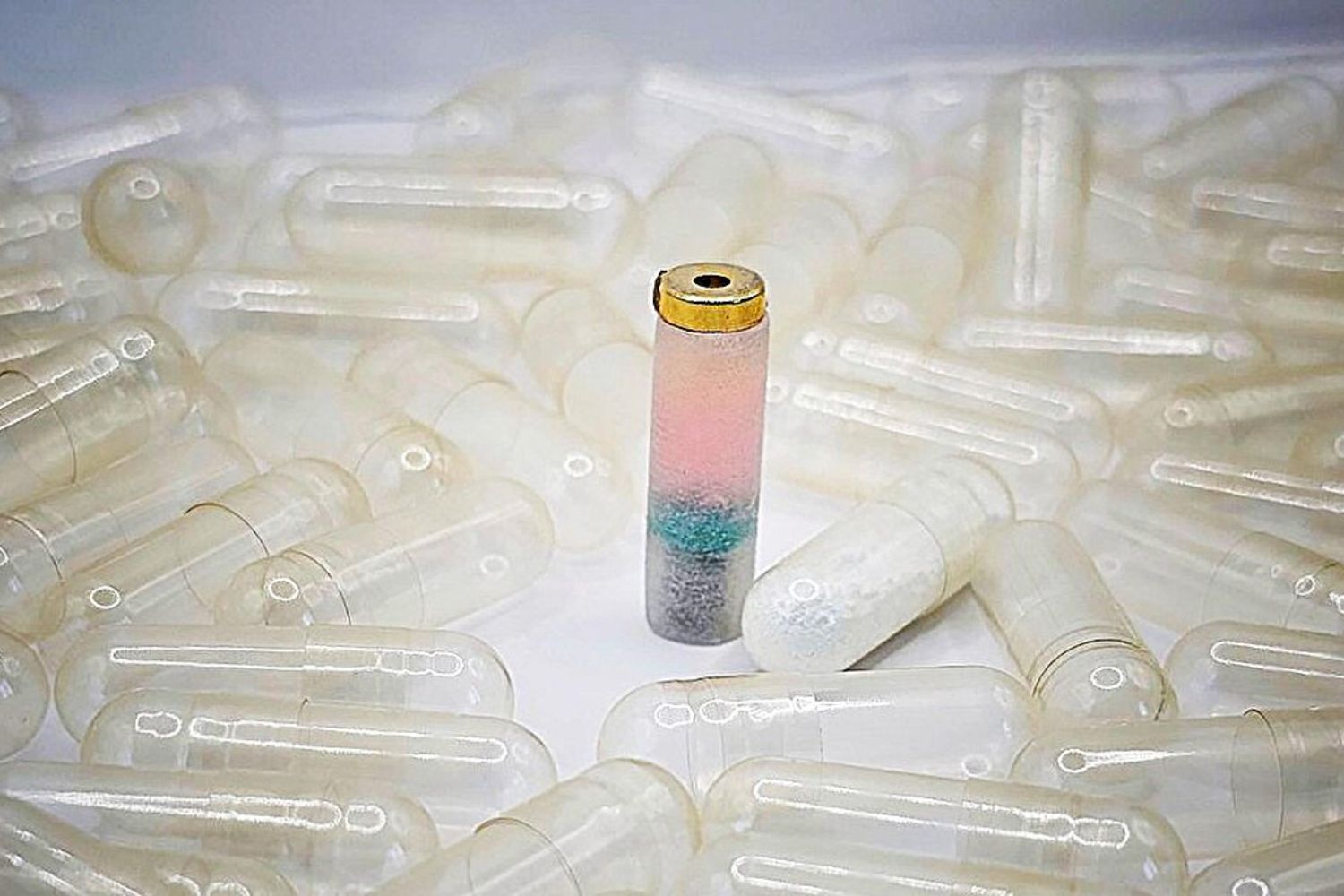
The results of the study, published in the journal Nature Geoscience, suggest that these glass beads may represent a new water reservoir on the Moon and play an important role in the water cycle on the surface of the Earth satellite.
In essence, they act as a buffer for the inflow and outflow of water produced by the solar wind. These beads, with water content of up to 2,000 µg.g-1 and extremely deuterium-consuming properties, are believed to originate from the solar wind.
The exploration is crucial for future lunar exploration missions, as the water resources on its surface can be used to recycle it in situ. The results also show that impact glasses on other airless bodies in the solar system can store and release water produced by the solar wind.
Source: Ferra
I am a professional journalist and content creator with extensive experience writing for news websites. I currently work as an author at Gadget Onus, where I specialize in covering hot news topics. My written pieces have been published on some of the biggest media outlets around the world, including The Guardian and BBC News.