A collaboration between researchers from Germany, Canada, Spain and the USA resulted in a study correlating: number of cells in the human bodyIts size and functions indicate a unique balance. When we talk about our most basic units, we can be mistaken that they are all the same, just distributed in different parts of our body.
But our cells very different from each other in size, function, or distribution. For example, a neuron can never be replaced by an epithelial cell, or even a unit of heart muscle can be transplanted into your biceps.
However, in addition to the organisms that make up the human body, we also harbor other types of organisms, such as bacteria. In total, it is estimated that there are at least 38 trillion bacterial cells living amicably inside us..
However, although we know their features, we still do not have a complete map. With this in mind, the international collaboration conducted a survey of more than 1,500 studies on the topic and grouped data from 1,200 cell groups.
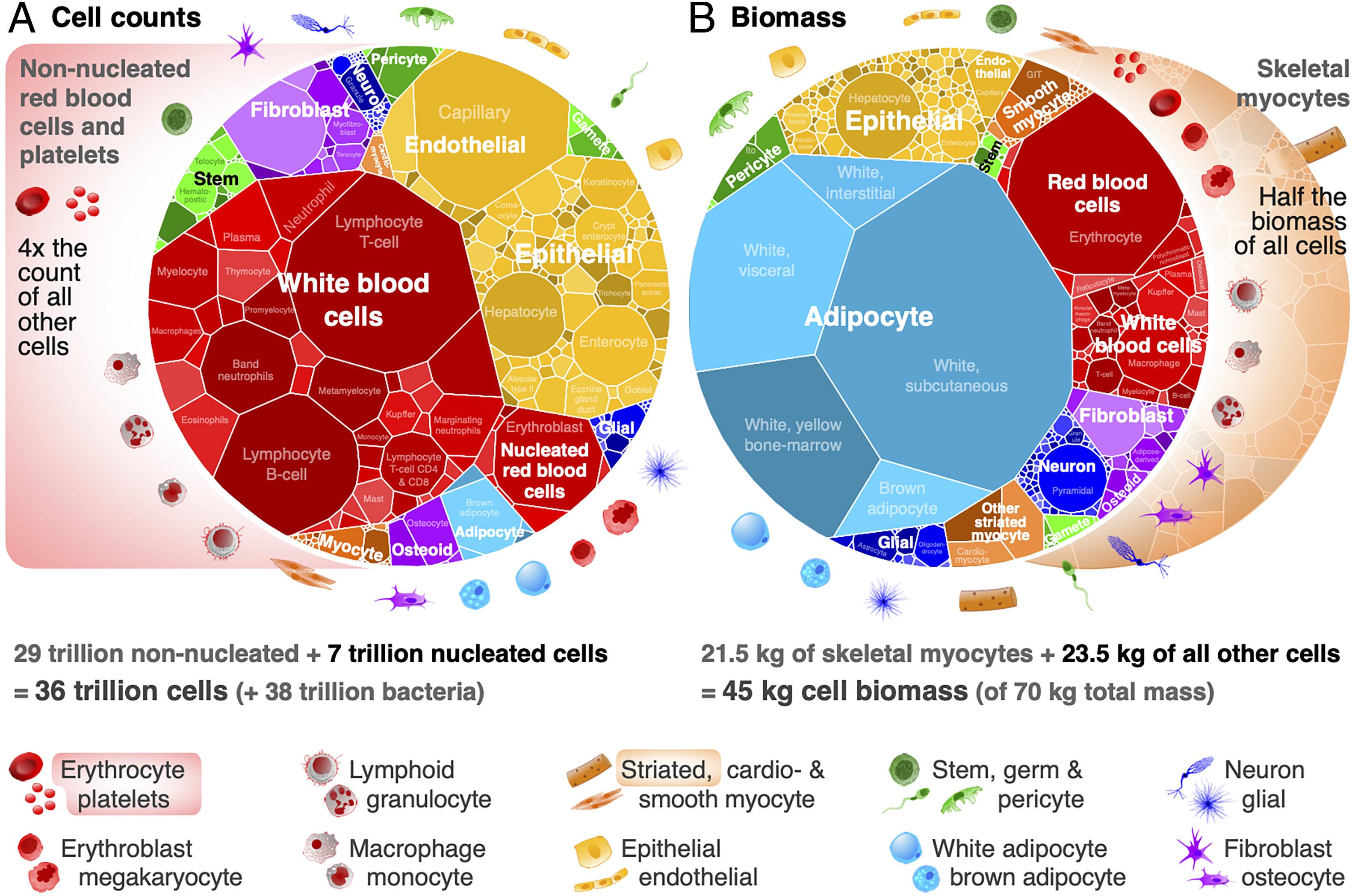
To make the data more accessible, they set up a website with mapping broken down by region and species. While analyzing the data, the group was able to observe some interesting things. The first is the relationship between gender, weight and quantities.
To give a practical example, it is estimated that a man with an average weight of 70 kilograms has an average of 36 trillion cells. Women weighing 60 kilograms can carry 28 trillion, and 10-year-old children can carry about 17 trillion.
But the real surprise lies in the inverse relationship between size and quantity. The smaller the cells, the greater their number in the body. However, different sets of cells contribute in a balanced way to the formation of body mass.
For researchers, they somehow maintain intelligent regulation among themselves, regulating their production and creating a homeostatic balance. It is as if 10 smaller cells need to exist for one larger cell to balance the scales of existence.
But not everything is so balanced. In the paper’s discussion, the researchers list several challenges in analyzing the data, such as outdated technology and inconsistencies between the literature and observational data on cell size, shape, and mass.
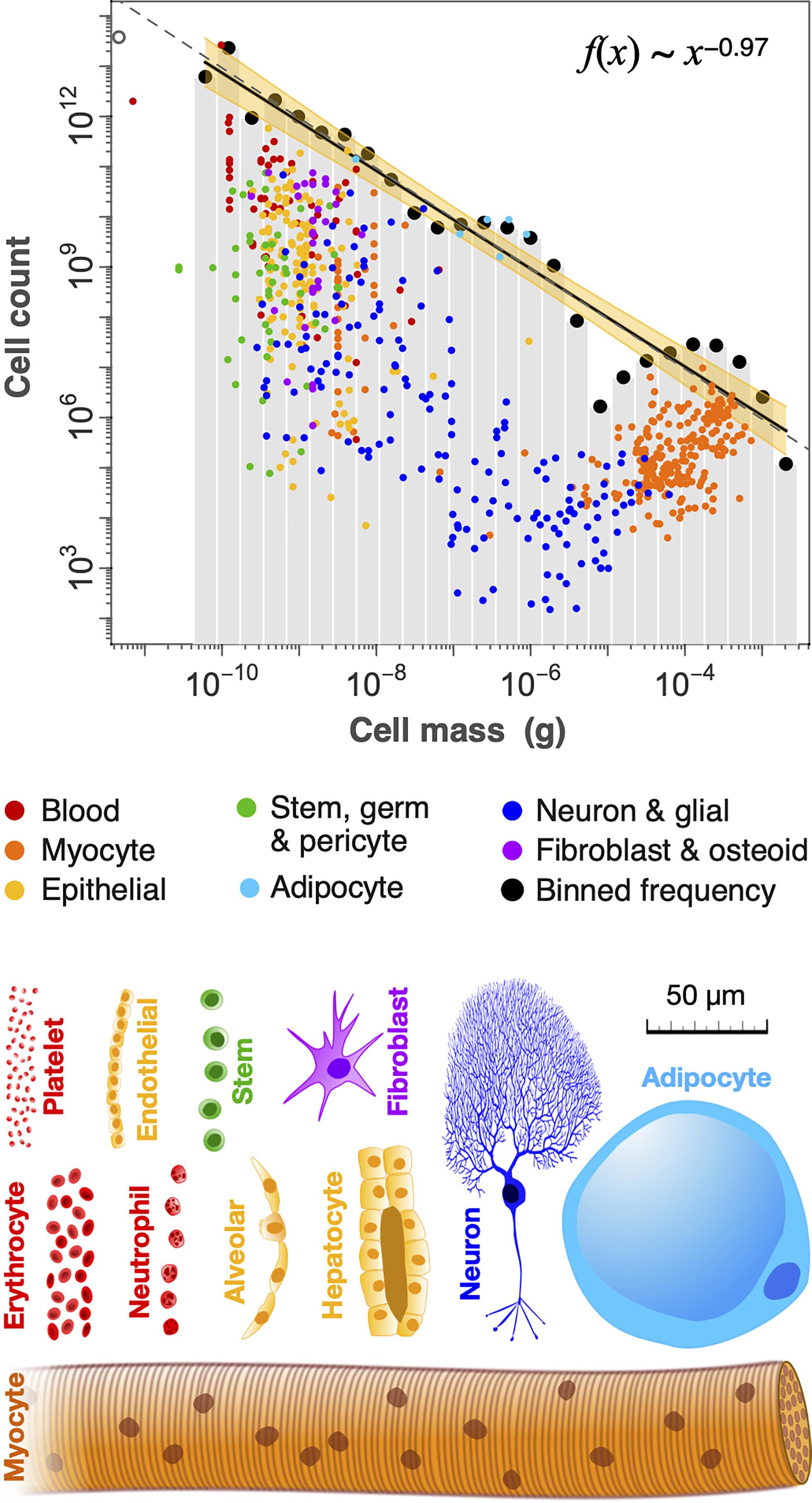
Therefore there is still a long way to go Can map and understand how cell regulation, formation and distribution occur in our body.
For researchers, understanding how this balancing mechanism occurs is of great importance for the advancement of medicine and health-related technologies.
Want to learn more about the human body and how it works? So discover what the human microbiota or microbiome is.
Source: Tec Mundo
I’m Blaine Morgan, an experienced journalist and writer with over 8 years of experience in the tech industry. My expertise lies in writing about technology news and trends, covering everything from cutting-edge gadgets to emerging software developments. I’ve written for several leading publications including Gadget Onus where I am an author.