Weekly TecMundo and #AstroMiniBR, twitter profile Bringing together astronomers and popularizers of astronomy, and sharing with you the interesting curiosities of our universe. Check out this week’s highlights below!
#1: A pale blue dot
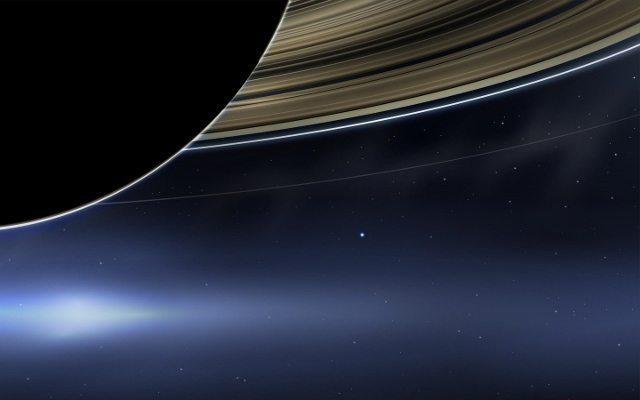
The iconic image you see below can be evaluated. as an updated retelling of the famous Pale Blue Dot image. The beautiful record was captured by Cassini, a space probe developed by NASA in July 2013 and launched into space in 1997 to study Saturn and its moons.
The image transcends mere astrophotography to remind us of the fragile, unique sphere we call our home.
Taken from a staggering 1.44 billion kilometers away, this unique image shows Earth as a tiny dot of deep blue light suspended in the dark void of space, seen beneath Saturn’s majestic rings. Various technical aspects made this capture possible.
The enormous distance from Earth to the probe at the time required meticulous planning to adjust camera settings on the probe, such as exposure and light sensitivity, to accurately capture Earth’s distinctive, pale blue light. Besides, Cassini had to orient itself carefully to prevent light from the Sun or Saturn from distorting the image..
This candid portrait of our planet represents the expanding frontiers of science and space exploration and invites humility that can remind us of the interconnectedness of all living beings and the importance of protecting and preserving our only refuge in the midst of the vast cosmos. In the face of this compelling vision, we are invited to reflect on our position as inhabitants of an interconnected world, awakening the desire to preserve and protect not only the Earth, but also the rich fabric of life it supports.
#2: The oldest light in the universe!
Cosmic background radiation is one of the most intriguing and revealing phenomena about the Universe around us. This is electromagnetic radiation that fills the entire space and is emitted approximately 380,000 years after the Big Bang. Originating from primordial matter and energy, this radiation is the oldest form of light we have been able to detect and study.
This radiation, which is only 2.7 degrees above absolute zero, gives very important clues about the formation, evolution and composition of the universe. For example, their detailed analysis has provided insights into the properties of cosmic expansion, the distribution of dark matter, and the formation of large structures.
Using advanced telescopes and precision instruments, the scientists mapped the cosmic microwave background radiation in unprecedented detail and found that small changes in the temperature of this radiation corresponded to slightly denser and less dense regions in the early universe that eventually gave rise to galaxies. clusters of galaxies we see today.
The cosmic microwave background is one of the key windows into the infancy of our Universe, and It allows scientists to unravel the history of the Cosmos from its origins to the present day, providing valuable insights into nature’s fundamental mysteries.
#3: Cosmic Dance of the Milky Way
In about 5 billion years, one of the biggest events in the Universe will happen with our cosmic island: The Milky Way will collide with our galactic neighbor, the Andromeda Galaxy.
The simulation above presents the theoretical model that predicts what this cosmic encounter will look like: Billions of years of galactic evolution of both systems will result in a gravitational dance that will result in the merging of these two giants.
As the two galaxies approach each other, gravitational forces kick in more sharply, distorting their shape and throwing the stars into entirely new orbits and also out of the galaxy.. Although both galaxies contain hundreds of billions of stars, the probability of direct collisions between stars is incredibly low due to the vastness of intergalactic space. However, interstellar clouds of gas and dust will come into contact, and as this matter interacts and compresses, it will cause a star-forming frenzy.
As galaxies intertwine for hundreds of millions of years, they will eventually merge to form a new structure and bring a new system to life: a giant elliptical galaxy!
Source: Tec Mundo
I’m Blaine Morgan, an experienced journalist and writer with over 8 years of experience in the tech industry. My expertise lies in writing about technology news and trends, covering everything from cutting-edge gadgets to emerging software developments. I’ve written for several leading publications including Gadget Onus where I am an author.