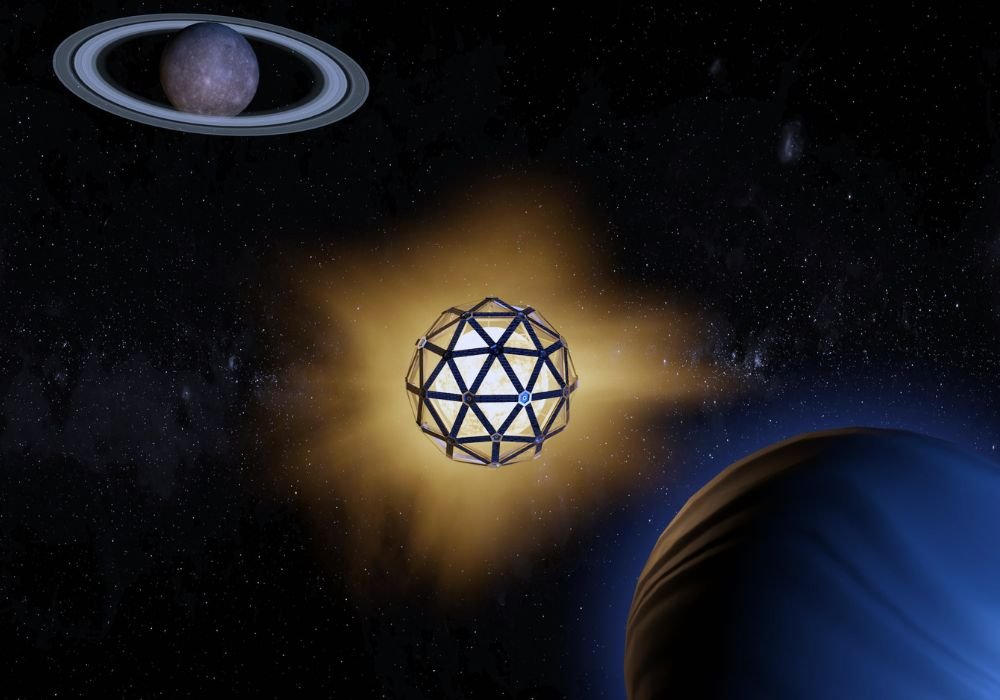
In the mid-1960s, physicist Freeman Dyson published a paper proposing a way to investigate alien intelligence: While investigating the theory of megastructures close to stars like the Sun, this concept was given the name Dyson sphere.. A new study, now published in the preprint journal arXiv, suggests that astronomers are looking for signs of intelligent life by probing other signals from Dyson spheres..
Study co-author Jason T. Wright, professor of astronomy at the Center for Exoplanets and Habitable Worlds in the United States and Penn State’s Center for Extraterrestrial Intelligence (PSTI), offered suggestions to scientists in the Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence (SETI). Look for signs of so-called Dyson sphere activity.
What are Dyson spheres?
Dyson spheres They are technological megastructures that can absorb the energy of a large star like the Sun and transform it into a type of energy that an advanced civilization can use..
These massive spherical structures will be built close to the star and feature thousands of solar panels that capture the energy and convert it into electricity; thus the ‘aliens’ would use energy from an extremely powerful source present in the universe.
In most theories, researchers point out that it would be possible to investigate the residual heat of these megastructures, but Wright recommends that the research be conducted to look for traces of the purpose of Dyson spheres. For example, SETI researchers believe the Dyson sphere could be used as a stellar engine or a massive supercomputer, known as the Shkadov Drive and Matrioshka Brain, respectively. Well, suggests looking not only for signs of heat, but also for adjacent traces of these purposes.
“Contrary to some authors’ expectations that Dyson spheres would be extremely large and cold to maximize their efficiency, I found that the optimal configuration with a fixed mass budget was actually for very small, hot spheres, allowing all of the light to escape. Therefore, we set our search parameters to 300K.” “We can expand to temperatures well above 1000 (slightly warmer than Earth) because extracting energy from starlight is most efficient closer to the star, where conditions are warmer,” Wright concludes in a message. sent to website Universe Today.
Megastructures or industrial planets?
In another paper written by a team of scientists from India, published on the arXiv server and under review in the scientific journal Astrophysics and Space Science, they propose a new alternative to searching for technological signatures of alien civilizations – without any direct correlation. With Dyson’s megastructures. The research was called ‘Making Habitable Worlds: Planets Versus Megastructures’ (Making Habitable Worlds: Planets Versus Megastructures in Portuguese).
Research leader and physics student at Bangalore Christian University Raghav Narasimha, perhaps the best alternative is to seek out ‘Service Planets’; The concept explains the existence of ‘industrial worlds’, i.e. planets built specifically to produce energy for a civilization..

Astronomers estimate that the Milky Way is home to at least 100 billion planets; so it might be much more “likely” for aliens to exploit a world until its resources are exhausted, and to continue the same process for an indefinite period of time. Theoretically, extraterrestrial civilization could move a planet into the habitable zone of a star using lasers of Zetawatt or Etawatt power (1024 W).
The team of scientists claim that ‘industrial planets’ can be detected using different technological signatures, such as narrowband laser data. They therefore recommend that astronomers look for signatures of Strange Exoplanet Architectures (SEAs).
“Planetary systems such as Kepler-20 or TRAPPIST-1, in which many Earth-like planets (low-mass rocky planets) are located close to their stars, at a distance smaller than the orbit of Mercury, represent another possible indication of this,” Narasimha said. “It seems unusual for the planet to be seen in such a narrow zone close to their star. This may suggest that these planets may have been deliberately moved into the habitable zone of their parent star,” he said.
Did you like the content? Stay up to date with more astronomy curiosities at TecMundo.
Source: Tec Mundo
I’m Blaine Morgan, an experienced journalist and writer with over 8 years of experience in the tech industry. My expertise lies in writing about technology news and trends, covering everything from cutting-edge gadgets to emerging software developments. I’ve written for several leading publications including Gadget Onus where I am an author.