The universe is a vast and mysterious place with countless celestial bodies, including planets beyond our solar system. Distant planets, also known as exoplanets, have captured the imagination of astronomers and space enthusiasts..
An exoplanet or extrasolar planet, is a planet orbiting a star outside our solar system. These planets can be rocky, like Earth, or gas giants, like Jupiter, and have a wide range of sizes, compositions, and orbital characteristics.
Fermi Paradox
The Fermi Paradox begins with the understanding of the Fermi Paradox, given the size of the universe and the existence of countless stars and habitable planets. We should expect to have already made contact with extraterrestrial civilizations.
The size of the universe is a very important aspect of the Fermi Paradox. There are 100 billion galaxies in the universe, each consisting of thousands of stars and planets. It is strange that we have not yet found signs of advanced alien life.
The strangest exoplanets ever discovered
55 Cancri and
55 Cancri is an exoplanet orbiting the star 55 Cancri, located approximately 40 light-years from Earth in the constellation Cancer. It was discovered in 2004 and has been called a “super-Earth” because it is larger than our home planet..
It was detected using the radial velocity technique, which measures the speed of a star as it is attracted to a planet orbiting it. 55 Cancri is located very close to its parent star and completes its orbit in just 17.7 hours.
H.R. 5183b
HR 5183b is an exoplanet orbiting the star HR 5183. It is located approximately 102 light-years from Earth, in the direction of the constellation Hercules. It was discovered in 2019 and belongs to a class of exoplanets called “giant exoplanets” because they are very close to their parent stars.
WASP-103b
WASP-103b was discovered in 2014 by the Wide Angle Search for Planets (WASP) project. using a transit method to detect exoplanets.
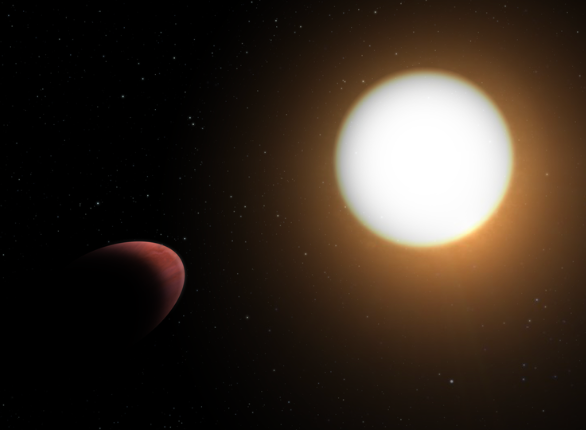

This method observes brightness of a star to describe periodic dimming It occurs when a planet passes in front of it. It is classified as a “Hot Jupiter,” and daytime temperatures on this exoplanet can reach 2,500 degrees Celsius (4,532 degrees Fahrenheit).
WASP-76b
WASP-76b is an exoplanet located in the constellation Pisces, also classified as a “Hot Jupiter”. The atmosphere is chaotic, with winds that can reach speeds beyond human comprehension..
HD 189773b
HD 189773b is a remarkable exoplanet located approximately 63 light-years from Earth in the constellation Vulpecula. It was discovered in 2005 using the transit method. An innovative technique that allows astronomers to detect momentary dips in a star’s brightness when an exoplanet passes in front of it.
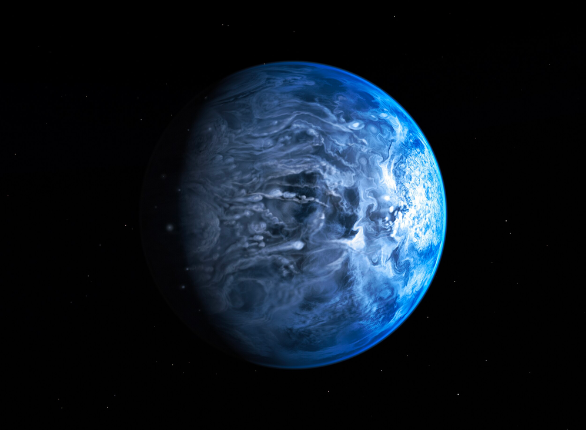

HD 189773b is a gas giant similar in size to Jupiter but with extreme conditions. The atmosphere, where temperatures exceed 1000 degrees Celsius, is filled with gases such as hydrogen and helium.
Also read:
OTS44
OTS44 was first discovered in 2010 by NASA’s Kepler Space Telescope, a mission to find exoplanets. It is located approximately 560 light-years from Earth, orbiting a star in the constellation Cygnus.
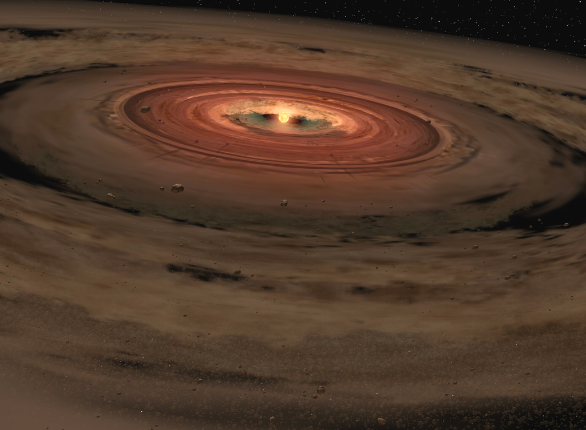

It is a gas giant, meaning it consists mainly of hydrogen and helium. This planet is so big, It has a much larger mass than Jupiter, the most important planet in our solar system..
HD 206893c
HD 206893 c orbits a star very similar to our Sun and is located about 195 light-years from Earth.
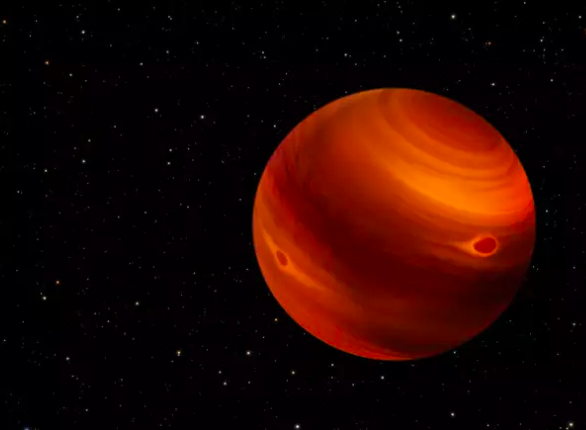

This exoplanet is classified as a super-Earth; that is, larger than Earth but smaller than gas giants like Jupiter. HD 206893 c raises questions about its habitability and potential for life, given its intriguing size and proximity to its host star.
Gliese 1132b
Gliese 1132b was first discovered in the Atacama Desert in Chile by the MEarth-South community in 2015.
This outer planet It orbits the red dwarf star Gliese 1132, located about 39 light-years from Earth in the constellation Vela. It is also part of the category of super-Earths whose mass and radius are larger than Earth but smaller than Neptune.
Kepler-10b
Kepler-10b was discovered by NASA thanks to the Kepler Space Telescope launched in March 2009. It is considered a hot exoplanet because it orbits very close to its host star. Kepler-10, a G-type star similar to our Sun.
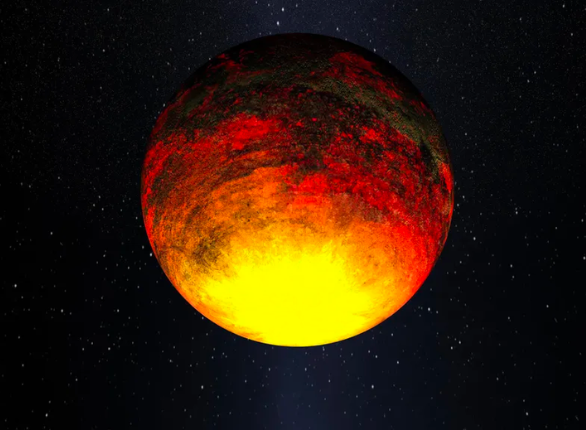

Its size and composition are fascinating; It is predominantly rocky and denser than Earth. It is a relatively small exoplanet, with a diameter approximately 40% larger than that of Earth.
TOI-3757b
TOI-3757 b was first identified by the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS), which detected periodic dips in the brightness of a star in the constellation Taurus.
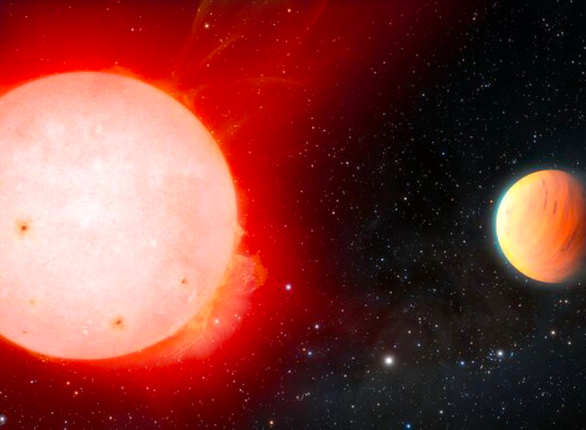

It is classified as “Hot Neptune”. This means A gas giant similar to Neptunehowever, it orbits its supporting star at a greater distance, resulting in higher temperatures.
Did you enjoy learning a little more about exoplanets and their properties? Stay informed about the latest astronomical discoveries at TecMundo and get the opportunity to visit the NASA observatory to search for life on exoplanets.
Source: Tec Mundo
I’m Blaine Morgan, an experienced journalist and writer with over 8 years of experience in the tech industry. My expertise lies in writing about technology news and trends, covering everything from cutting-edge gadgets to emerging software developments. I’ve written for several leading publications including Gadget Onus where I am an author.











