Research led by scientists at Macquarie University in Australia has presented a new approach to “sequestering sulfur in its oxidized sulphate form, as well as base and precious metals” from deep within the Earth’s inner mantle. Poured at low temperature and rich in carbon, these materials may contain a treasure trove of “green metals.”
It is not news to anyone that the global implementation of sustainable energy solutions naturally includes the availability of metals necessary for the production of battery components, solar panels, electric vehicles, among other “green” technologies.
The study, published in the journal Science Advances, was led by Dr. The team led by Isra Ezad, Managed to create small amounts of molten carbonate very similar to those present at a depth of 90 kilometersthrough high pressure and temperature experiment.
How did scientists extract green metals from Earth’s mantle?
Earth’s mantle, a rocky layer beneath the crust and above the core, consists of silicate rocks (composed of silicon and oxygen) that are part of the lava erupted from volcanoes. Despite, About 1% of these deep rocks contain carbon and waterThis allows rocks to be melted at lower temperatures than other parts.
What the scientists did was simulate in the laboratory the melting of carbonate rocks under conditions similar to the Earth’s mantle. They then measured the amount of metal and sulfur present in the molten liquid and finally compared their results to studies of volcanic rocks formed when magma rises to the surface from the mantle.
Although they previously knew that carbonate melts contained rare earths, the new research went even further. “We showed that this carbon-containing molten rock absorbs sulfur in its oxidized form, while dissolving precious and base metals extracted from the mantle (the ‘green’ metals of the future).”says Ezad.
Discovering green metals in the Earth’s core
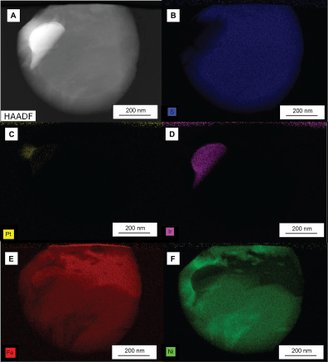
Dr. According to Ezad, the research topic was the increasing difficulty of finding reliable sources of essential metals needed for the development of batteries for wind and solar technologies. It is thought that it is essential to overcome this difficulty in the transition from fossil fuels to clean energy sources.
In this sense, the study shows that the new approach will make it possible to understand the large-scale redistribution of metals and the formation of ores on Earth over time. New data will allow us to explore carbonate melt deposits as a hitherto undiscovered source of essential and valuable minerals.
The author concludes: “Carbon-sulfur melts dissolve and concentrate these metals in separate regions of the mantle, transporting them to shallower crustal depths where dynamic chemical processes can lead to the formation of ore deposits.”
Is there anything you want to ask? Tell us on our social networks and get the opportunity to share the article. Until later!
Source: Tec Mundo
I’m Blaine Morgan, an experienced journalist and writer with over 8 years of experience in the tech industry. My expertise lies in writing about technology news and trends, covering everything from cutting-edge gadgets to emerging software developments. I’ve written for several leading publications including Gadget Onus where I am an author.