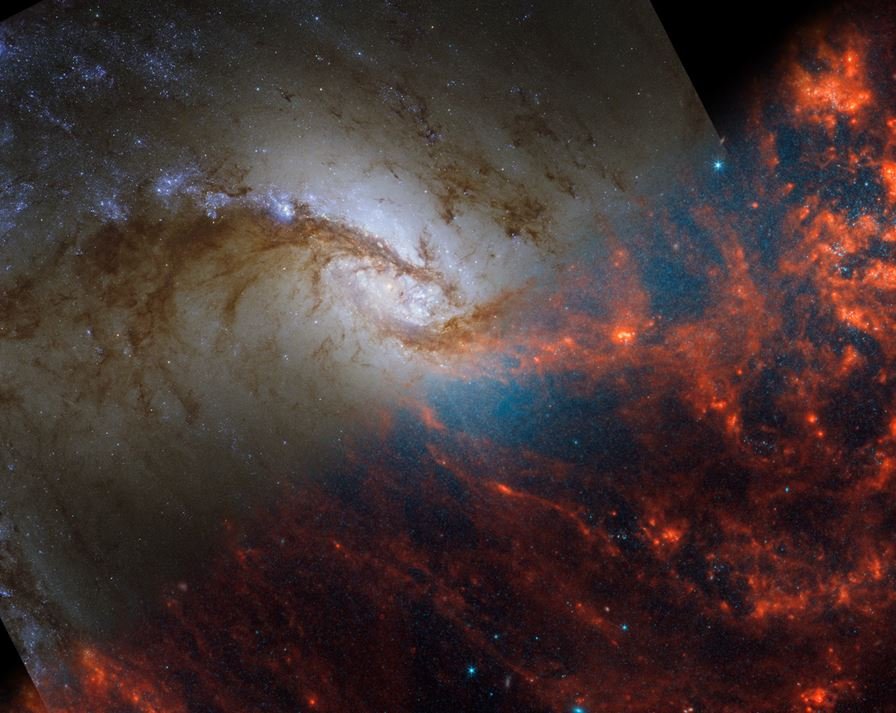
Last Monday (29), the United States National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) released several New images taken by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) showing different features of spiral galaxies.
The North American space agency has released a total of 19 images of these distant cosmic objects that could help scientists learn more about these massive structures.
Because JWST is a high-quality telescope, it was able to capture details that show that no two galaxies are the same when observed with extremely sensitive equipment.
In addition to spiral galaxies, The observations also provide interesting details about the stars, gas and cosmic dust surrounding these massive objects. The scientists’ goal is to use the data to improve understanding of star formation and the evolution of spiral galaxies.
In its official statement, NASA announced that the images are part of observations in the High Angular Resolution Physics in Near GalaxieS (PHANGS) program.
Before they began using James Webb’s data, the 150 astronomers who are part of PHANGS were already using images collected by the following instruments: the Hubble Space Telescope, the Multi-Unit Spectroscopic Explorer, and the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA).
“Webb’s new images are extraordinary. They are mind-blowing, even for researchers who have been studying the same galaxies for decades. Bubbles and filaments resolve to the smallest scales ever observed and tell a story about the star formation cycle,” the scientist said. Project proposals for strategic initiatives Janice Lee is from the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, USA.

spiral galaxies
JWST’s Near Infrared Camera (NIRCam) manages to capture millions of stars shining in shades of blue, while the Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI) presents the glowing cosmic dust around the stars; Stars in the process of formation are shown in red. According to University of Alberta physics professor Erik Rosolowsky, The photographs were taken from regions where the youngest and largest stars in the galaxies can be observed.

Photographs of spiral galaxies could help astronomers explore regions filled with gas and dust, researchers explain. For example, in the image of the galaxy NGC 5068, located 20 million light-years from Earth near the constellation Virgo, scientists were able to observe large empty holes that may have formed as a result of the explosion of massive stars.

“These holes may have been formed by one or more exploding stars, creating large gaps in interstellar material. Stars can live for billions or trillions of years. By fully cataloging all types of stars, we can build a more reliable and comprehensive picture of stars. Ohio State University in the United States “Life cycles,” said astronomy professor Adam Leroy of .
Did you like the content? Always stay up to date with the latest discoveries of the James Webb Telescope at TecMundo. If you wish, take the opportunity to understand what ‘impossible galaxies’ are.
Source: Tec Mundo
I’m Blaine Morgan, an experienced journalist and writer with over 8 years of experience in the tech industry. My expertise lies in writing about technology news and trends, covering everything from cutting-edge gadgets to emerging software developments. I’ve written for several leading publications including Gadget Onus where I am an author.