Anyone who works a lot with computers (whether laptop or desktop) usually keeps the HD (famous hard disk) partitioning application. This can be a very useful way to organize files and protect what you have stored on your machine.
That way, if something happens (like a virus attack or the need to reinstall a program), partitioned partitions are safe and you don’t risk losing important files or systems.
In this text we explain step by step how to partition your HD inside Linux system. Check out the tips below.
What is HD partitioning?
Partitioning a disk is nothing Split your HD into parts so they become independent of each other. This is often used to organize file storage. For example, you can create a specific partition to save only the operating system, another partition for personal files, and another partition for memory.
It is important to remember that these divisions are logical rather than physical. That is, partitions of space (for example 150, 10, 40 GB) will be reserved, not exactly “obvious” space for partitions. This way, when restarting/reinstalling a computer softwareor you can prevent certain files from being lost by formatting the machine.
Partitioning the HD is the first thing a user wants to do in most cases when switching from Windows to Linux. The reason for this is quite simple: Many people want to run more than one operating system on their computer.
This means you can have both Linux and Windows on your computer and use each in different situations. Ideal to do this is to render these partitions in HD.
How to create partitions in Linux
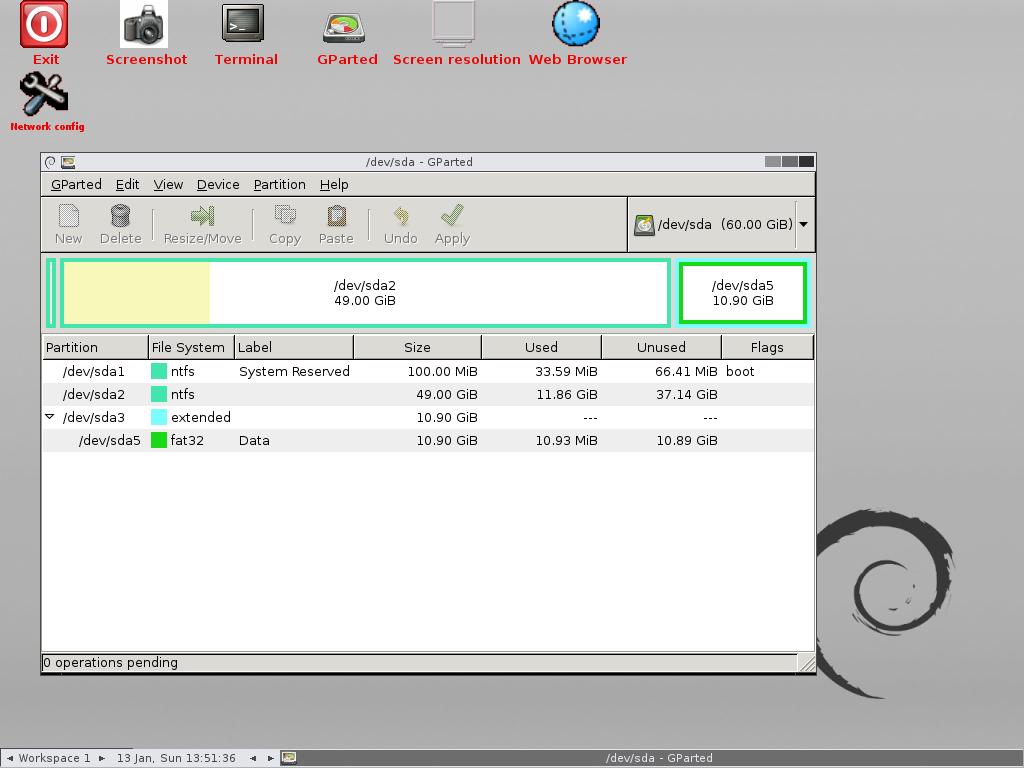
The first thing to do to partition your hard drive in Linux is to use a command line program. The most common way to achieve this is GParted (GNOME Partition Editor) is a GTK-based graphical user program. It is used to delete, create, move and copy hard disk partitions, as well as modify file systems.
So let’s look at the steps to take:
Installing GParted
On Ubuntu (the most widely used operating system on Linux), you will install GParted using a single command: sudo apt install gparted
Then check if GParted is successfully installed on your machine. To do this, use the command: sudo apt policy gparted
Using GParted
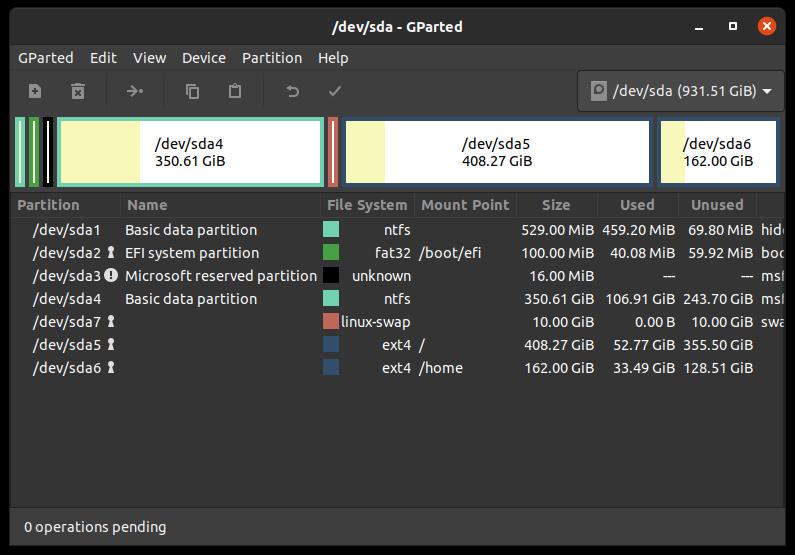
Then go to Events in Ubuntu. Click the GParted icon. The system will ask for your password, as the program requires sudo privileges.
Various options will appear in the GParted menu, allowing you to use the most common operations performed by users. Features include:
- New – Used to create a new partition.
- To delete – delete an existing partition.
- resize / move – for resizing, reducing or increasing the size of a partition.
- Copy paste – used to copy and paste text and information.
- Undo – undo previous action.
- To apply – Tool to confirm any selected action in GParted.
From here you can create and manage partitions created on your hard drive.
Partition Types in Linux
Partitions created in Linux have some minor differences from the same processes in Windows. Even so, it’s worth remembering that the function is always the same: logically splitting the HD into parts.
Both systems use “Primary” and “Logical” types (Linux also has “Extended” types). But there are some peculiarities: Linux partitions are also subdivided into “Data Partitions” and “Swap Partitions”.
See the characteristics of each type below:
- Priority: the type that stores the file system. Normally used for operating systems;
- Elongated: type that hosts logical partitions;
- Logical: Grouped in “Extended” and taking file systems;
- Data Sections: where are the files that start and run the system;
- Exchange Sections: Expand the physical memory of the computer by using the partition as a cache.
Linux table partitions

Another important piece of information is that there are two partition table standards in Linux that are used to define the appearance of partitions (that is, how you see the partitions on your machine). Let’s see what they are below.
MBR
MBR is the most common standard and this is found on older computers. It will later be replaced by the more modern GPT, which overcomes some of the limitations of the MBR.
Among these obstacles is that the MBR does not allow you to configure more than 4 primary partitions. Also, each of these partitions has a maximum of 2TB of space.
GPT
The GPT standard is supported by the UEFI interface and is available on newer computers.
As mentioned earlier, it offers more possibilities compared to MBR: It supports up to 128 primary partitions, each of which can store more than 2TB of files.
Precautions

If you make partitions to use both Windows and Linux at the same time, you need to take some precautions. This is because Windows usually uses a small special partition called EFI. This is done by the system with the install privilege. drivers with security.
EFI is hidden in the system but is revealed when you use the GParted program on Linux. However, you must be very careful not to format or delete this partition, as this will compromise your entire computer system and require reinstallation. So there is very little maintenance!
Source: Tec Mundo
I am a passionate and hardworking journalist with an eye for detail. I specialize in the field of news reporting, and have been writing for Gadget Onus, a renowned online news site, since 2019. As the author of their Hot News section, I’m proud to be at the forefront of today’s headlines and current affairs.










