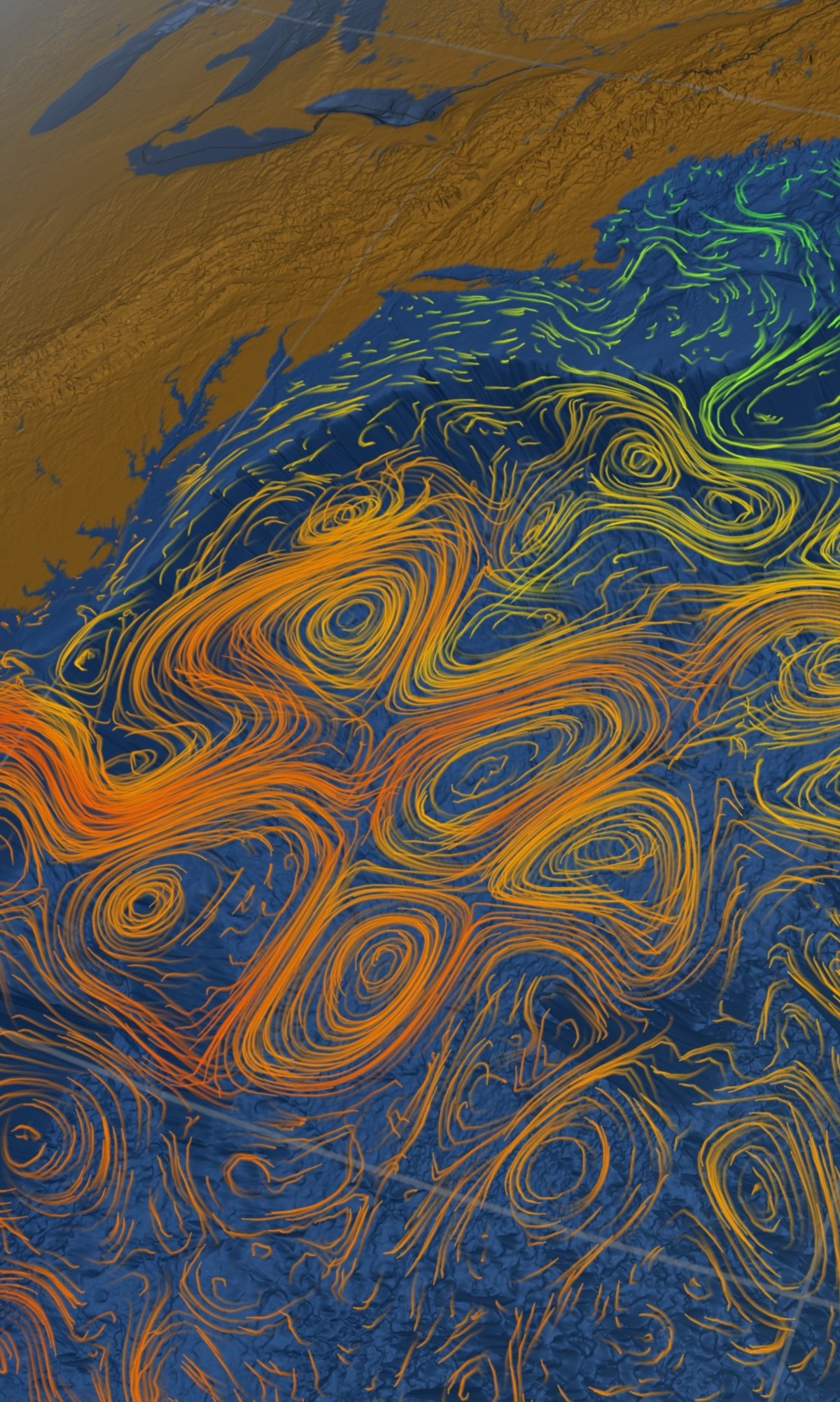
Like a huge artery, The marine current known as the Gulf Stream carries the heat and enormous amounts of nutrients necessary for life. Through the Strait of Florida, between this American state and Cuba, then passing the east coast of the USA and Canada, crossing the North Atlantic, it finally reaches Europe.
Being part of the Atlantic Meridional Circulation (AMOC), the Gulf Stream also participates in the system of transporting soft water from the tropical regions of the Southern Hemisphere to the Northern Hemisphere.
A new study published in the journal Science warns: “If anthropogenic climate change causes a decline in the strength of the AMOC and thus the Gulf Stream, then this food source will decline.” To examine the effects of a possible change in the flow of vital resources, They examined another time on the planet where the event occurred: the Recent Dryas.
What was the Late Dryas ice age?
The Last Dryas was a sudden and severe winter that froze the entire Earth at the end of the Pleistocene epoch, between 12,700 and 11,700 years ago, a period considered short in geological terms. The cold wave caused a drop in global average temperatures, temporarily reversing the ongoing warming period.
There are studies showing AMOC weakening during this freezing rangesays the research.
“Although the details of the background climate state and the temporal scale of change are different from today, this past climate event provides an opportunity to test the mechanisms identified in current climate models,” the authors conclude.
What did the study discover from Atlantic currents?
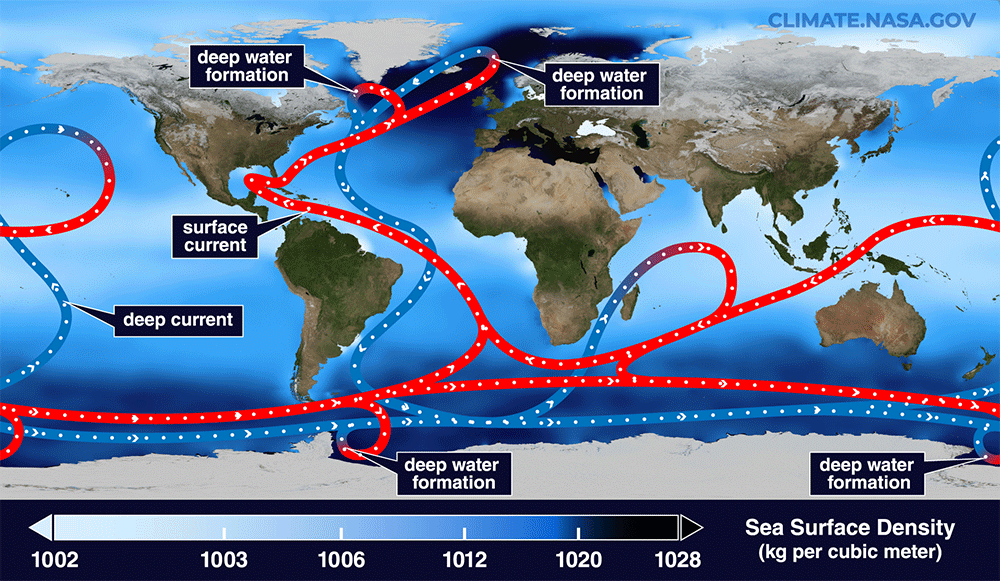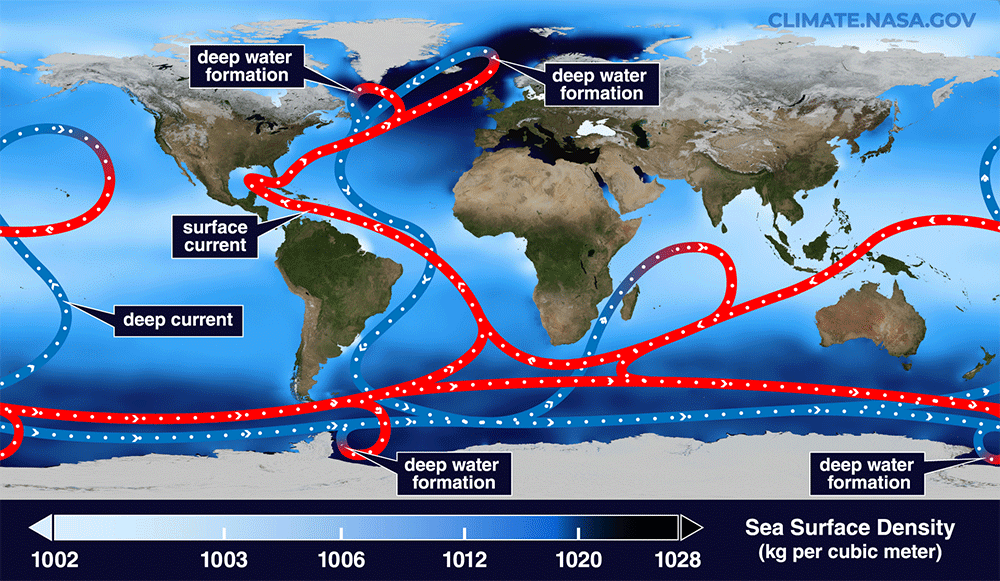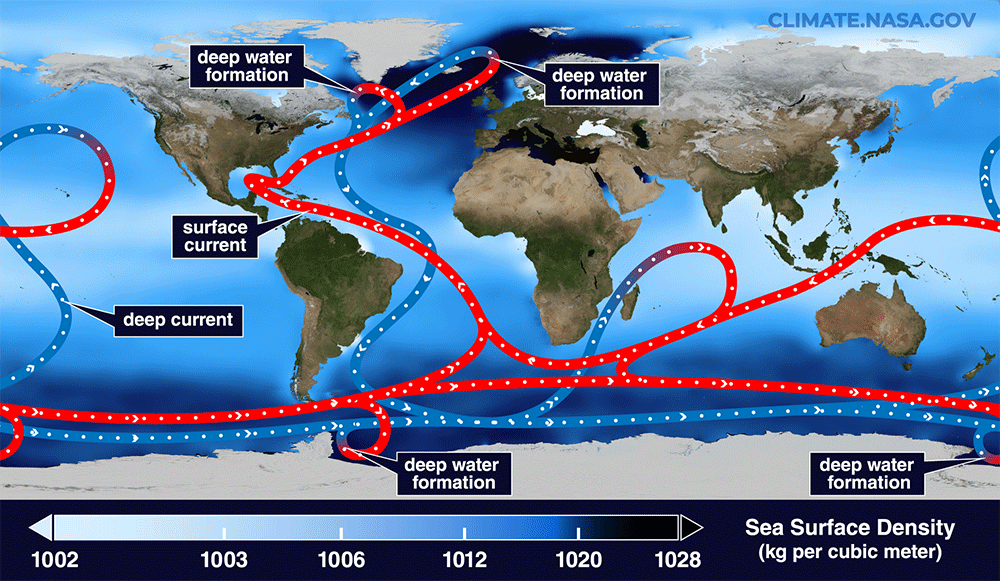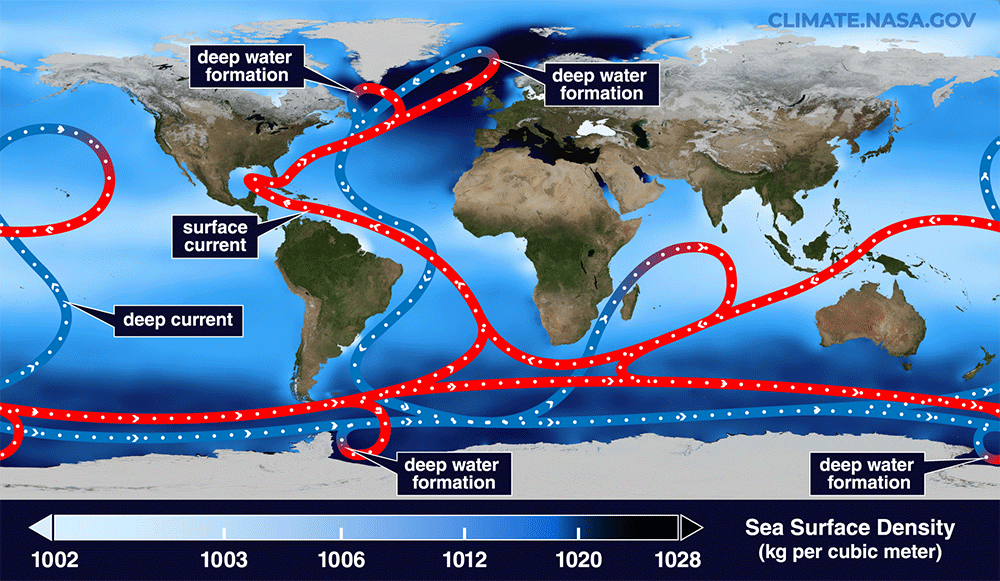
To accurately model the conditions common in the Gulf Stream during the Late Dryas, researchers analyzed microscopic fossils that lived in the ocean during the ice age. They also examined sediment cores, which are columns of rock that have accumulated on the seafloor since the Pleistocene.
Analysis of the fossils revealed that nutrient content dropped during the Last Dryas compared with previous and subsequent millennia. According to the research, this decrease in vital elements caused the North Atlantic phytoplankton to starve. The decline of these algae and other phytosynthetic organisms has had a strong impact on the marine food chain as well as oxygen production in the oceans.
This record of the last Dryas confirms the simulations of existing climate models, They predict a tipping point in nutrient transport to the North Atlantic if the AMOC and the Gulf Stream continue to slow. The effects would be catastrophic for fisheries in that region, because if the AMOC weakened during the ice age, its collapse would now become irreversible.
Is there anything you want to ask? Tell us on our social networks and get the opportunity to share the article. To the next one!
Source: Tec Mundo
I’m Blaine Morgan, an experienced journalist and writer with over 8 years of experience in the tech industry. My expertise lies in writing about technology news and trends, covering everything from cutting-edge gadgets to emerging software developments. I’ve written for several leading publications including Gadget Onus where I am an author.