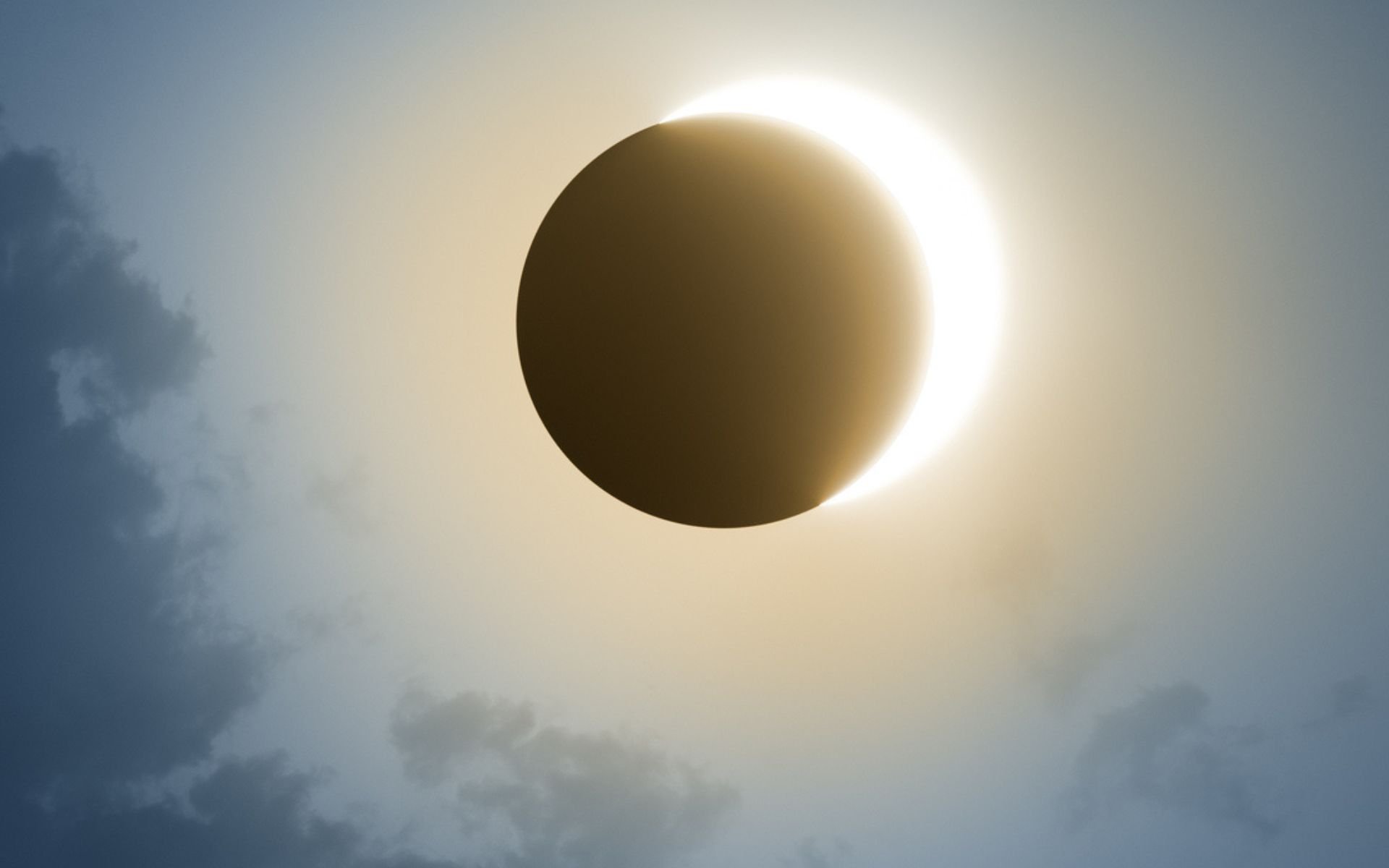
The solar eclipse is a natural event that occurs on October 14, 2023 and affects observers worldwide as the last annular event observable in Brazil. These solar events usually occur annually, but it is not possible to observe them in every region of the planet. For exampleThe next annular solar eclipse will occur on October 2, 2024, but a similar celebration can only be observed in Brazil in January 2028.
Although science knows some of the atmospheric phenomena that occur on Earth, many natural processes are still considered unknown or we know very little about them.
This is one of the interesting and mysterious effects clouds disperse during a solar eclipseSomething that was not fully understood by scientists until then.
To learn more about the effect, a team of scientists from the Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute (KNMI), in partnership with Delft University of Technology (TU Delft), conducted a study to explain why this occurs in the Earth’s atmosphere. The article was published in the scientific journal Communications Earth & Environment.
“During a partial solar eclipse, cumulus clouds over land begin to disappear almost immediately. Until recently, satellite measurements during the eclipse resulted in dark spots on the cloud map, but researchers from TU Delft and KNMI managed to recover the satellite measurements using a new method. “The results may have implications for proposed climate engineering ideas, as disappearing clouds may partially counteract the cooling effect of artificial solar eclipses.”
Clouds disappear during solar eclipse
The researchers explain that many effects of solar eclipses have been studied for decades, but little is known about the response of clouds during this category of events. Victor Trees, one of the authors of the study, states that observing their disappearance during a solar eclipse is not real evidence, after all, clouds are constantly changing in the sky.
Satellites are more reliable tools for collecting data on these impacts because they measure large areas simultaneously. Unfortunately, weather conditions during solar eclipses are not completely reliable because there is a significant decrease in light during these events.
When scientists examined the data, they noticed that this resulted in dark spots on the cloud maps. as a result, it invalidates the study of the phenomenon of disappearing clouds.
It is important to remember that the vanishing effect during a solar eclipse does not occur in all clouds in the sky; Cumulus clouds usually disappear. For this reason, weather conditions can be a problem when observing the event.
What is the reason for this effect?
After a thorough analysis, the researchers were able to restore satellite measurements during solar eclipses by calculating the percentage of time the Sun was obscured at each time and location on Earth.
“Most solar eclipses so far have consisted of a partial eclipse where there is still plenty of light out there. In this partial eclipse, satellites receive enough reflected sunlight to reliably measure clouds after dimming correction,” says Trees.
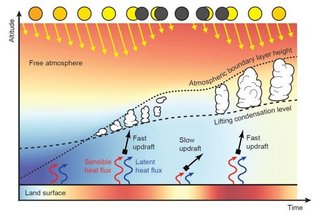
After the correction, the team had the opportunity to examine three solar eclipses that occurred over Africa. So they found that many clouds began to disappear when only 15% of these events were obscured; This incident occurred between 2005 and 2016. Using the data collected, the researchers ran computer simulations in software called DALES, aiming to understand why this occurred. mystery.
According to the simulation results, the disappearance of clouds during a solar eclipse is an effect caused by the Earth’s atmosphere. When light is blocked, the Earth’s surface cools and air currents decrease. Since these upward movements are necessary for the formation of cumulus clouds, some of them cannot continue their formation and begin to disappear.
“This could be a wake-up call for climate engineering. If we eclipse the Sun with technological solutions in the future, this could affect clouds. Fewer clouds could partially counteract the intended effect of climate engineering, because clouds reflect sunlight and therefore, Trees say, the sun and clouds “Help cool down beneath the Earth,” he concludes, describing the reaction of its effects.
Did you like the content? Follow all the curiosities about the solar eclipse on TecMundo. If you wish, take the opportunity to understand why solar eclipses will have rings after millions of years.
Source: Tec Mundo
I’m Blaine Morgan, an experienced journalist and writer with over 8 years of experience in the tech industry. My expertise lies in writing about technology news and trends, covering everything from cutting-edge gadgets to emerging software developments. I’ve written for several leading publications including Gadget Onus where I am an author.













