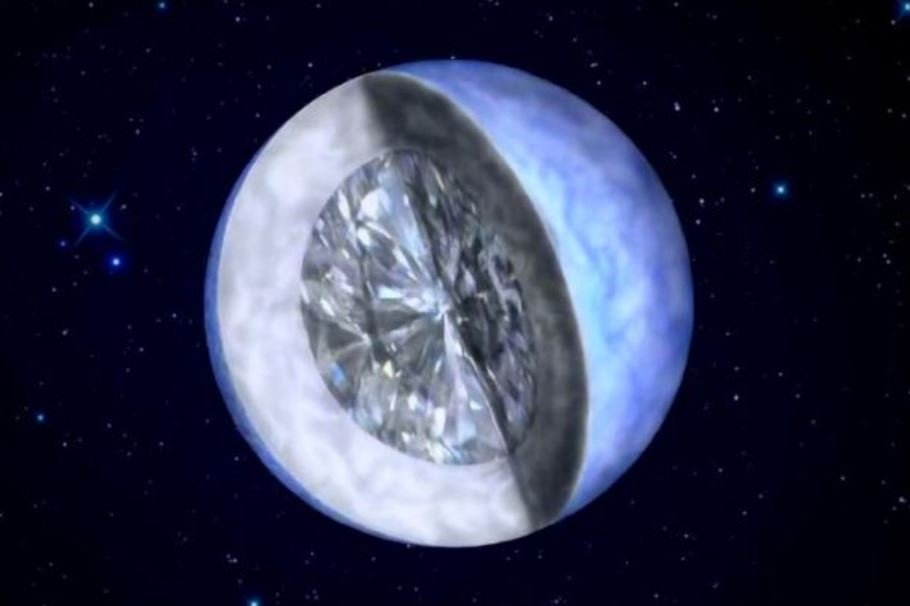
In a study accepted by the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical scientific journal, scientists describe the discovery of a white dwarf just 104 light-years from Earth. As the article explains, The star is dead and slowly hardening and cooling down to crystallize in space – just like a “cosmic diamond”.
An international team of astronomers has detected a white dwarf relatively close to Earth; The star is mainly composed of metallic carbon and oxygen. By analyzing the data, they realized that the stellar object had a temperature-mass profile that suggested the hardening and crystallization process.
The study also explains that The white dwarf, HD 190412 C, is part of a system of three other stars called HD 190412. – Similar to Sirius. They managed to discover some interesting information about the dwarf from data from other stars in the system.
“Thanks to its relationship with these main sequence companions, this is the first crystallizing white dwarf whose total age can be externally limited, a fact we have used when trying to empirically measure a cooling delay in the white dwarf caused by crystallization of the nucleus,” the researchers said in the study.
White dwarf and ‘cosmic diamonds’
Data collected by the European Space Agency (ESA) Gaia space telescope He suggests that HD 190412 C is about 4.2 billion years old in a star system about 7.3 billion years old.. The researchers believe that with a difference of 3.1 billion years, the rate of crystallization slowed the rate of cooling by about 1 billion years.
Typically, the density of white dwarfs is one million kilograms per cubic meter, but the density of diamond is 3,500 kilograms per cubic meter. Well, Scientists still do not know whether the star is made of diamonds – in any case, it is widely accepted that there are many diamonds in space..
Known celestial bodies white dwarfs are the result of an interesting phenomenon: the death of stars. To reach the level of a white dwarf, a star will shine brightly for billions of years until it runs out of fuel and spews foreign matter into the space around it. From there, the celestial body collapses and turns into an ultra-dense and compressed object.
Although dwarf stars are dim, they retain a glow, but are expected to turn into black dwarfs after they have cooled completely. Black dwarfs are crystalline carbon celestial bodies that no longer emit heat, but calculations show that it took longer than the current age of the universe to reach this state.
Source: Tec Mundo
I’m Blaine Morgan, an experienced journalist and writer with over 8 years of experience in the tech industry. My expertise lies in writing about technology news and trends, covering everything from cutting-edge gadgets to emerging software developments. I’ve written for several leading publications including Gadget Onus where I am an author.