The James Webb Space Telescope confirmed the presence of heavy elements in a gamma-ray burst (GRB). GRB 230307A. This is the second brightest gamma-ray burst ever observed from a kilonova.
The most important feature of the discovery presence of tellurium, a chemical element belonging to the complex kingdom of metalloids in the periodic table. Scientists also think that iodine, a non-metallic element vital to life on Earth, may also be present in the gamma-ray burst.
cosmic treasure
Andrew Levan, professor of astrophysics at Radboud University in the Netherlands and professor emeritus at the University of Warwick in the United Kingdom and lead author of the study, said: “It has been more than 150 years since Dmitri Mendeleev wrote the periodic table of the elements. James Webb Space Telescope “Thanks to this, we are finally in a position to begin to fill in the last gaps in our understanding of where everything comes from.”
despite Tellurium is one of the rarest elements on earth, even rarer than platinumIt can be used in a wide variety of applications such as semiconductors, oil refining and solar cells.
Tellurium is found in planetary nebulae and old stars, making it even rarer. Iodine, a coexisting element, plays a fundamental role in alleviating stress and inflammation in humans, highlighting its importance for life on Earth.
astronomical news
With an impressive duration of 200 seconds and an intensity approximately 1000 times greater than conventional GRBs, GRB 230307A first appeared on radar in March 2023, thanks to NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope.
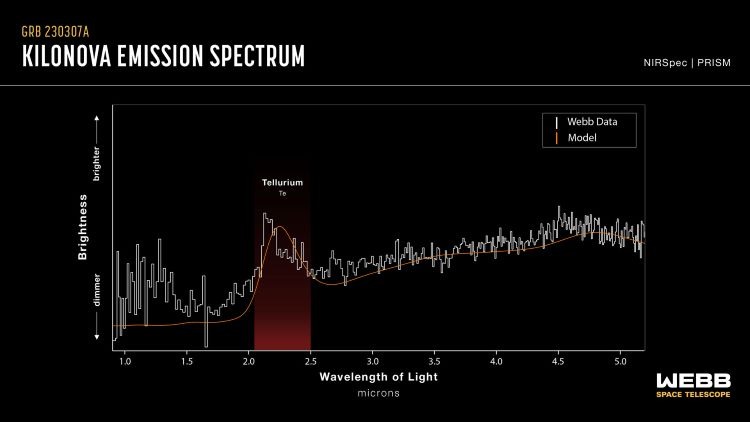
Subsequent observations were conducted 29 and 61 days after the explosion using JWST’s mid-infrared spectroscopy and imaging instruments. The first observations of this GRB date back more than fifty years; The first detection occurred on July 2, 1967, and official confirmation occurred in 1969.
GRBs are categorized as short or long, with short bursts lasting less than two seconds and long bursts lasting several minutes. Kilonovae, which arise from the merger of two neutron stars, are considered to be the birthplace of elements much rarer and heavier than iron.
However, similar to the elusive elements they allegedly reveal, they are extremely rare and extremely difficult to detect.
Did you like the content? So stay updated with more news like this about astronomical chemistry on TecMundo, and don’t forget to share the article on your social networks and with your friends who love these topics.
Source: Tec Mundo
I’m Blaine Morgan, an experienced journalist and writer with over 8 years of experience in the tech industry. My expertise lies in writing about technology news and trends, covering everything from cutting-edge gadgets to emerging software developments. I’ve written for several leading publications including Gadget Onus where I am an author.