TecMundo and #AstroMiniBR get together every week to share with you interesting and entertaining astronomical curiosities produced by collaborators From the profile on TwitterTo spread knowledge about Astronomy, one of the oldest and most relevant sciences in the scientific world. Check it out below!
#1: Sunspot cycle
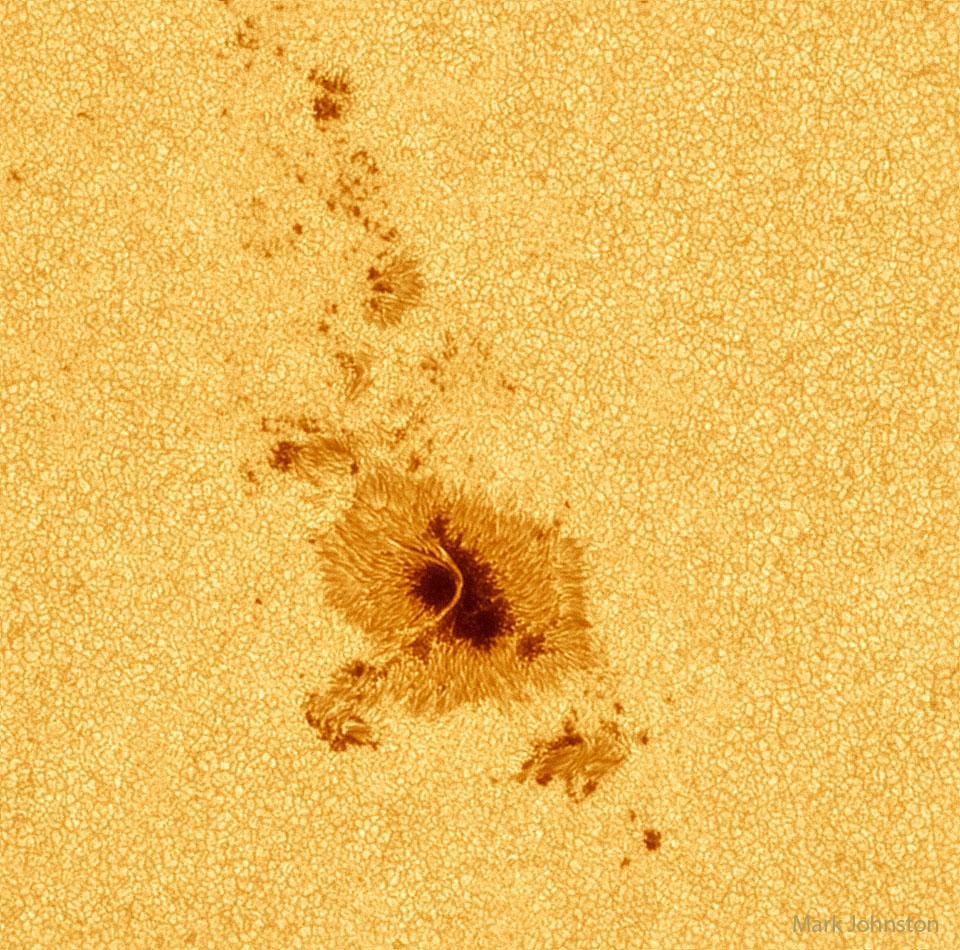
The sunspots that dot the Sun’s surface have fascinated astronomers and space enthusiasts for centuries. These are the regions where the solar magnetic field is concentrated, preventing the release of heat and light compared to the surrounding regions..
in this way they appear dimmer compared to the dazzling brightness of the adjacent sun’s surface.they reach temperatures between 4 and 6 thousand degrees Celsius, although in reality they are still extremely hot.
The sunspot cycle is one of the most remarkable aspects of their work: it is characterized by a periodic increase and decrease in the number of sunspots over time, with an average period of about 11 years. During the peak of the solar cycle, sunspot activity is intense and can be observed in greater quantities on the Sun’s surface. During periods of already low activity, few or no blemishes are visible.
#2: The future of our sun
And speaking of the Sun, our bright star, bathing the Solar System with light and warmth, is a living being that goes through a complex and glorious life cycle. Currently, the Sun is in a phase known as the “main sequence” where it fuses hydrogen in its core to form helium through nuclear reactions.. However, like everything in the universe, this situation is not permanent.
Over time, the hydrogen in the Sun’s core will inevitably run out, and when fuel runs out, gravity will kick in, causing the core to contract even more. This compression will allow helium to start converting into carbon and oxygen, resulting in even higher temperatures. This transformation will trigger a series of events, Including the sun turning into a red giant.
At this stage, it will increase significantly in size, possibly putting the closest planets, including Earth, on their way. After the red giant phase, the Sun will gradually shed its outer layers, releasing them into space, forming a planetary nebula with the remaining core being a white dwarf. Billions of years from now this will be the final stage in the evolution of the Sun!
#3: Why do we never see the full moon during the day?
A full moon is the lunar phase when the entire visible side of the Moon is illuminated by the Sun, making it bright and round in the night sky. The full moon appears at night because at this stage the Earth is on the opposite side of the Sun.. Therefore, when the Sun sets from the western horizon, the Full Moon is already rising from the eastern horizon, making it easily visible.
However, there are some exceptions where it is possible to observe the full moon during the daytime, but these are extremely rare cases: This can happen when the Moon is near the horizon, just after sunrise or before sunset. At these moments, the Moon can be seen close to the horizon where the Sun’s brightness is less intense, making it easy to observe its full phase even with solar illumination in the atmosphere.
#4: Did you know that Venus also has phases?
We all know that the Moon has different phases throughout the month, but it is far from the only celestial body in the Solar System to exhibit this phenomenon. Venus, for example, is one of the planets that shows different reflections of sunlight when viewed from Earth.
The phases of Venus express different aspects of its surface.As it orbits the Sun, it goes through several phases that are easily visible with the use of small telescopes, and this is due to its position relative to our planet and the Sun.
Venus is one of the brightest celestial bodies in the night sky, visible both at dusk and at dawn. As the planet moves in its orbit around the Sun, it goes through four main phases: growth, hump, hail, and contraction..
#5: Pareidolia in astronomy
Pareidolia is a psychological phenomenon that causes our brain to recognize familiar patterns, such as familiar faces or shapes, in random objects or abstract images. Although often associated with more mundane perceptions such as figures in clouds or everyday objects, This effect is also common in astronomical observations, where astronomers and enthusiasts often find recognizable shapes in distant objects..
A notable example of pareidolia in astronomy is the interacting galaxies NGC 2936 and NGC 2937, pictured above, in the constellation Hydra, about 326 million light-years from Earth. How do they look to you?
Did you like the content? So, hear about other astronomical curiosities here at TecMundo, and also take the opportunity to read: Scientists observe orbiting planets outside the solar system.
Source: Tec Mundo
I’m Blaine Morgan, an experienced journalist and writer with over 8 years of experience in the tech industry. My expertise lies in writing about technology news and trends, covering everything from cutting-edge gadgets to emerging software developments. I’ve written for several leading publications including Gadget Onus where I am an author.