Gravity is the curvature of space-time that occurs due to the presence of mass and energy; for example, the Earth’s center of gravity is in its massive core; Therefore, our gravity is not like that of the Moon. Microgravity is a space phenomenon in which objects or people appear weightless, as in the International Space Station.
The gravitational force of the Earth, Moon and Jupiter is called macrogravity; It is a normal phenomenon on the surface of some celestial bodies in the Solar System. For example, -most On the Moon, the gravity is significantly lower than that of the Earth, that is, about 16.5% of the Earth’s gravity, hence the feeling of reduced weight.
Despite the feeling of weightlessness, the Moon has no microgravity. However, astronauts from the United States National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and other space agencies do experience microgravity during missions inside the ISS. They feel this ‘feeling of weightlessness’ as they float completely in orbit inside or outside the station during the spacewalk.
Some interesting effects occur in space due to microgravity; for example, water will float ‘in the air’ when an astronaut pours it onto the station. So in a microgravity environment, the effect of some things will be completely different.
The aftermath of fire is widely studied in this type of environment, so scientists can understand the consequences of the event in a ‘zero gravity’ location.
“NASA must learn about the effects of microgravity to keep astronauts safe and healthy. Moreover, many things appear to behave differently in microgravity. Fire burns differently. Flames are rounder when there is no gravitational force. Crystals grow better. Their shapes are more perfect without gravity. NASA, microgravity conducts scientific experiments in gravity,” NASA explains in an official release.
What is microgravity
As mentioned before, microgravity is a state of space where objects or people appear to have no weight, as occurs when astronauts leave the Earth’s atmosphere and enter space. In ordinary gravity, objects and people are attracted to the planet’s center of gravity; Therefore, a glass falls when we drop it from a high place on the Earth.
The further an object like our planet is from its center of gravity, the weaker its center of gravity will be. Since the station is approximately 400 kilometers above the Earth’s surface, it is not surprising that Earth’s gravity is approximately 90% lower on the ISS. But if it’s only 90% smaller, why do objects and people levitate in microgravity? The answer is simple: Everything in microgravity is in free fall.
In the vacuum of space, it is as if an astronaut has become so light that he begins to slowly fall. So if you drop two objects that have extremely different weights, they will both fall slowly and together. In the case of the crew and objects inside the station, they fall together as everything ‘falls’ towards Earth, but they remain safe because they are in a stable, stable orbit.
“Microgravity is a measure of the degree to which an object in space is subjected to acceleration. In common parlance, the term is used synonymously with zero gravity and weightlessness., but the prefix micro denotes accelerations equivalent to one millionth (10-6) of the gravitational force at the Earth’s surface. Using microgravity (μg) as the unit of measurement, a particular medium can be characterized as providing, for example, 20 µg (20 microgravity),” explains the encyclopedia Britannica.
Currently, microgravity is considered a widely understood phenomenon by scientists, especially in theory. That’s why for decades, space agencies such as NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), the Canadian Space Agency (CSA), among others, have been We continue to conduct scientific experiments on the International Space Station and on unmanned missions.
How does fire behave differently in space?
The first experiments on fire in microgravity began several decades ago. Finally, Scientists and technicians wanted to understand what would happen if the ISS experienced an electrical problem that caused a fire. To date, NASA states that it continues to study the fire’s reactions in the space environment.
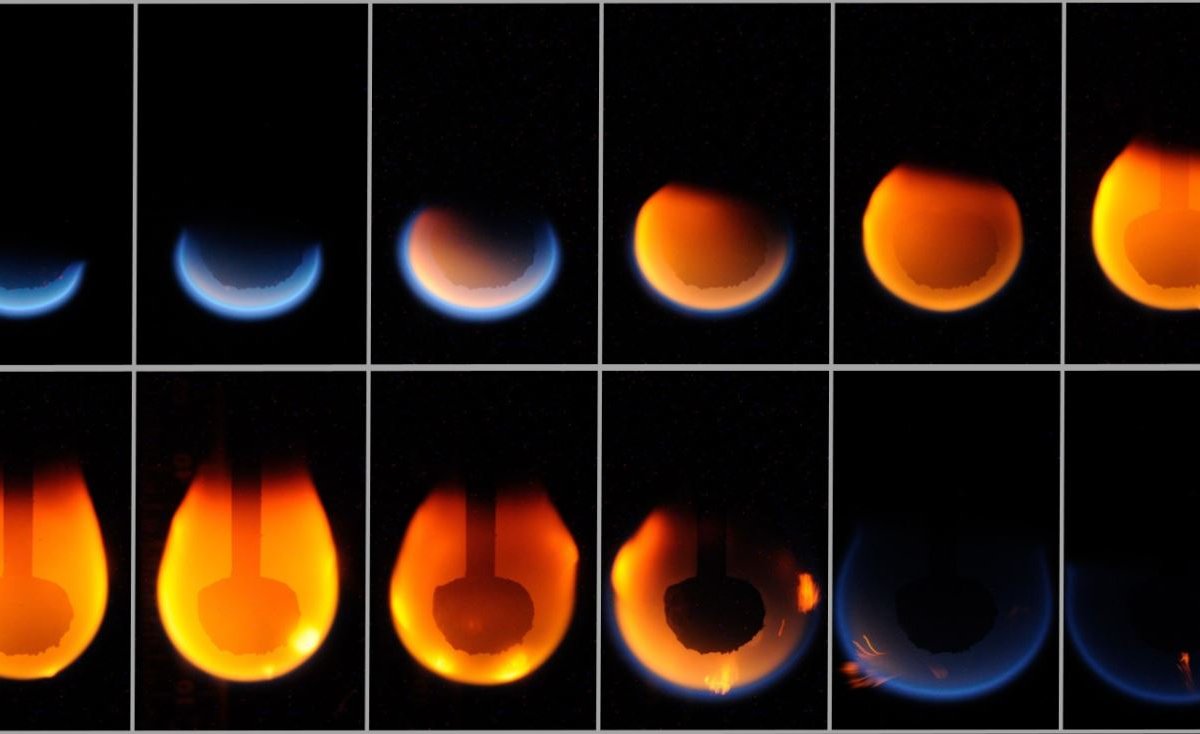
 NASA The image shows a test conducted in an environment that mimics microgravity; In the upper part the round flame of the fire seems to grow, while in the lower part it goes out.
NASA The image shows a test conducted in an environment that mimics microgravity; In the upper part the round flame of the fire seems to grow, while in the lower part it goes out.
After years of research, Researchers noticed that the behavior of flames in space is completely different, as changes in gravity and air flow make it harder to extinguish the fire. In fact, lack of oxygen does not seem to be a problem in the spread of flames. In tests in environments mimicking microgravity, a circular flame initially shrank but quickly split into other fires that moved across the surface.
The scientists’ goal is to understand how to prevent fires inside the ISS, or at least significantly reduce the likelihood of it occurring. For example, almost all of the materials developed to equip the ISS are manufactured to not burn easily. The goal is to understand the behavior of fire in microgravity to prevent accidents and even understand some flame processes on Earth.
“The experiments will also help NASA determine the best ways to extinguish fires or smoldering materials in space. [a agência] “NASA is preparing to go further and stay longer,” he adds.
Did you like the content? So, stay updated with more curiosities about astronomy at TecMundo. If you wish, take the opportunity to discover what the Kármán Line is, where the Earth ends and space begins.
Source: Tec Mundo
I’m Blaine Morgan, an experienced journalist and writer with over 8 years of experience in the tech industry. My expertise lies in writing about technology news and trends, covering everything from cutting-edge gadgets to emerging software developments. I’ve written for several leading publications including Gadget Onus where I am an author.