In the last 20 years, technology has radically transformed societies. The Internet has become a part of our daily lives, creating a true parallel reality; devices have become essential extensions of human capabilities in everyday life, and there are those who say we are on the verge of merging the physical and digital worlds.
But, Not all people and companies can keep up with the dizzying pace of technological innovation.and that doesn’t mean they don’t have the financial capacity to update their tools. In fact, some older technologies are more reliable and useful than newer ones. Therefore, it is still adopted by large companies and certain segments of the population. Check out five old technologies still in use today.
1. Floppy disks
When International Business Machines (IBM) created the first floppy disk in 1967, it revolutionized data storage as an inexpensive, reliable and portable system. At that time, although large companies were using hard drives in machines, people still used paper punch cards for data entry and software programming.
The first floppy disks were eight inches and had a storage capacity of 80 KB. Over time, as the data density increased, the device shrank in size and the storage capacity increased to the 3.5-inch version with 5.76 MB. However, the most popular version is the same size and is 1.44 MB.
By the mid-1990s, more than 5 billion units were sold each year, contributing to the revolution in the computer and software industry. Since the advent of compact discs (CDs), floppy disks have become obsolete. With the advent of the pen drive, the technology certainly seemed doomed, but it didn’t.
Floppy disks continued to provide secure and reliable data storage for US nuclear missiles until 2019. Some models of Boeing 747 and AirBus 320 commercial aircraft, as well as ATMs, use these legacy devices to update systems.
2. Magnetic tapes

in the 1950s, Engineers discovered that magnetic tapes used to record audio could be used to store other types of data. Magnetic tapes such as digital audio tape (DAT) and linear tape open (LTO) have become the standard way to store large volumes of information that does not need to be accessed very often.
This hasn’t changed at all. Despite the advent of hard drives (HDs) and solid state drives (SSDs), older technology manages to be cheaper and store much more. The first DAT tapes could store up to 2MB, an impressive amount for the time, and they continued to improve their capacity. The latest version of the LTO driver allows you to save up to 580TB of raw data.
Tape libraries, which allow complex backups to be performed without human interaction, continue to be widely used to store archive content in the entertainment industry and other general digital storage applications where low cost is more important than fast access.
Magnetic tape, far from becoming extinct, is seen as the most cost-effective way to store large amounts of data, such as large tech parks or companies offering cloud services. Then, Major manufacturers such as IBM and Sony continue to invest in technology and develop new products.
3. pagers

When they were introduced in 1950, pagers were large, bulky and weighed almost a pound. Over time they got smaller and cheaper, became popular. In 1994, more than 61 million pagers were in use worldwide. But since the advent of cell phones in the late 20th century, this usage has waned.
they have approximately 5 million pagers are currently in service. This is because pagers have strengths that the new technology does not. It’s cheaper than smartphones, easier to carry, and virtually immune to hacking. Allowing only one-way communication prevents users from getting distracted.
About 80% of US hospitals still use pagers, according to a study by Hospital Journal medicine. Reliable communication is especially important during a major emergency. The equipment allows the simultaneous use of hundreds of people, does not distract users and still allows to separate personal and professional life.
Hospitals have areas where cell phones don’t work. Some walls are built to prevent X-rays from getting in, making it difficult for cell phone signals to pass through. Pagers do not have the same problem as they communicate using very high frequency radio signals such as FM radio broadcasting.
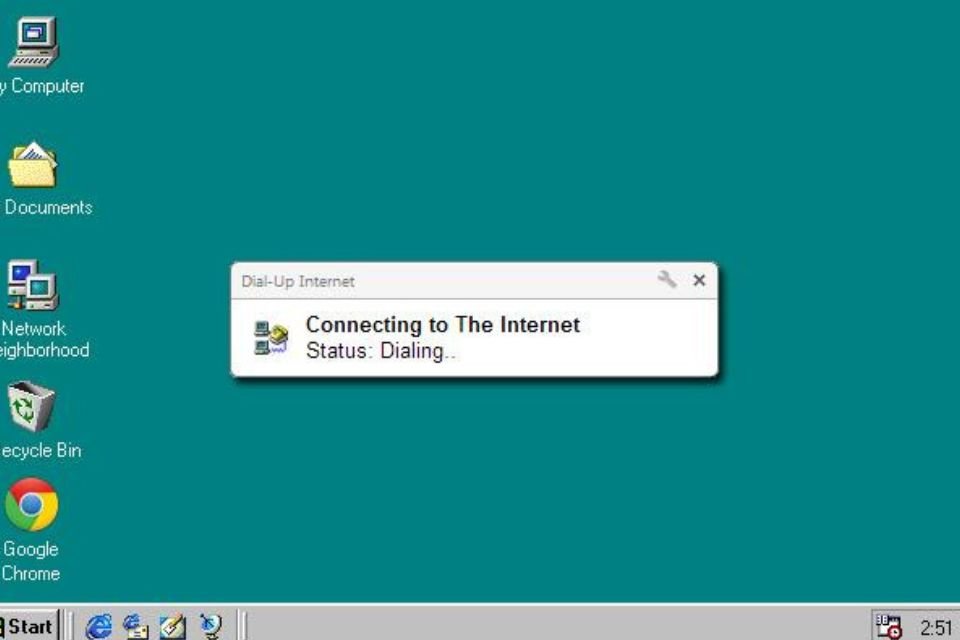
4. Dial-up Internet

Anyone who used the internet in its early days during the 1990s should remember the sequence of sounds announcing the dial-up connection. In the 2000s, technology was replaced by broadband, which provides faster, quieter internet connections without hindering phone use. Then came ways to connect to mobile devices, and dial-up was shelved.
But there are still those who remember this service and really need it. For users in regions without cable or satellite Internet or with economic restrictions, dial-up provides a way to connect. As a result, nearly 2 million people in the United States still connect by phone.
Dial-up internet works by taking the signal from an existing telephone line and converting it from voice communication to data communication. The amount of data that the dial-up Internet can transfer over the phone line is very limited, which often results in slow speeds of up to 56 kbps.
The service remains useful for users who don’t watch or stream videos, play games online, or share photos. However, dial-up internet is great for anyone who is overwhelmed by the complexity of modern high-speed internet plans and is looking for a simple way to check their email.
5. Voyager probes

Space travel represents one of humanity’s greatest achievements, but it also represents a great challenge. Once the spacecraft is launched, repairs or hardware upgrades are nearly impossible. For this reason, some spacecraft in Earth orbit use older technologies.
This is the case for Voyager I and II. The interstellar vehicle was launched in 1977 to gather relevant information from the universe. They also carry messages of humanity with photographs, music and greetings in various languages, carefully selected by astrophysicist Carl Sagan and his wife Ann Druyan.
The mission was intended to explore Jupiter and Saturn, but soon the program was expanded to send back information from Uranus, Neptune and Pluto. By the 1990s, the ships had already achieved these goals, and the mission once again gained a new goal: to leave the Solar System.
Traveling at more than 60,000 kilometers per hour, Voyagers I and II have become the most distant man-made objects and are more than 23 billion kilometers from Earth. All this with the same onboard computers as in the 1970s.According to the estimates of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), the spacecraft will continue to operate until 2025.
Source: Tec Mundo
I am a passionate and hardworking journalist with an eye for detail. I specialize in the field of news reporting, and have been writing for Gadget Onus, a renowned online news site, since 2019. As the author of their Hot News section, I’m proud to be at the forefront of today’s headlines and current affairs.