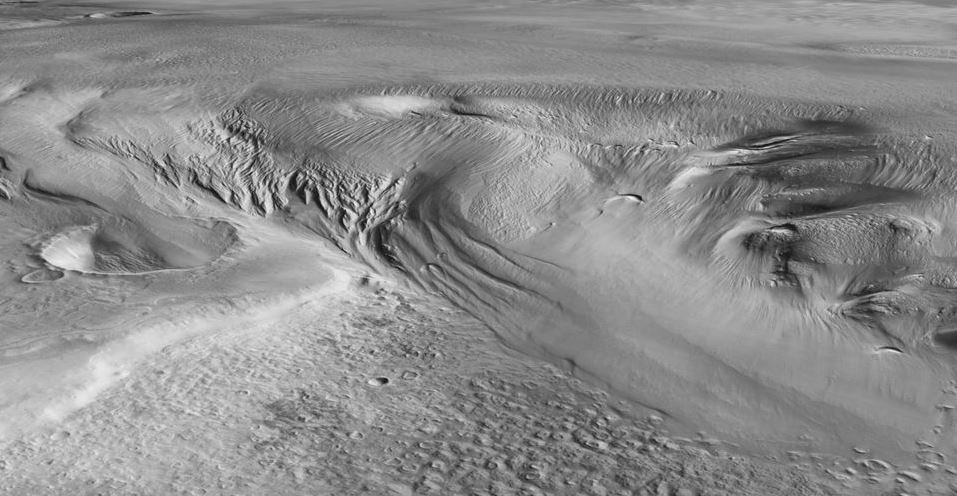
In a recent study published in the scientific journal Geophysical Research Letters, a team of scientists say: Water ‘plates’ detected in a region at the equator of Mars. The data was collected by a European Space Agency (ESA) probe and suggests that water would be enough to cover the entire surface of Mars in a large shallow ocean.
During ESA’s Mars Express mission, researchers used the probe to study the region known as the Medusae Fossae Formation (MFF). By analyzing the data, they discovered: There are ‘sheets’ of buried water on the planet’s surface, between 1.5 and 2.7 meters deep, which would form a shallow ocean, but the water must be frozen.
According to scientists, The puddles extend up to 3.7 kilometers underground and are covered with a layer of dust hundreds of meters thick. It is known that the MFF region hosts many deposits in an area of approximately 5 thousand kilometers, but scientists still do not know the true origin of these deposits.
“We re-explored the Medusae Fossae Formation using newer data from Mars Express’ MARSIS radar and discovered that the deposits are thicker than we thought: up to 3.7 kilometers (2.3 miles) thick. It’s exciting that the radar signatures match what we expected,” said Smithsonian Institution geologist Thomas Watters. “The signals we see in the ice sheets are similar to the signals we see in the polar ice caps of Mars, which we know are rich in ice,” he said.
Frozen water on Mars
As scientists explain, This is the largest amount of water ever found on Mars, but it’s no surprise that the red planet offers water. Science has long found evidence of water on Mars, but astronomers say no form of liquid water has yet been found.
One of the goals of searching for water on Mars is to know where to extract water for use in future human missions to the planet. But, The Medusae Fossae Formation’s water cannot be easily extracted because it is buried several hundred meters below the Martian surface.is covered with layers of dust.
“This latest analysis challenges our understanding of the Medusae Fossae Formation and raises as many questions as it answers. How long ago did these ice deposits form and what was Mars like at the time? If water ice is confirmed, These massive deposits will change our understanding of the climate history of Mars. “Any reservoir containing ancient water would be a fascinating target for human or robotic exploration,” said ESA planetary scientist Colin Wilson.
Always stay informed about the latest research on the Red Planet at TecMundo. If you wish, have the opportunity to see the Mars ‘world map’ created by scientists to help future missions.
Source: Tec Mundo
I’m Blaine Morgan, an experienced journalist and writer with over 8 years of experience in the tech industry. My expertise lies in writing about technology news and trends, covering everything from cutting-edge gadgets to emerging software developments. I’ve written for several leading publications including Gadget Onus where I am an author.