In a new study published in the journal Nature, scientists used computer modeling to investigate. melting The West Antarctic ice sheet is inevitableIt raises a global alarm about the climate crisis.
The research takes into account climate variables such as the infamous El Niño. The results do not show significant differences between medium-term emissions scenarios and the more ambitious targets of the 2015 Paris Agreement.
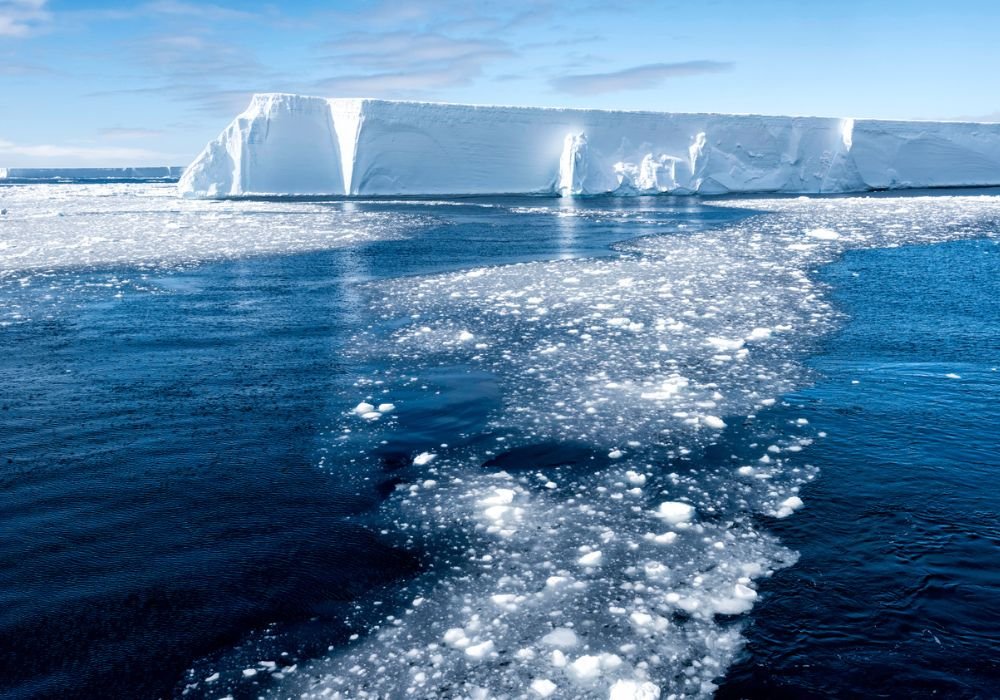
The loss is mainly caused by warming of the Southern Ocean, particularly the Amundsen Sea region. This ice sheet contains enough frozen water to raise global sea levels by five metres. Melting of West Antarctic ice shelves is expected to accelerate significantly in coming years.
Kaitlin Naughten, lead author and researcher at the British Antarctic Survey, paints a worrying picture: “We appear to have lost control over the melting of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet. If we want to preserve it in its historic state, Decades ago we needed measures against climate change. “On the positive side, by recognizing this situation in advance, the world will have more time to adapt to approaching sea levels.”
Simulation scenarios
The research team created five scenarios simulating the 21st century, including a historical representation of the 20th century. These scenarios revolved around stabilizing global temperatures in line with the targets of the Paris Agreement (1.5°C and 2°C) or followed standard projections of medium and high carbon emissions.

All scenarios depicted a future in which melting of the Amundsen Sea’s ice shelves would intensify, resulting in significant and widespread warming.
Even in the best-case scenario, the warming of the Amundsen Sea accelerates dismally by a factor of three, while ice shelves melt, It plays an important role in balancing internal glaciers., followed the same path. The good news is that the rate of melting slowed, albeit slowly, towards the end of the century.
The worst-case scenario envisioned further melting of the ice shelf, but this would occur specifically after 2045. The study emphasizes that this scenario of high fossil fuel levels, characterized by rising emissions, is unlikely, although there is a warning about the consequences. .
Is there anything you want to ask? Tell us on our social networks and get the opportunity to share the article with your friends!
Source: Tec Mundo
I’m Blaine Morgan, an experienced journalist and writer with over 8 years of experience in the tech industry. My expertise lies in writing about technology news and trends, covering everything from cutting-edge gadgets to emerging software developments. I’ve written for several leading publications including Gadget Onus where I am an author.