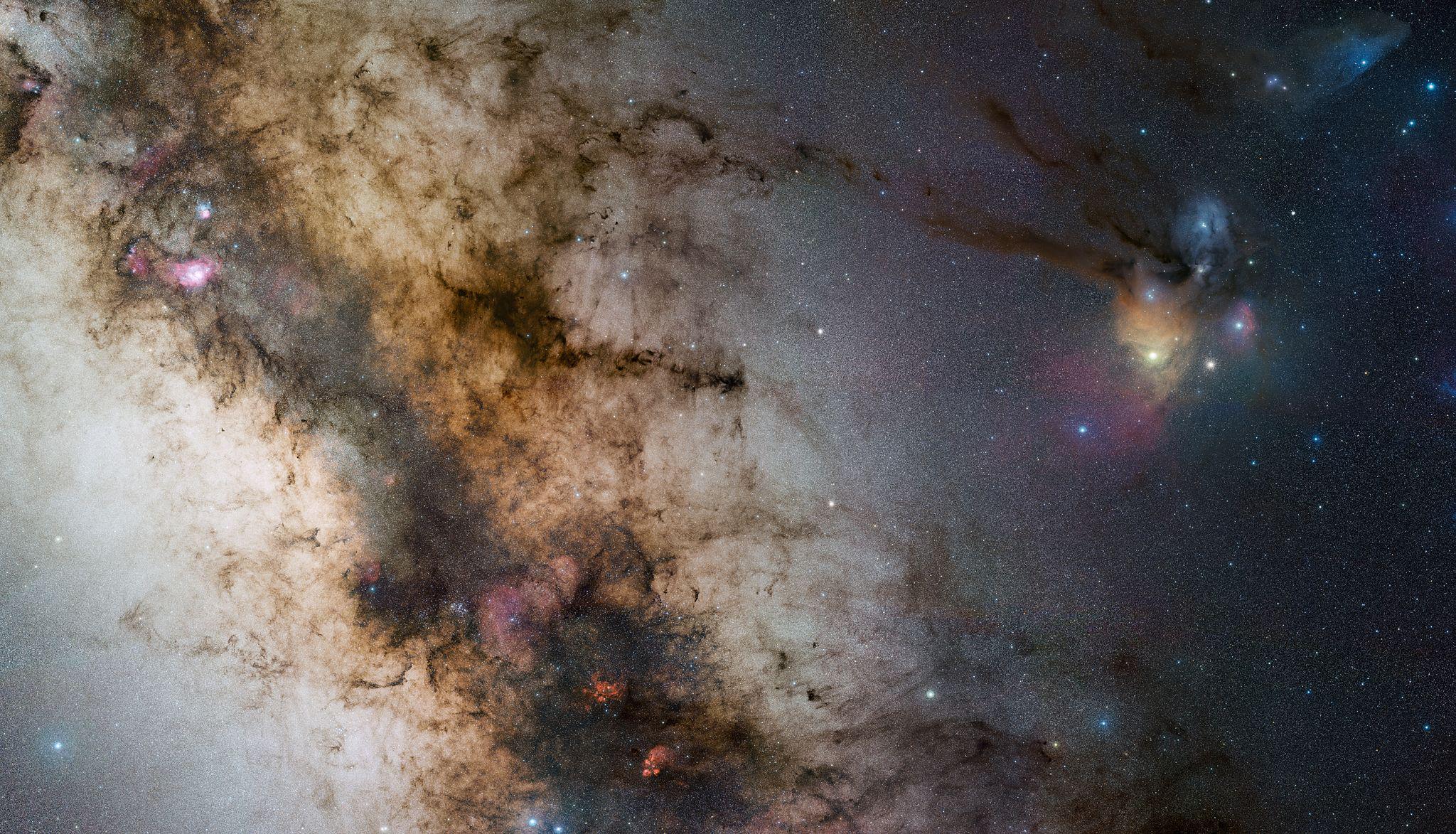

This Hubble Telescope He added strength to the theory by photographing these so-called smaller clusters of space objects.
Until the beginning of the 20th century, everything in the universe was thought to exist. It was in our own galaxy. But some astronomers have hypothesized that there might be more here.
They pointed to spiral bubbles in the sky and called them the universe. islanders. Until then they were believed to be composed of dust and gas, but in 1924 Edwin Hubble identified clusters of pulsars that were beyond the reach of the Milky Way.
What kind of galaxies?
Today we already know millions of them and can classify them according to their properties. In general, someone’s shape says a lot about them, so that’s the first factor we take into account. There are two main groups.
hour galaxies ellipticals, as the name suggests, is an ellipse with no spiral arms. Therefore, they have a more homogeneous distribution in the three directions of space without a rigidly organized structure.

Their form changes. Some are almost spherical and others are very long. They tend to have less gas and dust and older stars that may have more random orbits.
Some astronomers believe that ellipticals are actually formed from two (or more) collisions. galaxies spirals. This second type is the one with arms like ours that rotate around its center.
It represents most of the galaxies we know. Their shape is due to the translational motion of all the gas and dust they contain around their centers at hundreds of kilometers per second.
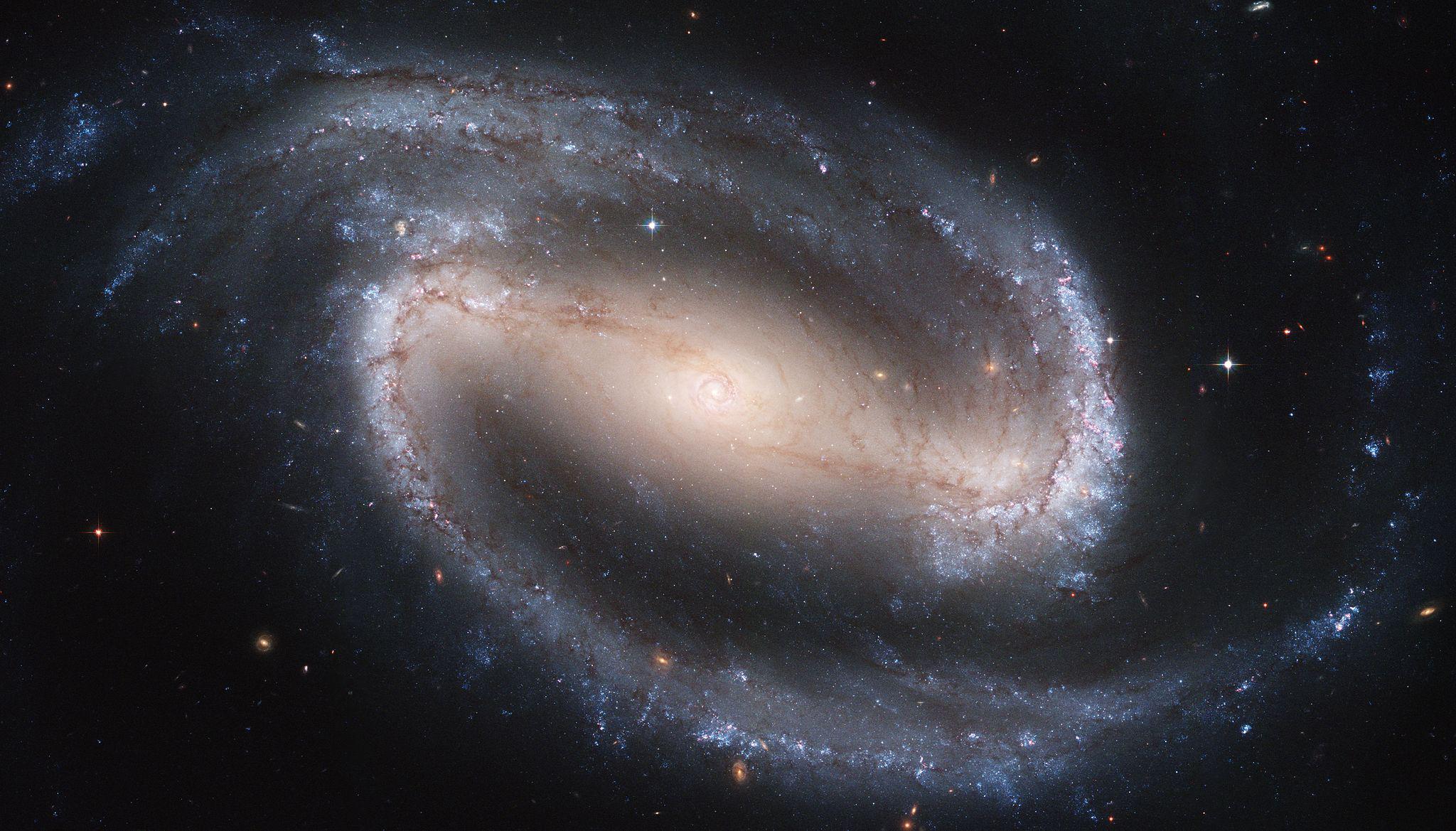

They all have two arms that can be more or less tight around the core. Some are also blocked, meaning they have a linear band of stars in their centre. This is our situation.
In general, the closer to the center, the older the stars. Where star forming regions are concentrated in the arms.
The core of these galaxies It consists of very old stars and are very close to each other. Additionally, they often have one or more black holes, which in some cases can be very large and massive.

Even more impressive are those that have a quasar at their centre. These objects are the result of a supermassive black hole, the largest in the entire universe, which can release an enormous amount of energy.
Other galaxies, namely those that are not ellipses or spirals, are grouped under the heading irregular or strange. They come in a wide variety of forms and structures and are very interesting.
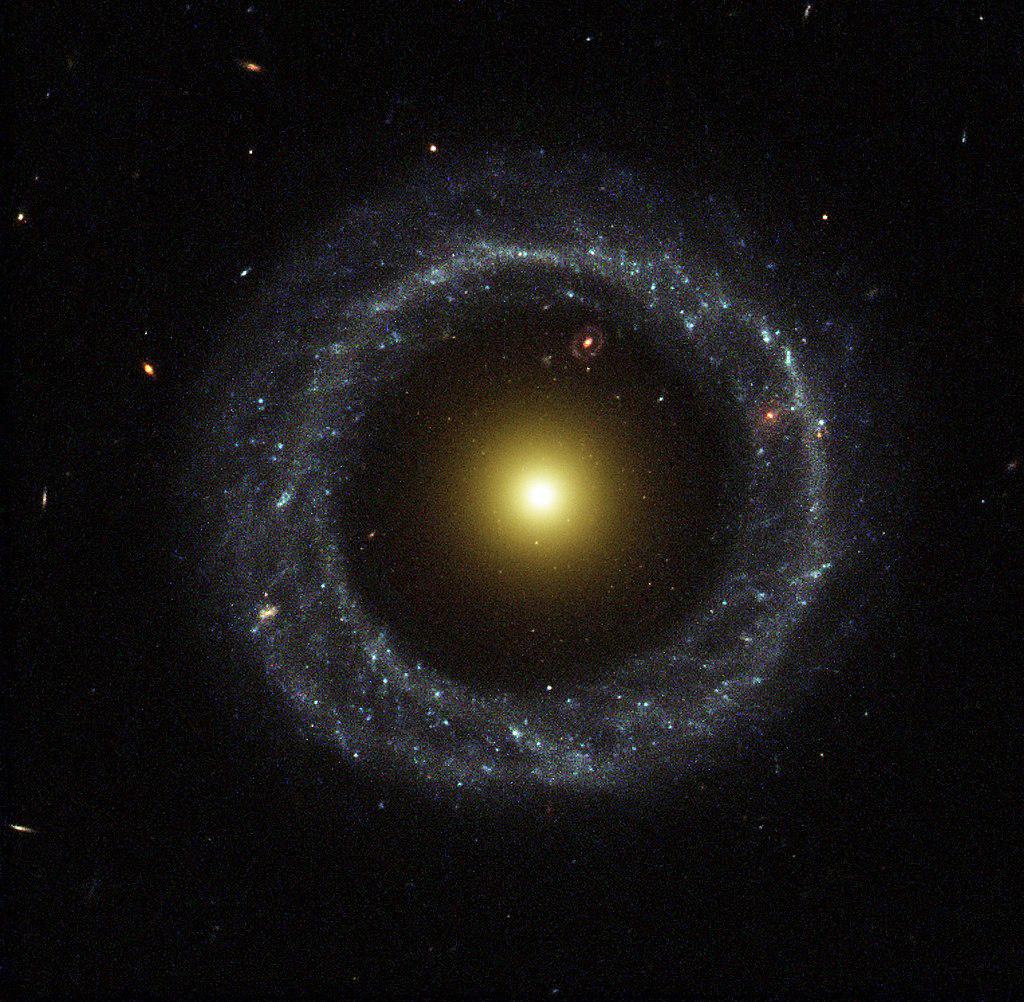
one of them galaxy ring consisting of a group of stars surrounding an empty core. It is believed that they are formed through the passage of time. dwarf galaxy by the core of a larger spiral that destabilizes it.

Another curious species is galaxies lenticular. They are midway between the elliptical and spiral: they consist of very long disks, but do not form arms. In general, young stars are few.
There are also dwarves and moons. That is, smaller groupings or accompanying galaxys bigger. There are more than 50 in the Milky Way alone. The two of them can be seen at night and have been known since ancient times. These are the Small and Large Magellanic Clouds.
Galaxies are fascinating star objects that have fascinated humans since the beginning of time. We’ve progressed a lot in research over the past century and learned more about them, but there’s still a lot to explore in our sky.
Source: Tec Mundo
I am Bret Jackson, a professional journalist and author for Gadget Onus, where I specialize in writing about the gaming industry. With over 6 years of experience in my field, I have built up an extensive portfolio that ranges from reviews to interviews with top figures within the industry. My work has been featured on various news sites, providing readers with insightful analysis regarding the current state of gaming culture.