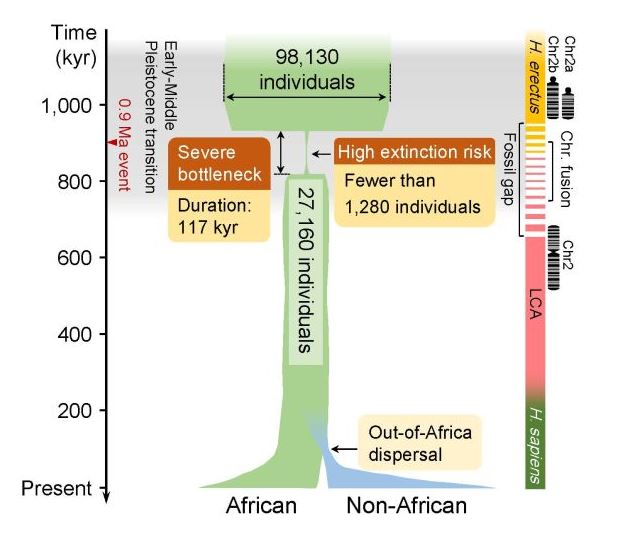
As explained in a new study published in the journal Science, About a million years ago, a catastrophic event nearly wiped out our ancestors. The research, conducted by a team of scientists from the Chinese Academy of Sciences and East China Normal University, suggests that the population at that time had dropped to just 1,280 individuals.
After analyzing the genomic data (DNA) of 3,154 modern humans, the scientists found that the population of our ancestors dropped from 100,000 to 1,280 individuals. about 900,000 years ago, there was a 98.7% decrease in the population at that time.
With only a little over a thousand ‘hominids’ remaining, this was a period that lasted about 117,000 years and nearly brought the end of humanity as we know it. Even scientists believe this discovery could help explain a thing. Mysterious gap in the human fossil record during the Pleistocene epoch.
“The results show that our ancestors experienced a severe population bottleneck that began about 930,000 years ago and lasted for about 120,000 years. It is estimated that this reduced the number of breeding individuals to about 1,300 and brought our ancestors closer to extinction.”
Nearly extinct ancestors
The scientists came to this conclusion from a new method called the infinitesimal fast coupling process (FitCoal), which is responsible for presenting the backlog of errors that may occur when investigating catastrophic events in the past. The method analyzed genomic data from 10 African and 40 non-African populations., to understand the population bottleneck that occurred almost a million years ago.
Population bottleneck is a term used to describe significant reductions in a group and is not uncommon in Earth’s history. The last event that caused the population bottleneck occurred about 7,000 years ago, when the human population in the Northern Hemisphere suffered a significant decline.
The population decline that nearly wiped out human ancestors occurred between 930,000 and 813,000 years ago. Seems like, This bottleneck also contributed to the fusion of important chromosomes in the human genome: the formation of chromosome 2.
“These findings are just the beginning. With this information, future goals aim to paint a more holistic picture of human evolution during this transitional period from the Early Pleistocene to the Middle Pleistocene, which will continue to unravel the mystery of early human lineage and evolution.” Chinese Academy of Sciences study and geneticist Haipeng Li.
You can find up-to-date information on the latest scientific discoveries here. Technology World! If you wish, read about the fossil ape living in Europe that could change the history of evolution.
Source: Tec Mundo
I’m Blaine Morgan, an experienced journalist and writer with over 8 years of experience in the tech industry. My expertise lies in writing about technology news and trends, covering everything from cutting-edge gadgets to emerging software developments. I’ve written for several leading publications including Gadget Onus where I am an author.












