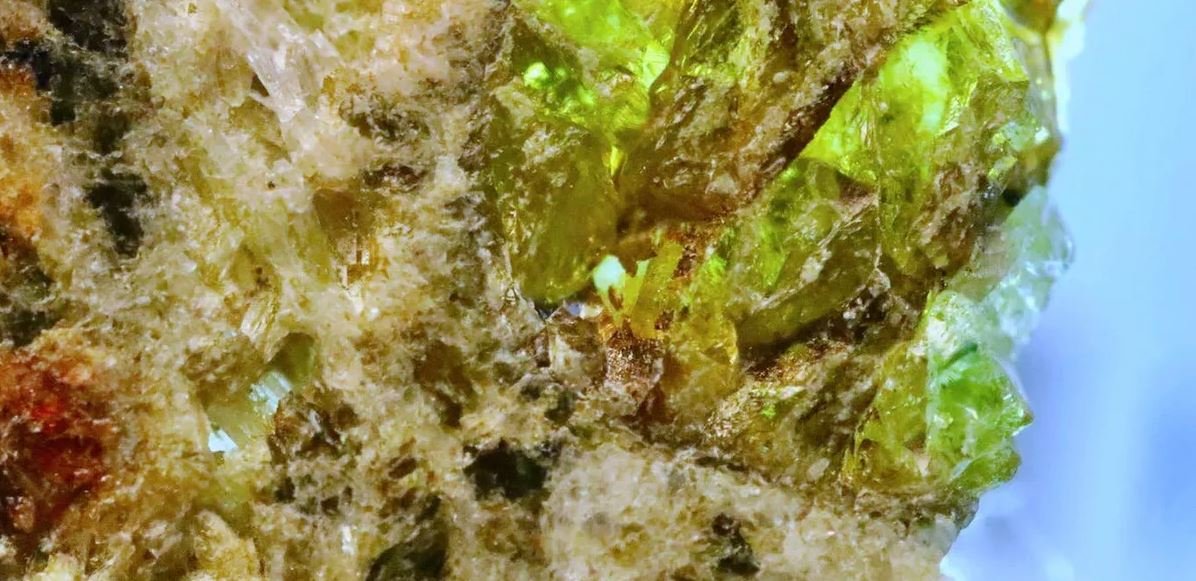
In mid-2020, a team of scientists collected samples of a 4.6 billion-year-old meteorite found during an expedition in the Algerian region of North Africa. According to a new study published in the scientific journal Nature Communications, Ancient cosmic rock may help better understand the birth of our Solar System.
It is named after Erg Chech 002. The meteorite is considered the oldest rock of volcanic origin ever found, surpassing all rock types ‘born’ on Earth.. An isotope detected in the samples indicates the presence of radioactive material from stars exploding towards the end of Solar System formation; With a better understanding of the material, scientists are trying to find answers to the secrets of the universe’s past.
Although it is considered the oldest volcanic stone, it was not found in ordinary volcanoes. The data suggest that the meteorite emerged from explosions in the early Solar System, possibly as part of an eruption. planet A baby interrupted by a collision with another cosmic object.
“The isotope of aluminum-26 (26Al) [detectado no Erg Chech 002]A short-lived radionuclide is an important heat source for early planetary fusion. The aluminum-26 — magnesium-26 (26Al-26Mg) decay system also functions as a high-resolution relative chronometer. In either case, however, it is crucial to determine whether 26Al is distributed homogeneously or heterogeneously throughout the solar fog,” explains the study.
4.6 billion year old meteorite and the Solar System
The stable isotope detected in the rock is magnesium-26, a decay of the radioactive isotope aluminum-26; both are usually caused by the death of massive stars. By making comparisons with other meteorites, scientists found: Erg Chech 002 had much more aluminum-26; other elements were probably ejected by supernovas and other cosmic events in the early Solar System.
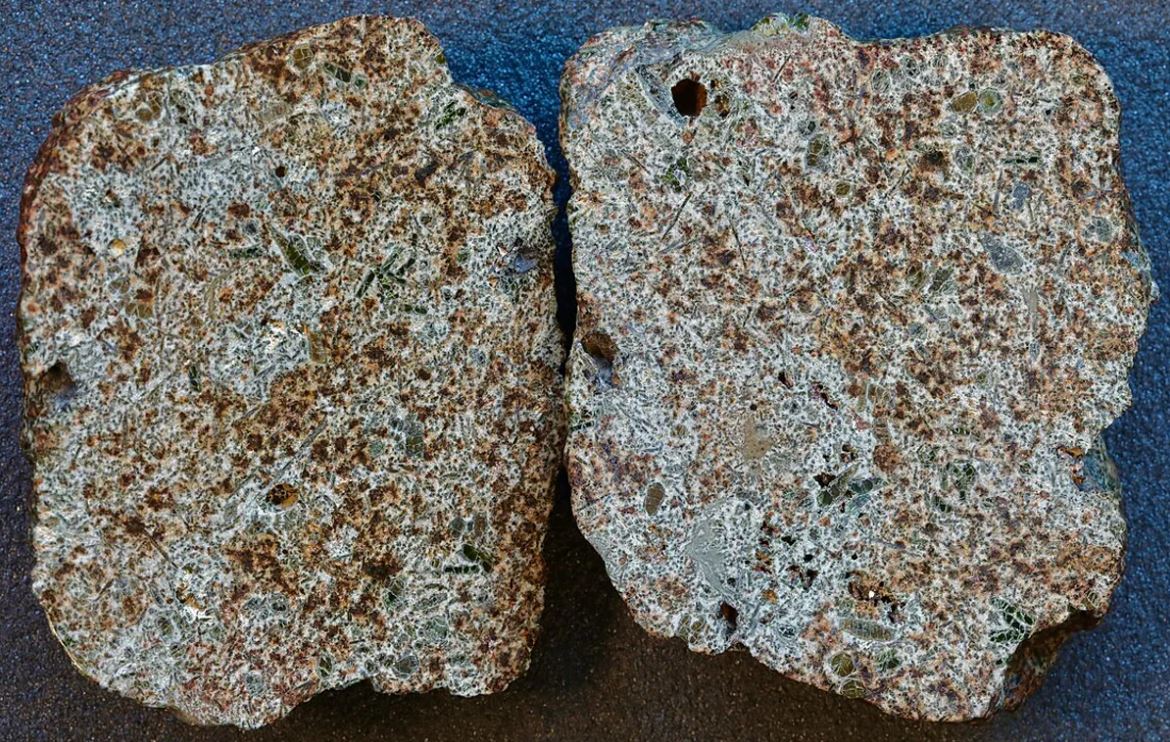

Other studies also explain that various radioactive materials were present in the formation of the Solar System, possibly produced during supernova explosions, as in the Erg Chech 002 meteorite. In any case, the researchers will continue to examine the samples to learn more about the discovery.
“Here, we show that the available data clearly show 3-4-fold spatial heterogeneity of aluminum-26 in the solar system’s precursor molecular cloud or protoplanetary disk, possibly related to the late entry of stellar materials with newly synthesized radionuclides,” the study explains.
You can find up-to-date information on the latest discoveries in astronomy here. Technology World. Also, take the opportunity to explore how the disappearance of Neptune’s clouds might be linked to the Solar System cycle.
Source: Tec Mundo
I’m Blaine Morgan, an experienced journalist and writer with over 8 years of experience in the tech industry. My expertise lies in writing about technology news and trends, covering everything from cutting-edge gadgets to emerging software developments. I’ve written for several leading publications including Gadget Onus where I am an author.