TecMundo selects the most relevant astronomy news every week, so you can always stay up to date on the latest news about our fantastic universe. Check out today’s #AstroMiniBR below!
1. Earth will gain a temporary Moon this month!
In the coming days, Earth will get a new mini-moon that will be temporarily captured by the planet’s gravity. The asteroid 2024 PT5, about 10 meters in diameter, was discovered in August 2024 by the ATLAS system, which tracks near-Earth asteroids.
Between September 29 and November 25, 2024, This small asteroid will deviate from its orbit around the Sun into a temporary orbit around Earth, becoming a mini-Moon for about two months.Despite the scientific interest, the asteroid will be nearly invisible to amateur observers due to its small size and faint brightness.
But this phenomenon is not uncommon: Earth has already caught mini-Moons in 1981, 2020 and 2022. After this short visit, asteroid PT5 will return to its heliocentric orbit and pass by Earth again in 2025 and 2055.
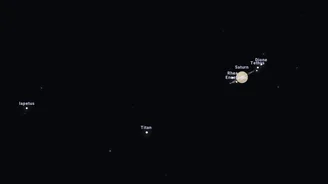
2. Large family of satellites of Saturn and Jupiter
The gas giants Saturn and Jupiter have once again been in the scientific spotlight this month due to new data and new discoveries regarding their moon systems. Saturn currently has 146 known moons, and the family continues to grow! The most prominent member is the moon Titan, which is the largest and can only be observed with a small telescope due to its imposing size.
Having an atmosphere rich in nitrogen and methane Titan is the focus of future exploration, with the Dragonfly mission expected to take place in the 2030s, to investigate its potential to host life forms..
Jupiter also stands out with its four largest moons, Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto, which can be easily seen with binoculars. Europa, in particular, continues to attract NASA’s attention due to the possible presence of an ocean beneath its icy crust, and the Europa Clipper mission is set to explore this further soon.
3. Multispectral images of galaxies with Hubble
Last Friday, the 20th, Hubble Space Telescope reveals new, detailed image of galaxy NGC 1559Located approximately 35 million light-years away in the constellation Reticulum, this barred spiral galaxy has been captured in various bands of the electromagnetic spectrum from ultraviolet to near-infrared, allowing the study of various astrophysical processes.

The multispectral image reveals not only stars at different stages of evolution, but also large regions of star formation. Reddish hues across the galaxy indicate the presence of ionized hydrogen, while bright spots correspond to areas of intense star birth activity. Such observations help scientists better understand how galaxies evolve and how new stars and planetary systems form.
Did you like the content? So share the astronomy news of the week with your friends on your social networks. See you next Monday!
Source: Tec Mundo
I’m Blaine Morgan, an experienced journalist and writer with over 8 years of experience in the tech industry. My expertise lies in writing about technology news and trends, covering everything from cutting-edge gadgets to emerging software developments. I’ve written for several leading publications including Gadget Onus where I am an author.













