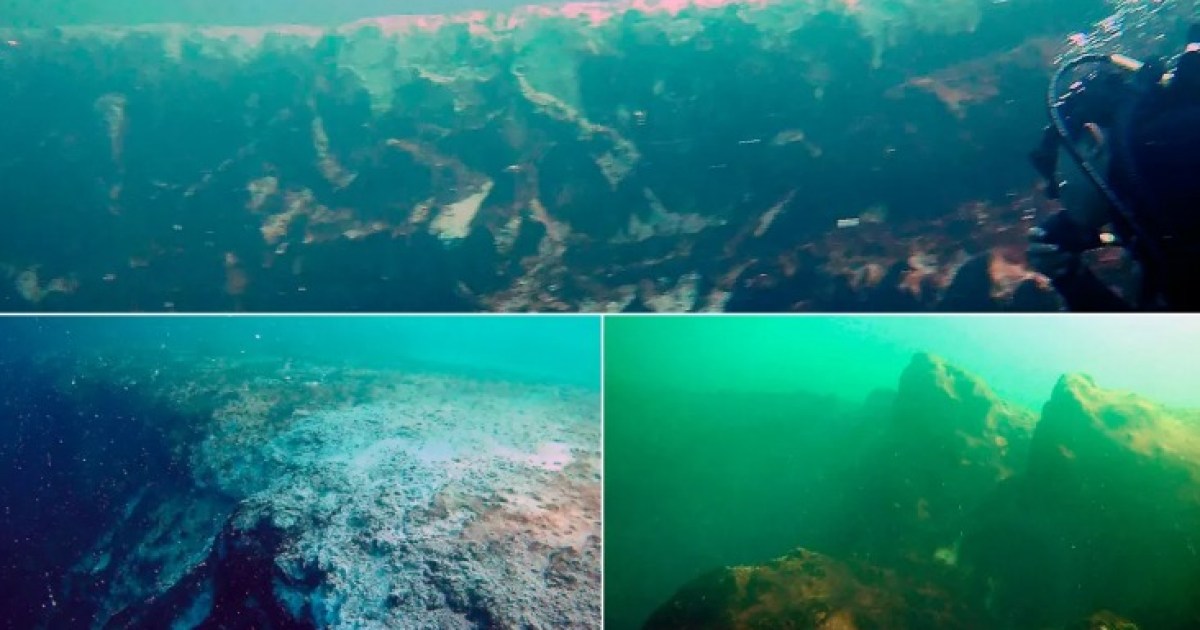
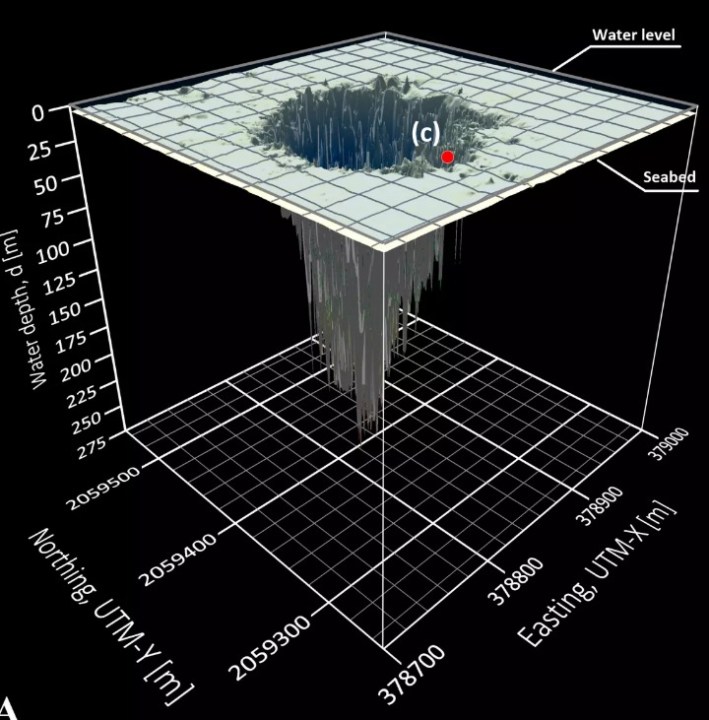
blue hole underwater geological formation which is characterized by having a depth much greater than the surrounding area. Blue holes are formed by the erosion of limestone rocks by fresh or salt water over thousands or millions of years and can support a wide variety of marine life and are of interest to divers and scientists.
And on the Yucatan Peninsula in Mexico, the second largest blue hole in the world has just been discovered. The giant underwater cave, located in Chetumal Bay, is about 900 feet (274 meters) deep and covers an area of 147,000 square feet (13,660 square meters).
This is slightly short of the record set by the world’s deepest known blue hole, the Dragon Hole in the South China Sea, which was discovered in 2016 and is believed to be over 980 feet (300 m) deep.
Many of the world’s blue holes probably formed during past ice ages, when repeated flooding and coastal drying eroded rocks and created voids. When the last ice age ended about 11,000 years ago and sea levels rose, these caves filled with water and some were completely flooded.
Blue holes can give a glimpse of what life was like thousands of years ago. The researchers note that without a lot of oxygen or light, fossils can be well preserved, allowing scientists to identify the remains of extinct species.

Blue holes can also tell us more about life on other planets. In 2012, researchers studying blue holes in the Bahamas found bacteria deep in caves where no other life forms lived.
Source: Digital Trends
I am Garth Carter and I work at Gadget Onus. I have specialized in writing for the Hot News section, focusing on topics that are trending and highly relevant to readers. My passion is to present news stories accurately, in an engaging manner that captures the attention of my audience.