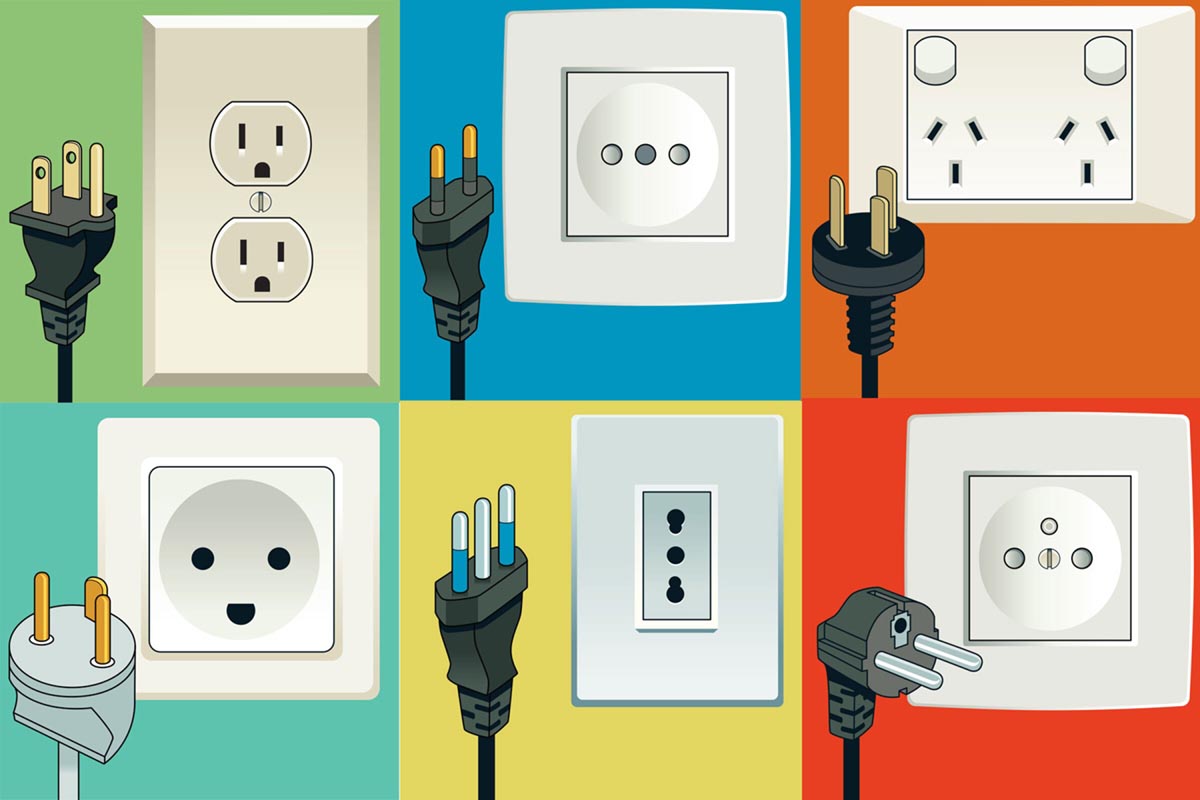
One of the most common things in any home or office is an electrical outlet. At least a dozen of these means of connecting electrical appliances are now near each of you.
We think about other types of sockets and plugs only when buying an iPhone from the USA or before a vacation in a distant country. In fact, there are more than ten common and varied types of plugs/sockets around the world.
Each one was designed with a specific purpose and poor yeast compatibility in mind. Now let’s look at all the exceptions and features of these types.
How did electrical outlets come about?
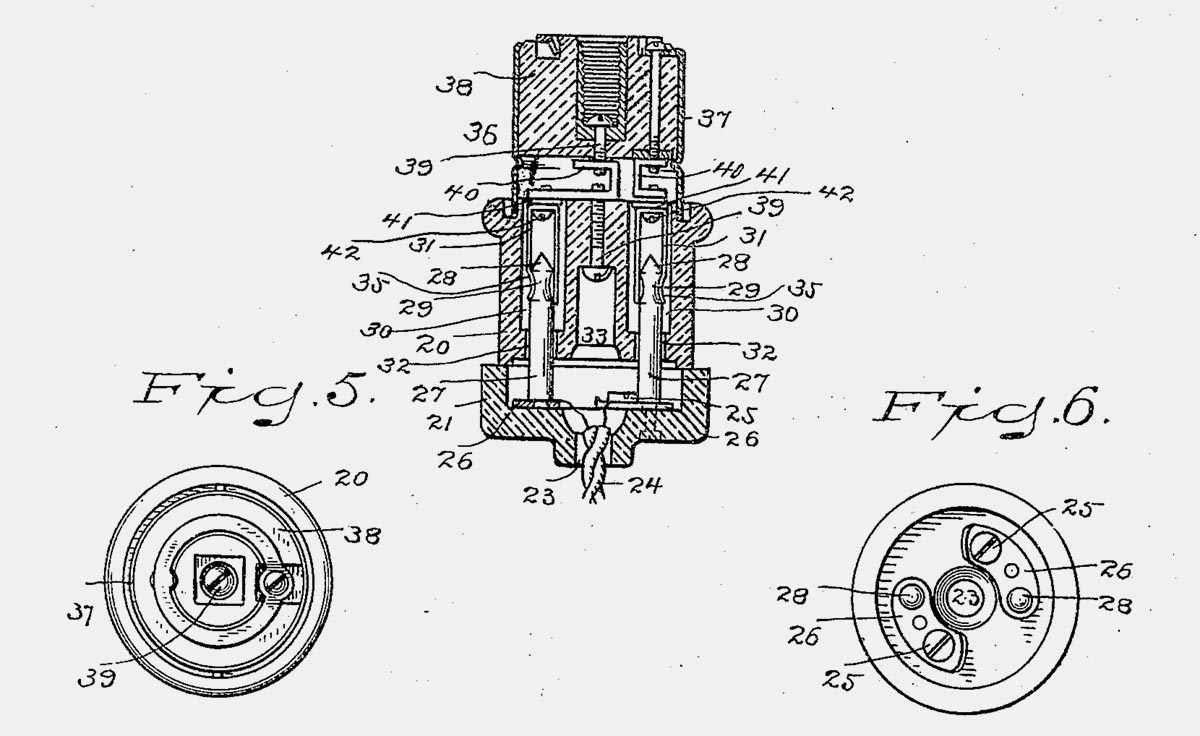
First patent describing a socket Harvey Hubbell (1904)
Electric socket is an electrical device for the mechanical connection and disconnection of standard circuits.
lighting in everyday life was used exclusively for lighting and appliances powered by a network of simply opaque. When using incandescent lamps powered by the first generation DC network, they were connected through a cartridge instead of a cartridge. It was inconvenient and not very safe.
So already at the beginning of the 20th century, developers first thought about creating a new standard for connecting to the network for electrical appliances. In 1904, the first receipt of the registration of a patent for a socket and plug occurs. The author was Harvey Hubbell (Harvey Hubbell).
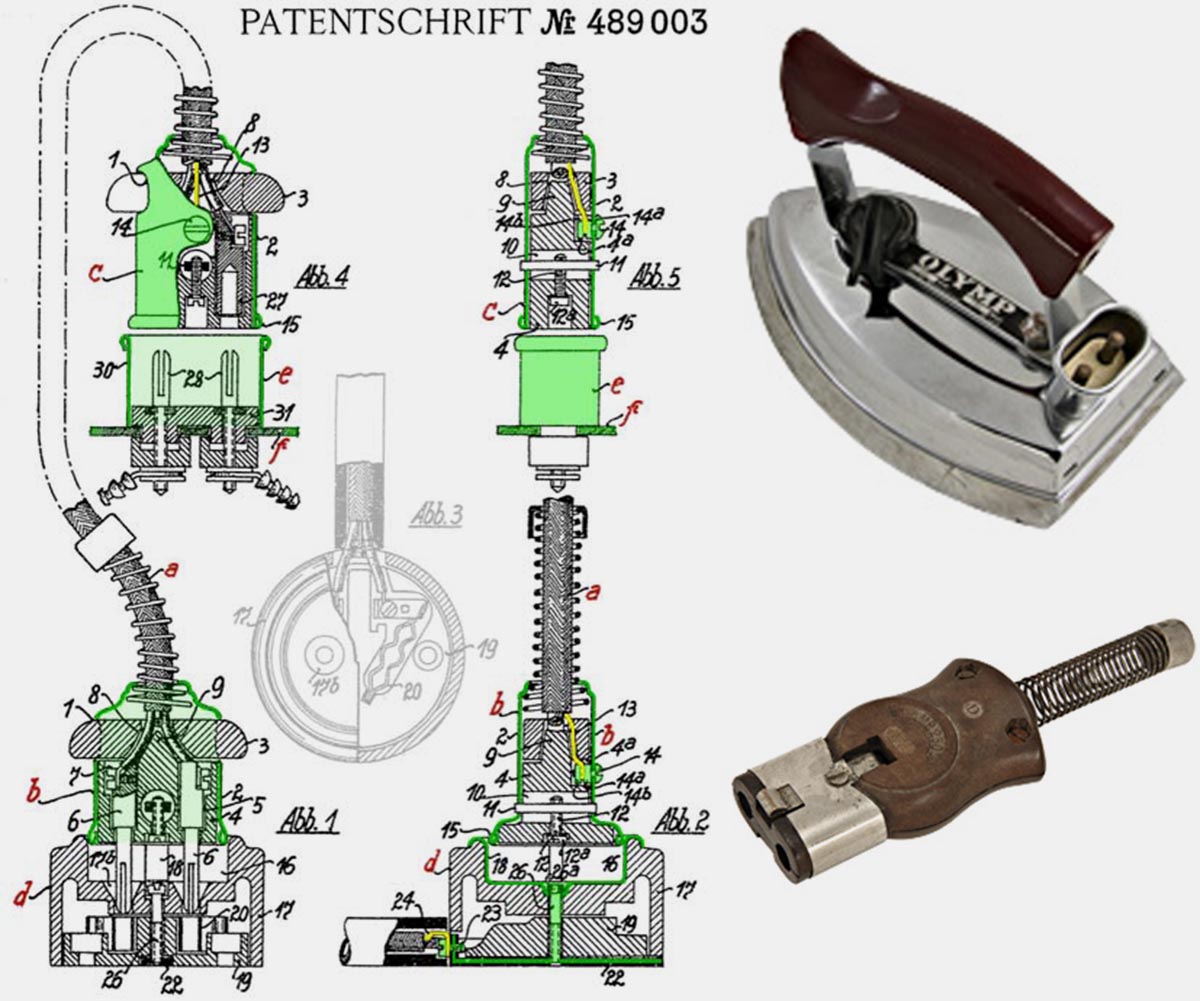
Patent measuring socket Albert Buettner (1926)
Over the years, many electronics manufacturers have begun to use this standard, but others have suggested a way to connect via socket adapters. Edison.
Later it became obvious that in addition to powering electrical appliances, additional applications were needed. In 1926 Albert Buettner (Albert Buettner) patented the system familiar today Shuko with monitoring contact.
Similar developments were carried out in other countries of the world, which cover a large number of different options for sockets and plugs for connecting electrical appliances.
Such disagreements were often caused by economic factors, when developing countries did not want to pay for expensive patents or be dependent on other countries. Sometimes the decision to create its own connection standard is purely political, when the state wanted to appear proud and free from its neighbors.
In addition to the best connection, the main parameters of the electrical networks were also different. Different parts of the world used different voltages and frequencies, which made it impossible to connect foreign devices even after changing the plug.
Standardization helped only partially
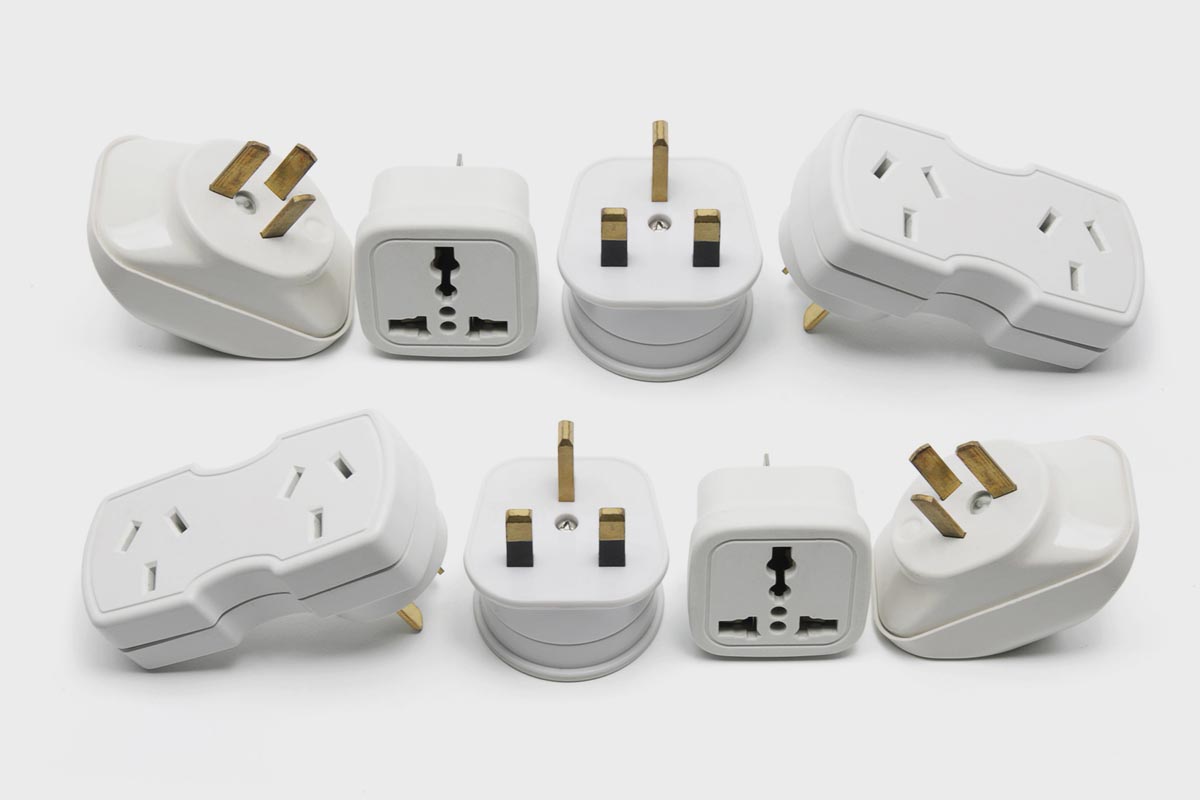

Already in the middle of the 20th century, it became clear that a huge number of devices spoils the concentration and development of electronics. After a large number of meetings, conferences and conferences, we managed to get together for general meetings.
Two main standards have been adopted worldwide: American 100-127 volts 60 hertz and European 220-240 volts 50 hertz. Many countries used strict frequency standards, but some adhered to the norms, although they used their own voltage and frequency values in the power grids.
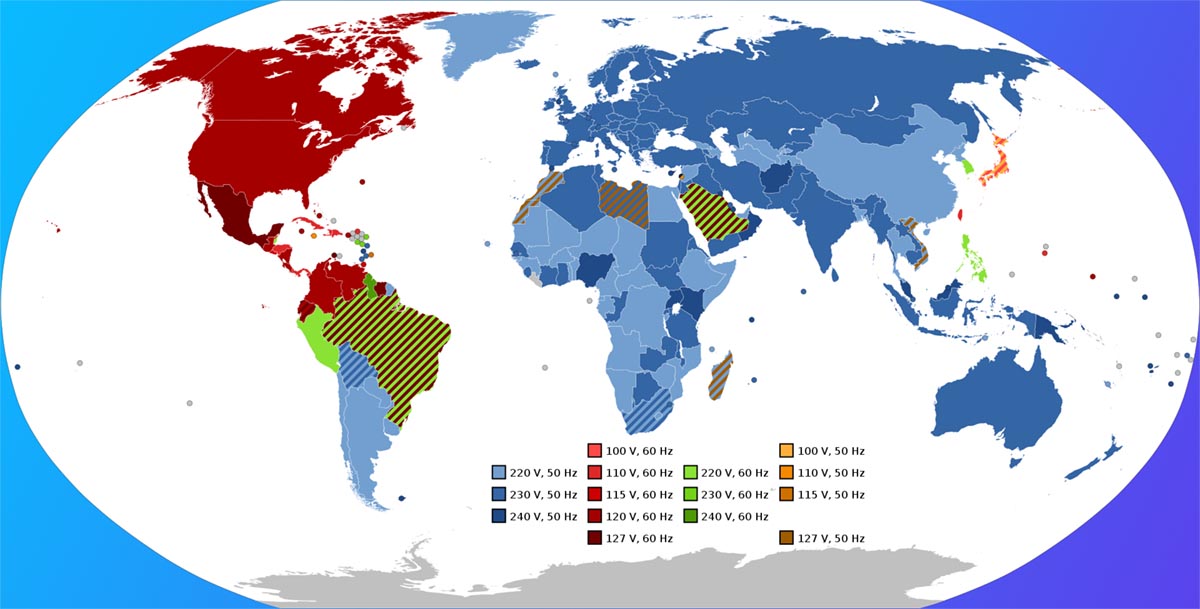
Accepted norms of rated voltage and current frequency in power networks
Different standards can occur even within the same country. So, for example, in Japan The voltage in the mains is the same everywhere – 110Vbut the frequency, depending on the region, is 50 or 60 Hz. And in Brazil reverse situation: at a frequency 60 Hz in different parts of the country there are networks on 127V or 220V.
This is due to the use of equipment from different countries in the electrification of regions. And if in the direction of promotion everything became relatively easy, then the ability to connect to the network turned out to be very difficult.
In the transition to standards 110/220V many agreed on the outcome of using the fork types A and B at deputies and forks types C and M at European type of power supply. This is not the case in all countries of the world.
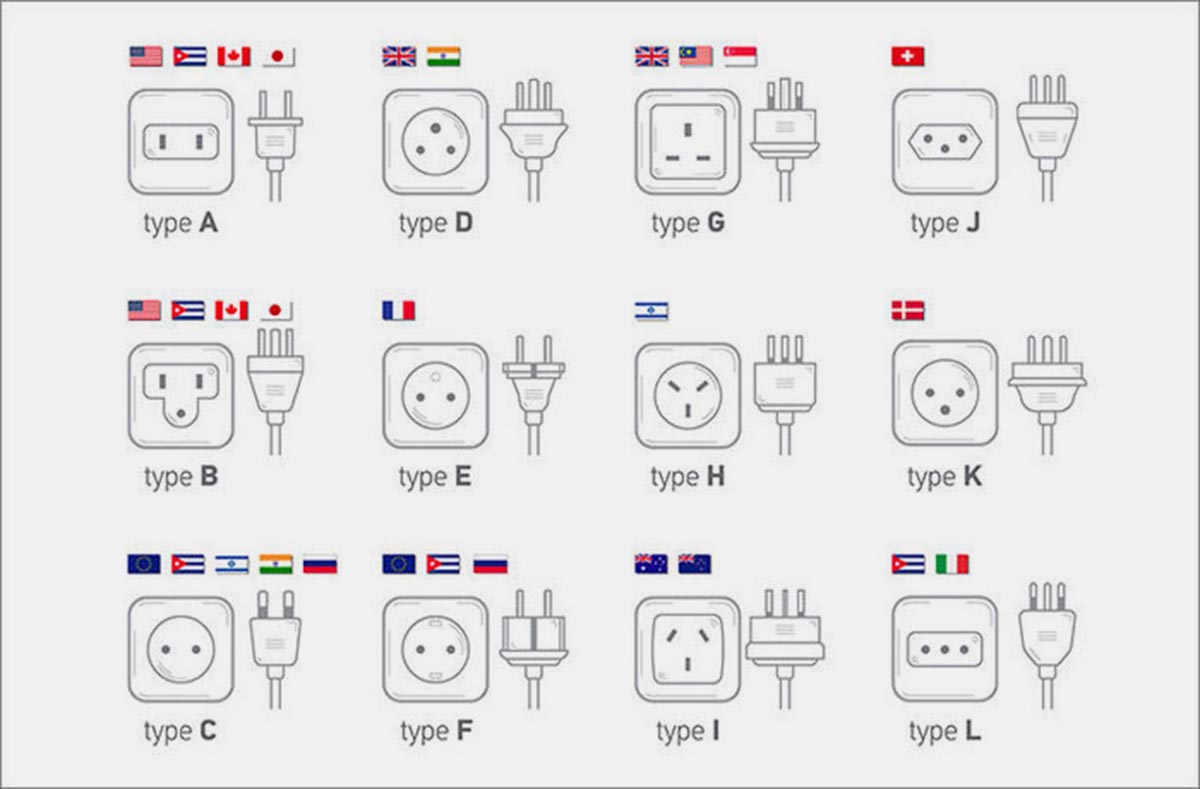
Different types of plugs and their distribution by country
Many were already manufacturing and selling more appliances with plugs of their own type, which made the transition standard long and costly for the public. So in the world contradiction appeared 12 main types socket and plug.
Almost fifty applications for connection. Against the background of such diversity, the transition to 12 main types already looked victorious.
You can conditionally divide all types into two- and three-pin. The first ones simply bring the phase and neutral contacts, and the second is supplemented with a contact for research.
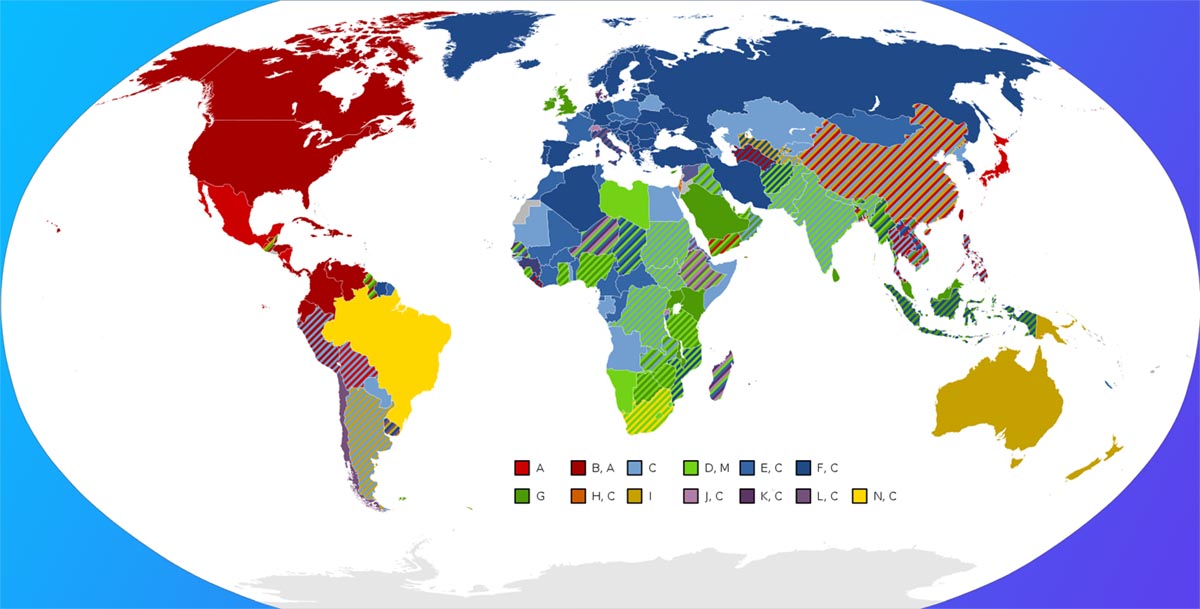
Distribution of types of different plugs and sockets by country
Apart from this case, some connections are polarized, plugging into such a socket may be the only possible case of polarity detection.
If the second half of the 20th century covered electronics manufacturers, then with the beginning of a new world problem, consumers also touched. People began to travel more and carry a lot of gadgets with them. Previously, travelers needed only the ability to connect a razor or hair dryer, but now there are a dozen different devices in the trunk that require connection to a foreign outlet.
Under today’s standard conditions, the transition of all countries to generally accepted electrical networks or to comparable characteristics of sockets for connecting appliances seems like a utopia. At the same time, a minimum of the federal states of the world can incur heavy expenses for re-equipment and re-equipment.
Until that happens, perhaps a few basic types of connections.
American plugs types A and B
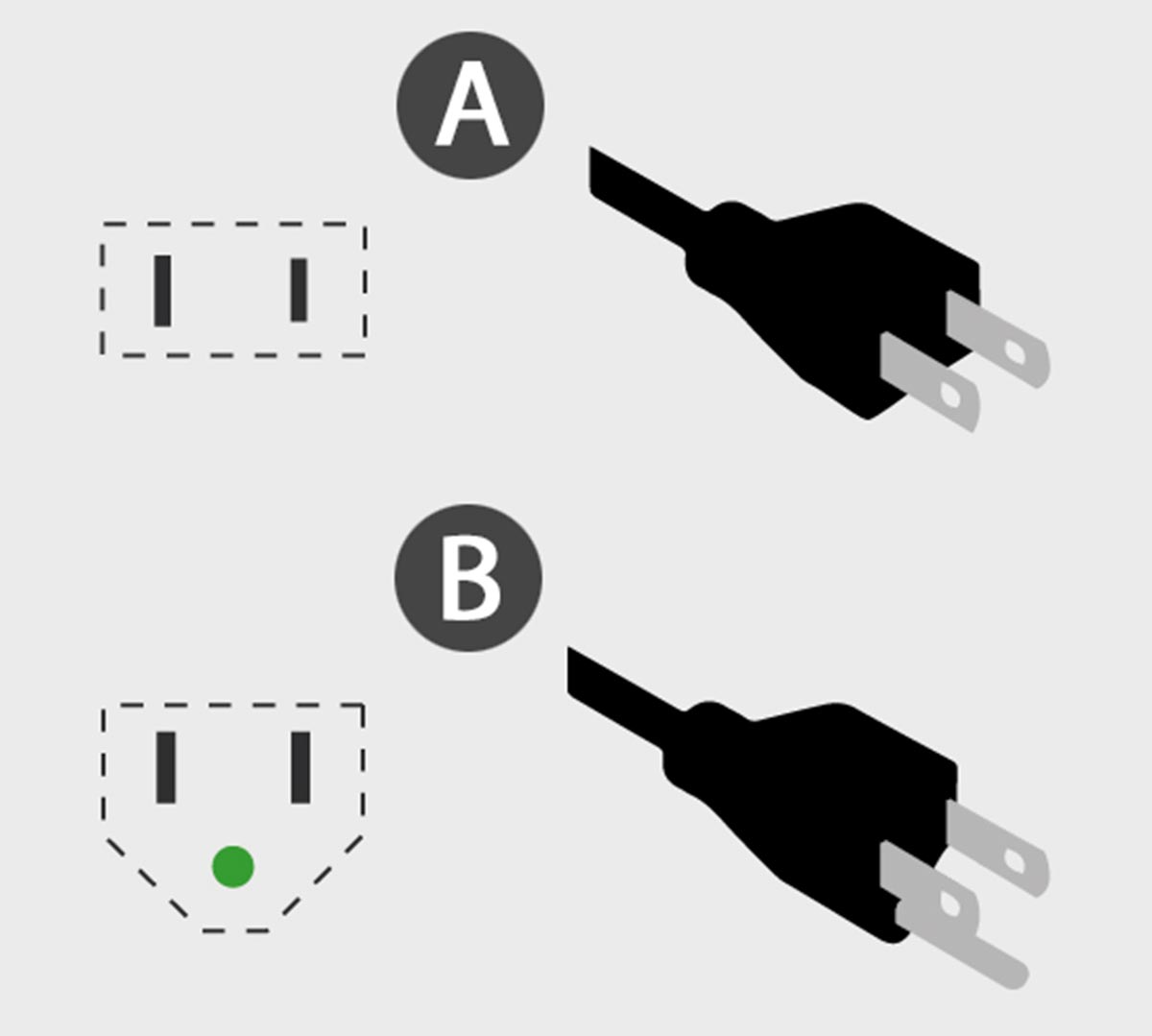
In which countries is it used: USA, Canada, Mexico, Japancountries and partly South America.
Type of connection to standard electrical networks 100-127V and 60 hertz. Distinguished by a pair of flat spores.
Between themselves BUT and B implies the presence of a grounding contact at the latter. This is a newer and more modern connection method with a U-type or used contact.
low forks types C and F
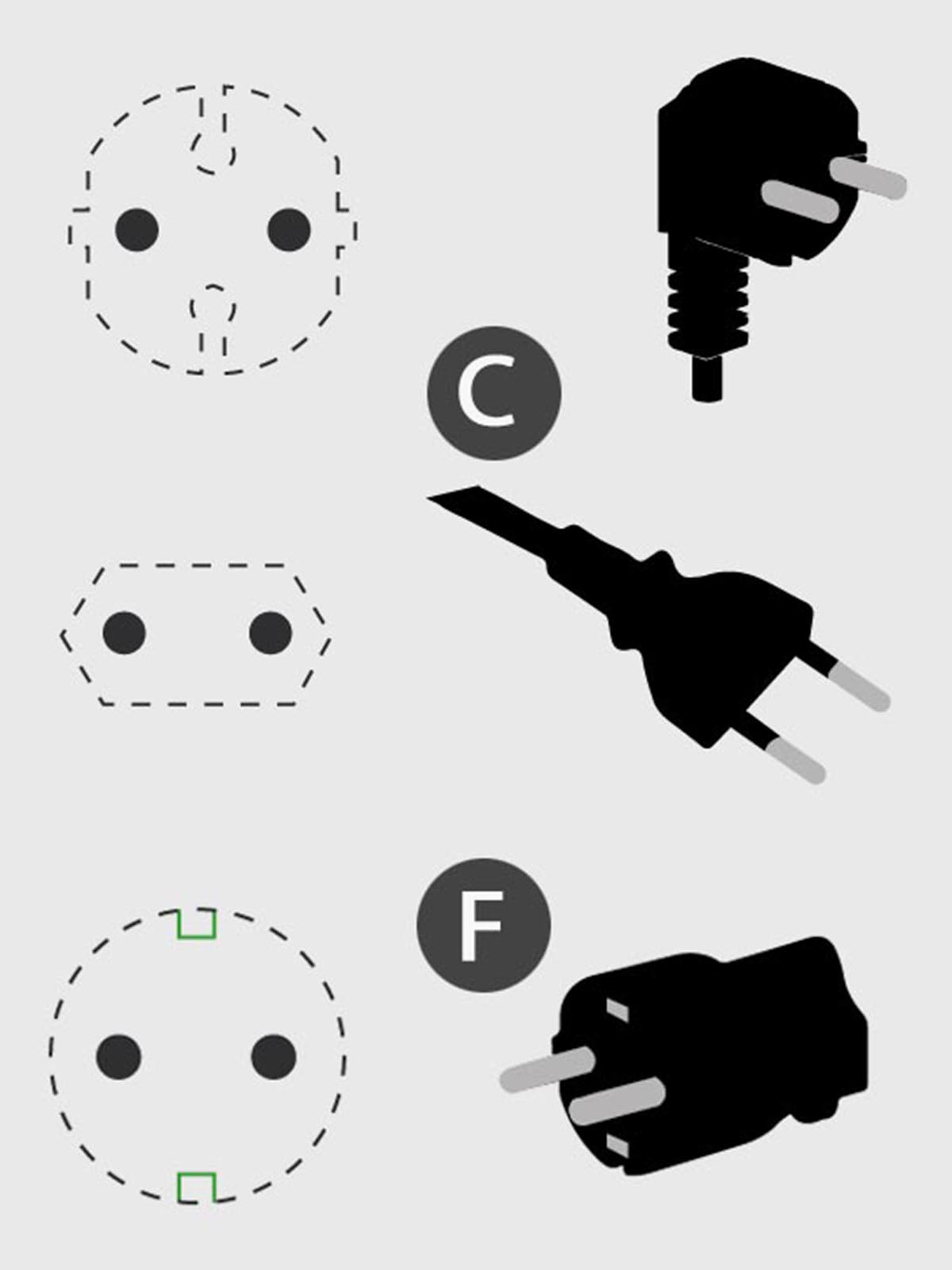
In which countries is it used: Russiamany countries Europenorthern and central countries photosome countries Asia.
This type of connection is mainly designed for mains 220-250V and 50 hertz. A pair of round connections are used for connection, which are suitable for connection. plug type FROM assumes the thickness of each contact 4 to 4.8 mmwhich often creates connection difficulties.
Many acceptable countries of the post-Soviet space at one time experienced problems with plugs of different types for domestic devices and new gadgets for the European market.
Newer connection type F it is assumed that there are two grounding disputes, which are closed with mating parts at the ends of the plug.
British plug type G
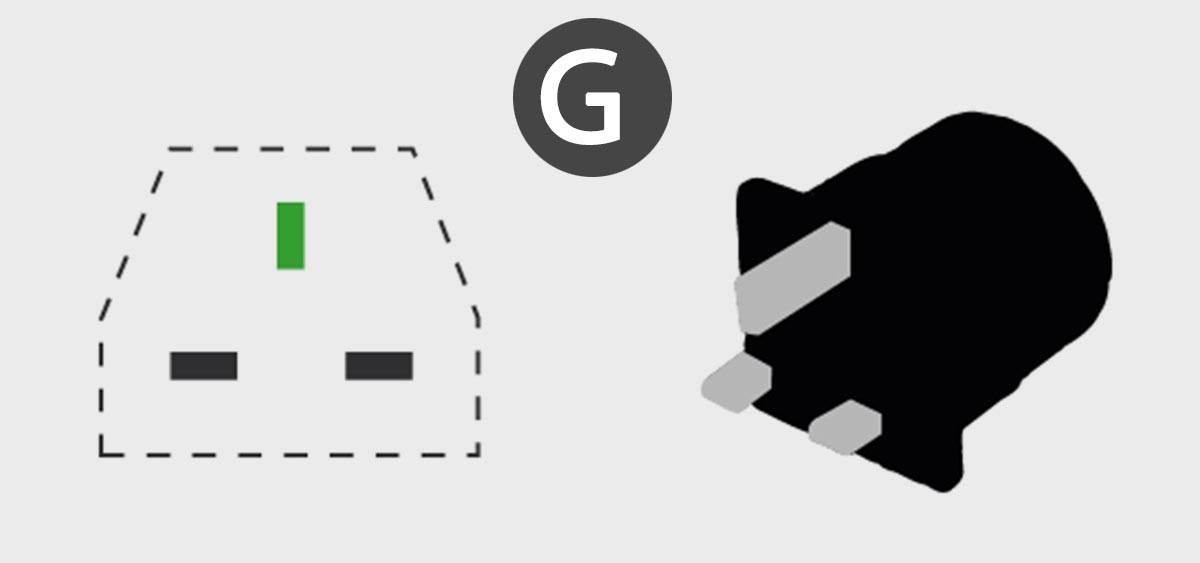
In which countries is it used: Great Britainits former colonies and dependent territories.
This is one of the most complex connection systems. Standards are being developed in the middle of the 20th century, but its stocks with changes still continue to be used.
Two horizontal rectangular pins are used for power, and a vertical vertical pin meets above them. The standard does not imply the use of plugs without consideration, because protective shutters are installed in the sockets. When the plug is connected, it is the deployment pin that allows you to open the protective shutters, and without it, the plug simply will not enter the outlet.
Some plugs have a plastic prong instead of a ground prong. This allows you to respect the polarization and protective shutters.
In addition, all UK-type plugs must have a built-in fuse. 3, 5, 10 or 13 ampsto keep electronics from power surges users. In addition, a clear requirement is put forward for various troubles inside the fork. The phase contact should always be fastened with an interference fit, and the neutral contact should always sag. Since in the event of a sharp impact and a wire break, the circuit is always de-energized.
British D and M forks for colonies
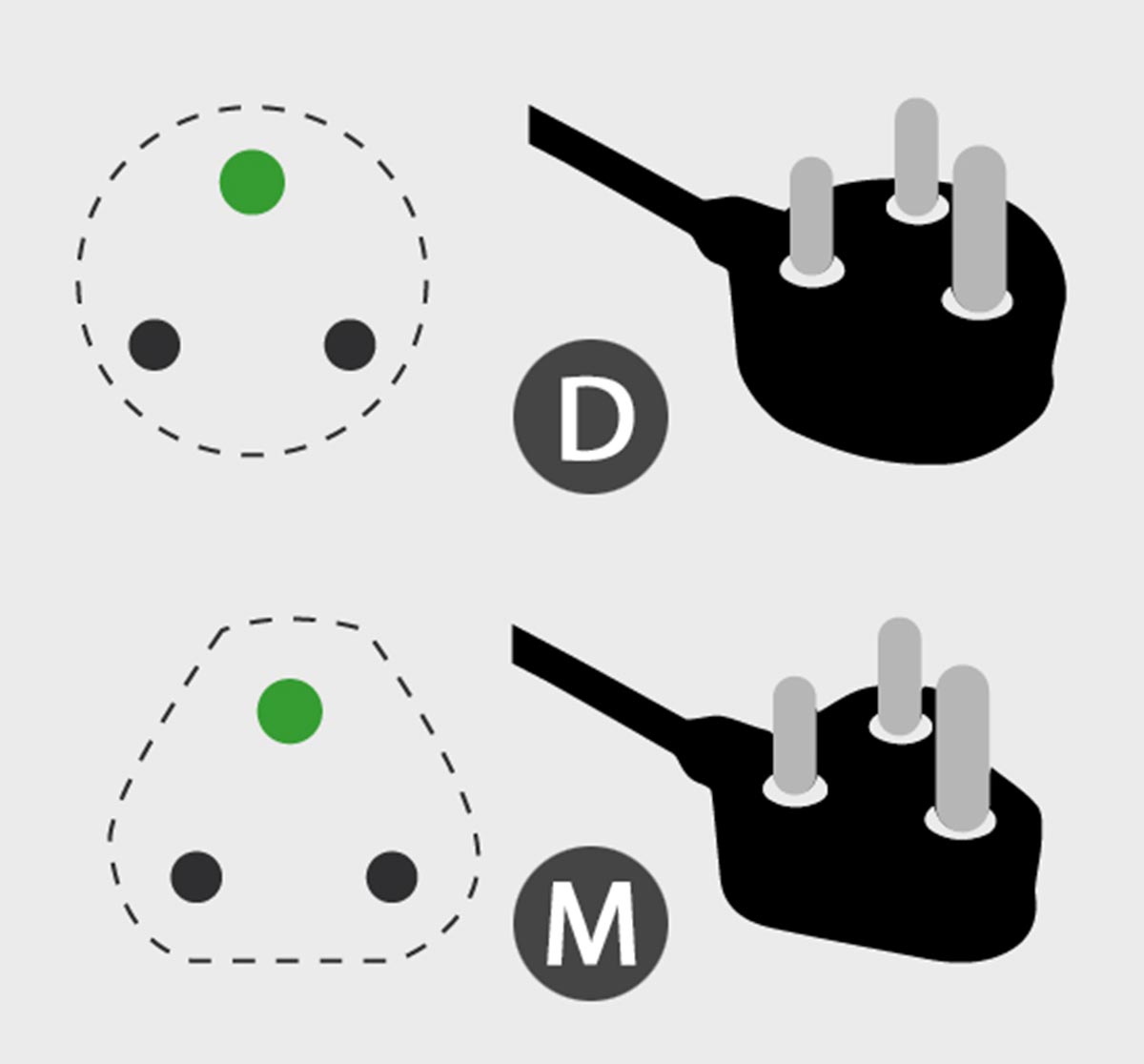
In which countries is it used: India, Hong Kong, Qatarsome countries of the center and south photosome countries Asia.
The standard is similar to the British one, but does not include shades of contrast on the fork. The location is similar to the progenitor, and the type itself was developed for use during colonization. In some former British dependency types of territories D and M is saved.
Currently, only in some cases there are problems associated with its development.
the main and more massive type Dtype of M considers it an active public. These include more stringent requirements, This allows you to apply the type M for 15 amp stops.
Australian Type I Plugs
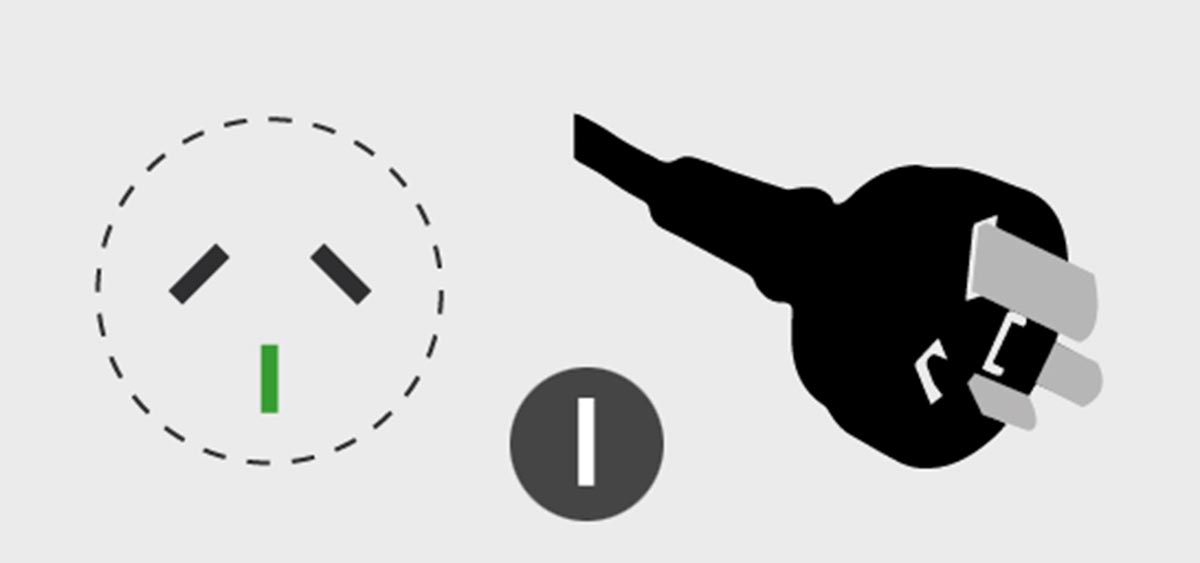
In which countries is it used: Australia, Argentina, China, New Zealandsome countries Oceania.
This type of fork is equipped with a pair of flat spores that fit at an angle of 60° to each other. If there is an external ground contact, it appears between the external manifestation at an angle of 30°.
This plug standard is quite common in mainland China. Many gadgets with AliExpress come with just such a plug for connection. In addition, there is a slightly different standard for 16A load. It does not support marking, but it does not fit into a classic socket of another type. I. When buying gadgets, high power or a special outlet can get into an unpleasant situation.
So, for example, the nearest contacts of a smart socket Xiaomi/Akara to control the air conditioner.
It is curious that a similar type of connector is used to connect industrial, medical and industrial equipment in the USSR from the 60s to the end of the 80s.
Local and less common types E, H, J, K, L
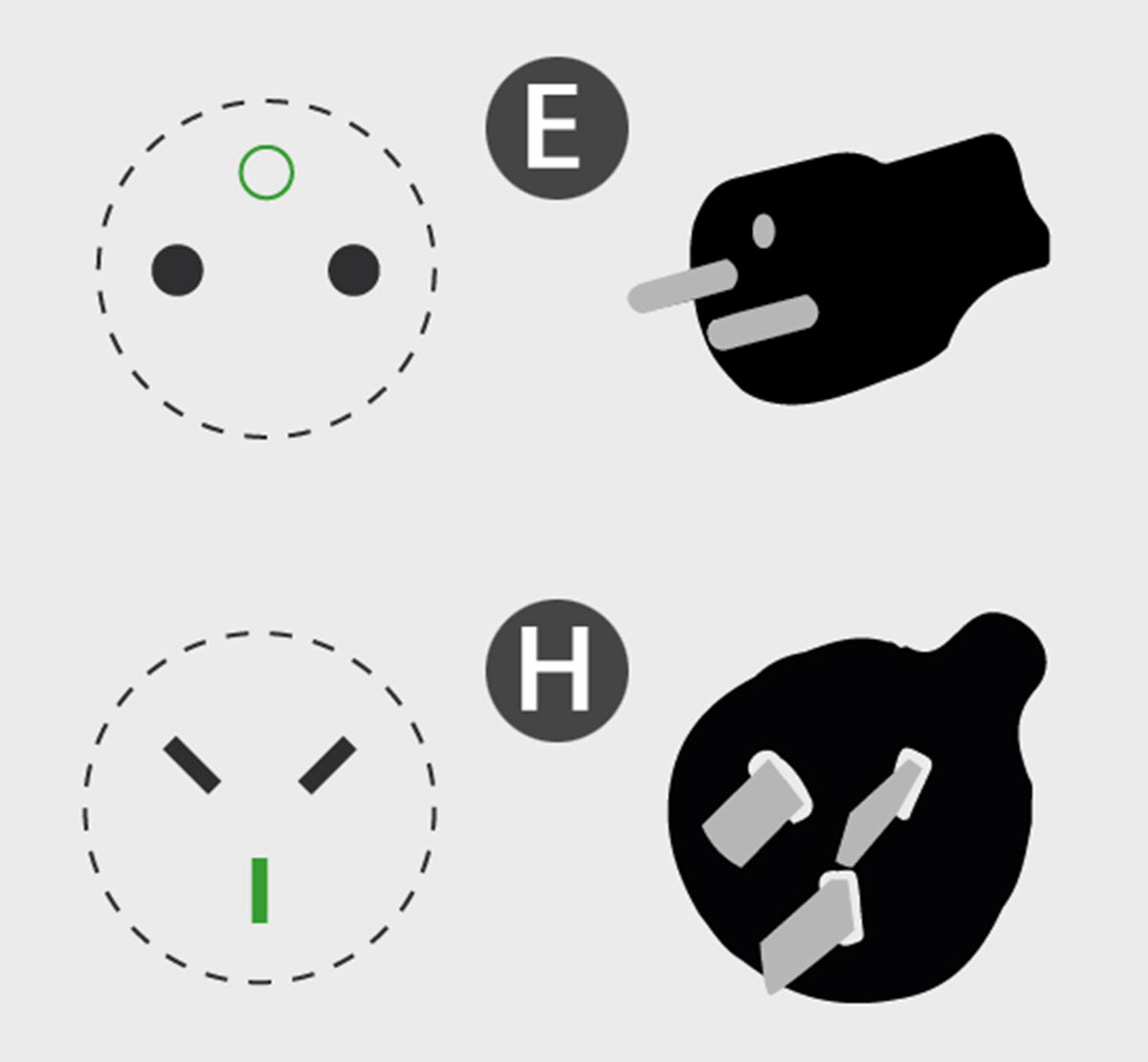
Type E originally developed for France and arrested in her former colonies. The type differs from an ordinary plug in thicker pins and the presence of a connector for the grounding pin of the socket.
Type H use the electronics connection standard for Israel. It is not applicable in other countries and may not be compatible with other combined plug/socket types. The old standard calls for three flat contacts in letter shapes. Dupdated – three round pins at an equal distance from each other.
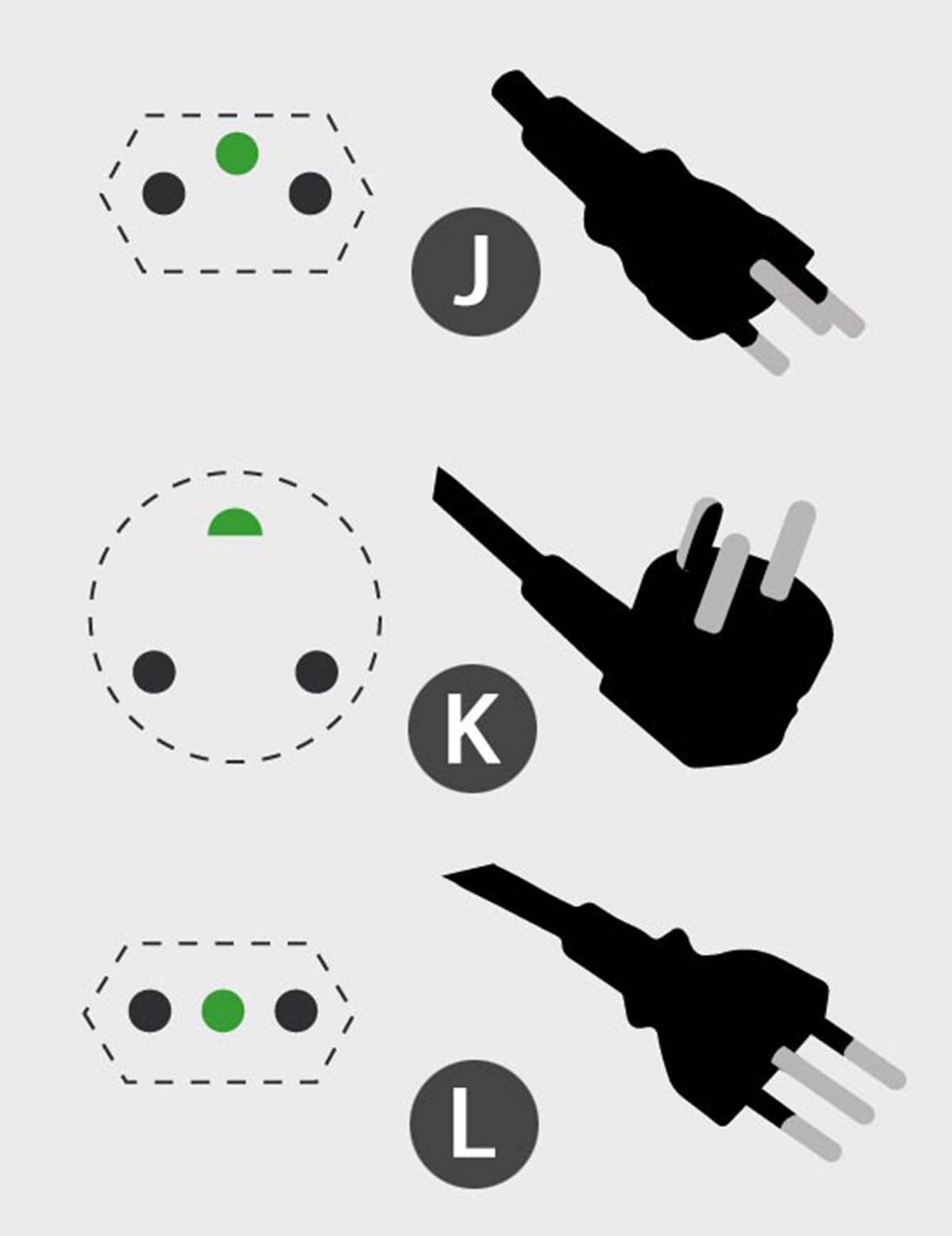
Type J standard for standard developmentswhich is similar to the European type FROM. It matches the offset square pin and the socket has a shallower plug depth. low prices work well in advertisements, but not vice versa.
Type K fork standard in Denmark. It has some distribution in other countries of the world and is similar to France. type E, differs from it in the location of the examination pin on the plug, and not in the socket. Danish sockets accept European plugs without problems, but not vice versa.
Type L connection of the standard in Italy. Consists of a calculation in a row of pins that can be larger than the diameter and at a greater distance for the load 16 A. The connection type was developed in the middle of the 20th century to connect instrument lighting (for a long time, your own payment tariff is required).
Tariff sharing is a thing of the past, but connection type detection is still found in this European country.
Such an abundance of circuits and connection types exist in the world of electronics. For half a century, mankind has not been able to reach agreements or compromise to limit the number of types of plugs and sockets produced.
At the same time, some countries and survey data are at war with Apple and full Type-C consumers.
Source: Iphones RU