The Curiosity rover made another beautiful recording of the Martian landscape as it explored the planet’s surface in search of signs of microbial life. The image (13), released by NASA on Tuesday, yielded an impressive result. “postcard” from our space neighbor.
According to the US space agency, the image shows the same region of the Red Planet at two different times, one in the morning and the other in the afternoon. The panoramic photo taken by the mission cameras shows the Marker Band Valley where the robot was traveling.
The photos were taken in black and white using navigation cameras on April 8 this year. The first of these was clicked by Curiosity at 09:20 local time, while the second was taken at 15:40 taking into account Mars time.
Recordings taken by researchers on the ground resulted in the creation of a postcard from Mars after processing, just as the agency did in 2021. Photos have been colored from original images.allowed to control different lighting conditions in the morning and afternoon.
Items shown on Mars postcard
The photo, taken as Curiosity climbs Mount Sharp, located 5km high inside Gale crater currently explored by the mission, shows various elements of the Martian region. “Bolivia” and “Deepdale” hills and a canal called “Paraitepuy Pass” are among them.
Directly in front of the robot is the Marker Band Valley, while in the background is the rim of Gale Crater, among other familiar areas. On closer inspection, we can even see ruts of equipment amongst the dust of the Red Planet.
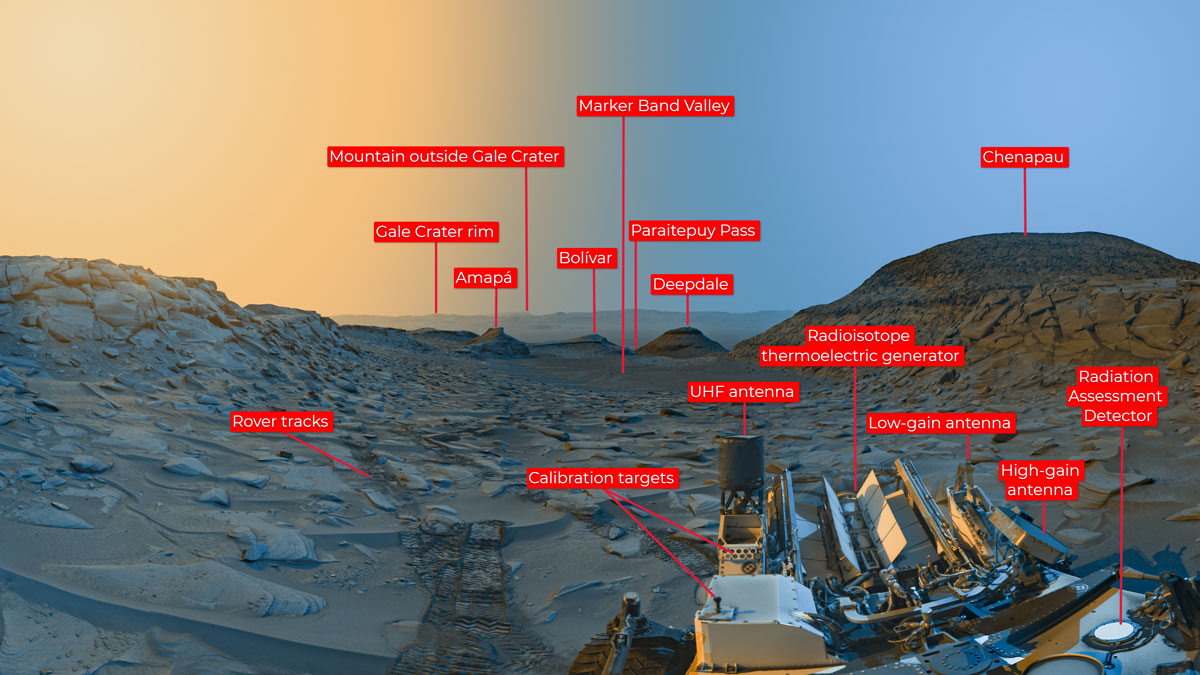
The rover itself is also included in the image, allowing a glimpse of the communication antennas and nuclear power source. Another envisioned device is the Radiation Evaluation Detector (RAD), which collects important data for future manned missions.
According to Doug Ellison, mission engineer responsible for image processing, The recordings were taken during the Martian winter, when the shadows were at their deepest and darkest., due to reduced dust levels in the atmosphere. “The shadows on Mars are sharper and deeper when there is little dust, and softer with a lot of dust,” he explained.
Source: Tec Mundo
I’m Blaine Morgan, an experienced journalist and writer with over 8 years of experience in the tech industry. My expertise lies in writing about technology news and trends, covering everything from cutting-edge gadgets to emerging software developments. I’ve written for several leading publications including Gadget Onus where I am an author.













