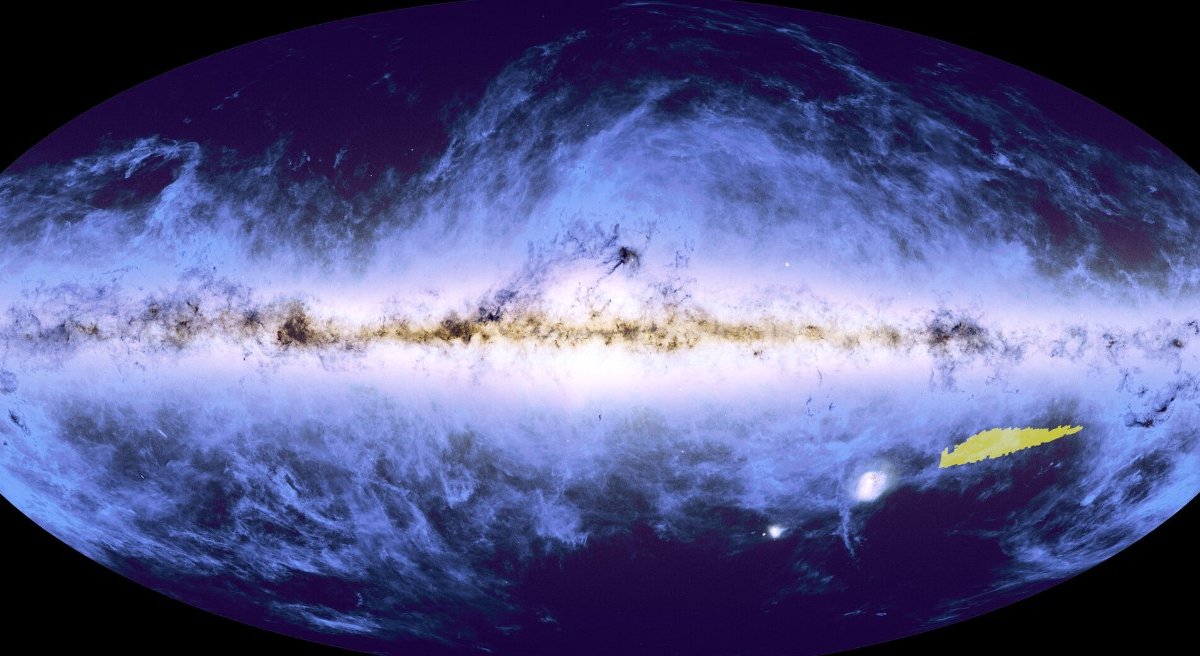
A team of researchers Euclid Telescope creates a ‘cosmic atlas’ with images captured by the mission in recent months; They recently introduced a scaled down version of this map. The telescope, operated by the European Space Agency (ESA) in partnership with NASA, was launched into space in July 2023 and will spend the next six years examining galaxies and distant parts of the universe.
In its official statement, ESA announced that the mosaic presented was produced from 260 observations made between March and April 2024. These initial observations already include 100 million celestial objects, including stars, galaxies and others. now This map represents only 1% of the research Euclid will conduct throughout its years of operation.
The team’s goal is to create the largest 3D cosmic map science has ever produced. According to scientists, the published version is just a sample of the details Euclid could reveal. They hope to map about a third of what’s in the sky within the next six years.
“What really struck me about these new images is the tremendous variety of physical scales. The images capture detail from clusters of stars near a single galaxy to some of the largest structures in the universe. “We’re starting to see the first hints of what the full Euclidean data will look like once the main survey is complete,” said project scientist Mike Seiffert. ” he said.
Cosmic Atlas and Euclid Telescope
The space agency claims that the telescope’s cameras captured the regions in such rich detail that some areas of this atlas were magnified up to 600 times. One of the most interesting aspects of the image are the dark clouds between the stars, a mixture of cosmic gas and dust that appear light blue, contrasting with the dark background of space.
Atlas was presented for the first time during the International Astronautical Congress in Milan and has a quality of 208 gigapixels. The team has not yet announced when it plans to publish the entire cosmic atlas, but stated that new data from Euclid will be presented in March 2025. Additionally, data from the first full year of collection will only be released in 2026.
“We have already seen beautiful, high-resolution images of individual objects and groups of Euclidean objects. This new image finally gives us an idea of the size of the sky area that Euclid will cover, giving us detailed measurements of billions of galaxies,” he said. Jason Rhodes, an observational cosmologist at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory and part of the Euclid team.
Get up-to-date information about astronomy at TecMundo. If you wish, take the opportunity to understand how telescope lenses contributed to the evolution of astronomy.
Source: Tec Mundo
I’m Blaine Morgan, an experienced journalist and writer with over 8 years of experience in the tech industry. My expertise lies in writing about technology news and trends, covering everything from cutting-edge gadgets to emerging software developments. I’ve written for several leading publications including Gadget Onus where I am an author.