A team of researchers from Delft has succeeded in teleporting quantum information over a small network of three nodes. This breakthrough is a big step towards a future quantum internet and has been made possible by improvements in quantum connections and quantum memory. The results of QuTech, a collaboration between TU Delft and TNO, were published today in the well-known scientific journal Nature.
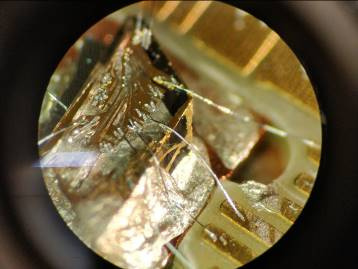
An interesting fact is that the qubits used are small diamonds powered by gold electrodes on the surface.
The nodes of the quantum network consist of processors between which information must be sent. Qubits are usually sent with photons over a fiber optic cable, but the longer the cable, the less likely they are to arrive. It is impossible to copy a qubit, so the loss of a photon means an irreversible loss of information.
One solution to this is teleportation. Yes, you read that right: the quantum bit disappears near the transmitter and reappears near the receiver without having to go through the gap in between. This requires a mixed connection in addition to a temporary storage method and a reliable read option.
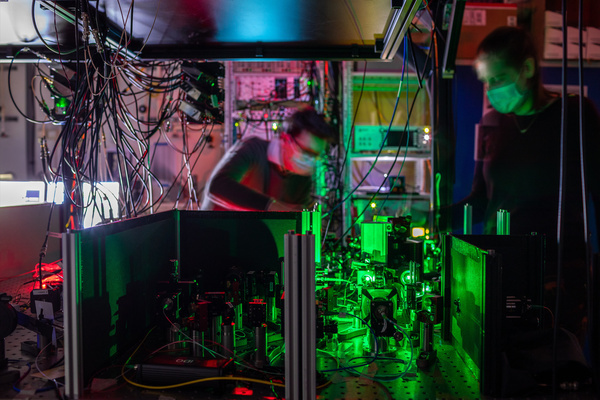

Previously, QuTech had managed to teleport qubits between two nodes. This has been achieved with all three from A to C via node B. To do this, A and B must first be circulated, then this must be stored. Now B and C are connected via entanglement and entangled with a “quantum mechanical trick” so that A and C are linked together.
After that, the information needs to be prepared so that it can be sent in encrypted form. After mutual communication about the measurement results, the bit can be decrypted and the information transmitted securely. Also see the QuTech animation where the method is also explained.
Subsequent investigations must reverse the order so that the qubit is prepared and stored first, and then teleportation is prepared. This is advantageous because the transfer can be performed on demand, multiple times if necessary. In the long run this should form the backbone of the quantum internet, which can be used, for example, for the reliable transfer of encryption keys.
Source: Hardware Info