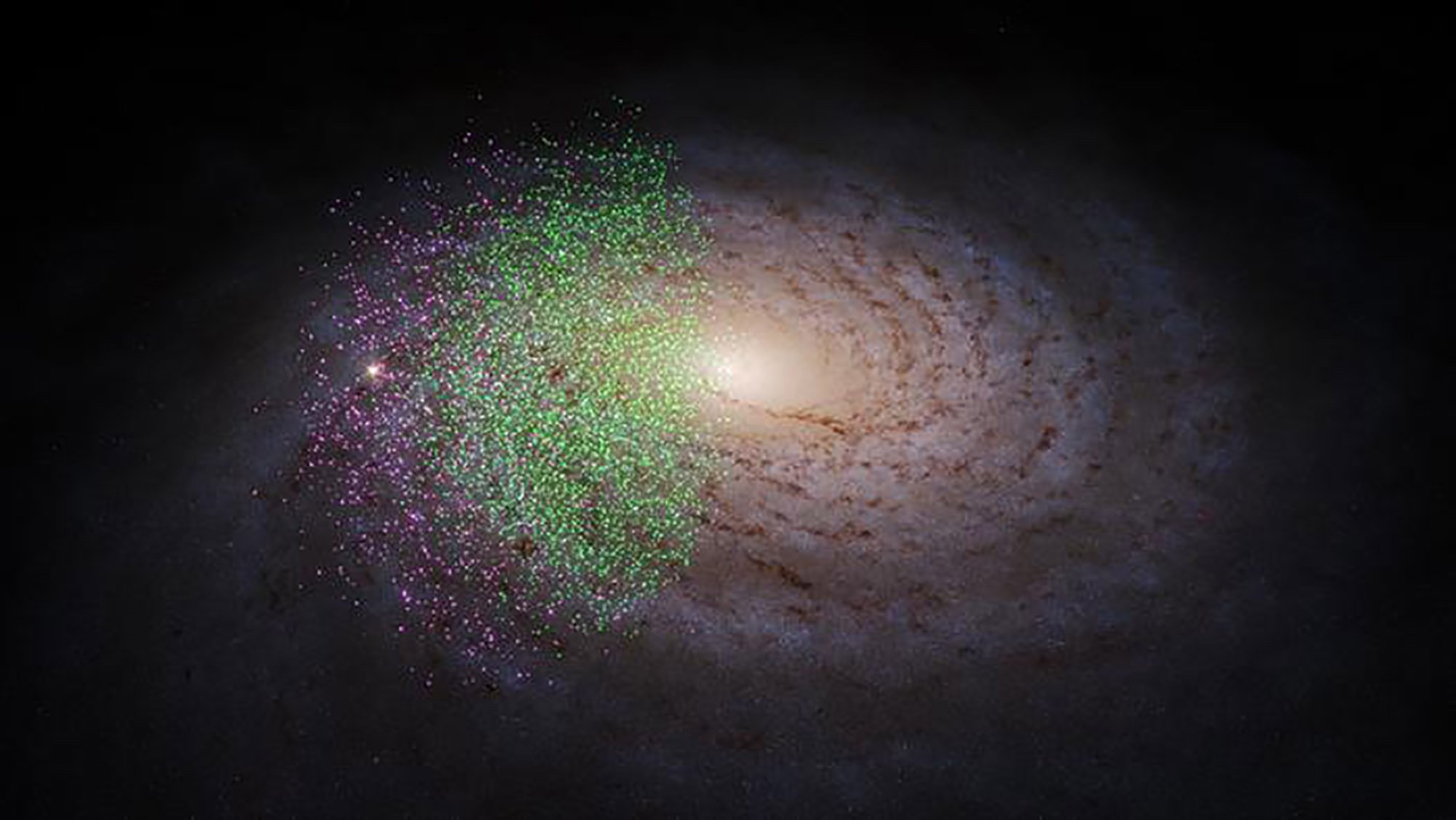
In a study recently published in The Astrophysical Journal, astronomers from the Max Plank Institute for Astronomy (MPIA) in Heidelberg, Germany, have revealed two of the first possible building blocks of the Milky Way that can still be detected.
These two components, called Shakti and Shiva (Hindu gods of the creation of the world), are protogalactic parts, i.e. Huge clumps of gas and dust merging into the younger version of our galaxy12 to 13 billion years ago, when most galaxies in the universe formed.
The structures were identified by combining data collected by the European Space Agency’s (ESA) Gaia astrometric satellite with data from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS) database. To team leader Khyati Malhan, ““The surprising thing was that we were able to detect these ancient structures.”stated in a statement
Milky Way Archeology Through Star Tagging
The astronomers’ surprise is justified. After all, the Milky Way has undergone significant changes over billions of years, and being able to group these ancient stars together is a remarkable achievement. The reality occurred in 2022, when Gaia was conducting a form of galactic archaeology. What the new study did was mark the stars according to the moment they merged with our galaxy.Even before it takes its spiral shape.
Near the heart of the Milky Way, Shakti and Shiva have similar orbital trajectories and each have about 10 million suns with ages between 12 and 13 billion years. These stars lack metals because they were born when the universe consisted mainly of hydrogen and helium.It is produced by the fusion of two primordial gases.
Naturally, the first generation of stars had long since died, exploding as supernovae and spreading the heavy elements they had created over the ages into the cosmos. And these metals organized themselves into a second generation of stars that followed the first, a continuous process of life, death and rebirth. Thus, astronomers can estimate the age of stars simply by observing their metal content.
Differences between Shakti and Shiva
Although it was known that more than 12 billion years ago the Milky Way probably consisted of long filaments of dispersed gas and dust, Gaia found that “the stars at the heart of our galaxy were poor in metals, That’s why we call this region the ‘poor old heart’ of the Milky Way.”Study co-author Hans-Walter Rix, one of the galactic archaeologists of 2022, said:
The individuation of Shakti and Shiva not only marked the first stages of the growth of our galaxy, but also but also understand that there are some fundamental differences between its earliest pieces.
Did you like the content? Follow the latest studies on our galaxy like at TecMundo and get the opportunity to examine the simulation of the collision between the Milky Way and Andromeda.
Source: Tec Mundo
I’m Blaine Morgan, an experienced journalist and writer with over 8 years of experience in the tech industry. My expertise lies in writing about technology news and trends, covering everything from cutting-edge gadgets to emerging software developments. I’ve written for several leading publications including Gadget Onus where I am an author.