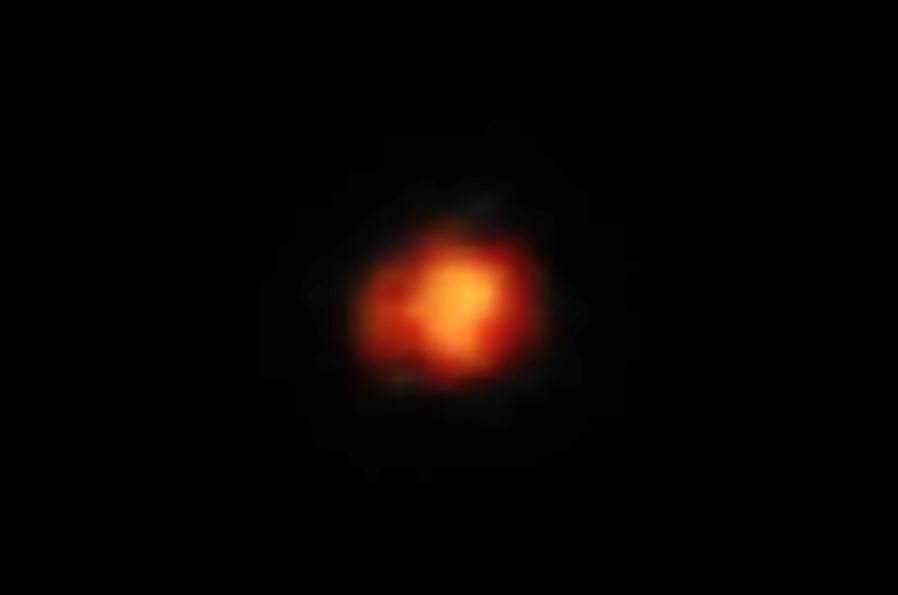
According to a new study published in the science journal Nature, a team of scientists explains that they have confirmed the observation of the most distant galaxy detected by James Webb. The galaxy known as Maisie lies about 390 million years after the Big Bang.; that is, considering that the universe is about 13.7 billion years old, it is very far from Earth.
The galaxy was spotted by the James Webb Space Telescope last year, but has only now been confirmed to be the most distant galaxy humanity has ever observed. Actually, Maisie was discovered by the Cosmic Evolution Early Release Science Survey (CEERS) team in June 2022.
The distance of the galaxy was verified using the redshift phenomenon. Redshift is detected by infrared devices when the wavelength of light from a distant cosmic object, such as a star or galaxy, approaches the red light spectrum.
“The interesting thing about Maisie’s galaxy is that it is one of the first distant galaxies identified by the JWST and is the first galaxy in this set to be truly spectroscopically confirmed,” said the University of Austin Professor of Astronomy, Director of CEERS. Researcher and study author Steven Finkelstein—scientist named the galaxy after his daughter because it was discovered on her birthday.
Is the Maisie Galaxy the farthest away?
Initial analysis estimated that Maisie was born 366 million years after the Big Bang, but scientists after analyzing data from the James Webb Telescope determined that she appeared 390 million years later.
Although considered the most distant confirmed galaxy, Scientists are already evaluating ten galaxies that may have been born several million years before Maisie’s appearance.. So, it shouldn’t take long for another similar cosmic object to refute the title of the most distant galaxy ever detected by humanity.
The same study also examined the galaxy CEERS-93316, which is estimated to be born about 250 million years after the Big Bang, but they found it to be one billion years away. The observations were verified using data collected by JWST’s NIRSpec spectroscopic instrument.
“This was a bit of a strange situation. Among dozens of spectroscopically observed high redshift candidates, this is the only case where the true redshift is much less than our initial estimate. It would be really difficult to explain how the universe could have created such a large galaxy so early. time was the most likely outcome because it was too extreme, too bright, and there was a high redshift in sight,” Finkelstein added.
Did you like the content? Therefore, stay up to date with the latest astronomy news here. Technology World.
Source: Tec Mundo
I’m Blaine Morgan, an experienced journalist and writer with over 8 years of experience in the tech industry. My expertise lies in writing about technology news and trends, covering everything from cutting-edge gadgets to emerging software developments. I’ve written for several leading publications including Gadget Onus where I am an author.