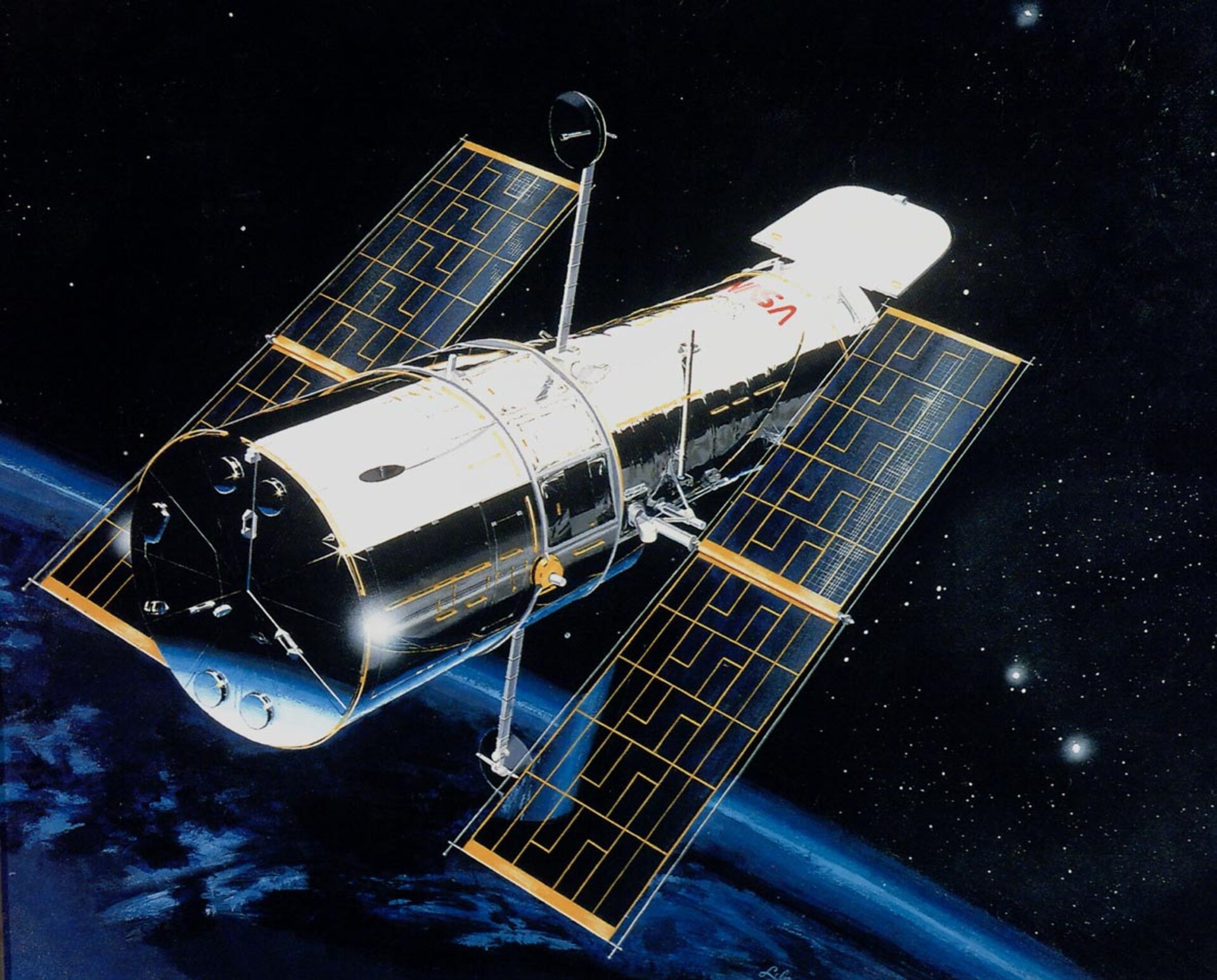
The Hubble Space Telescopefrom ESA and NASA has observed stars that, like i checkers of some galaxiesdraw what spirals. These move to Small Magellanic Cloud where there is a huge star cluster.
The research, conducted by Space Telescope Science Institute of Baltimore, was published in the magazine The Astrophysical Journal and enables you to help understand the early universe. This is because the chemical composition of the Small Magellanic Cloud is very simple compared to that of many other galaxies, so it is considered very similar to the newborn universe, which is about 2 or 3 billion after the big bang.
The Italian researcher Elena Sabbicwho led the team of researchers exploited the images captured by Hubble to measure how the stars have moved in 11 years. These were found to travel at a speed of 3,200 kilometers per hour, a displacement of nearly 322 million kilometers in 11 years. The sensitivity of Hubble’s instruments made it possible to very accurate measurements of the star cluster located about 200,000 light-years from Earth.
The movement itself was studied by a research group from theEx (European Southern Observatory) thanks to Very large telescope (vl). Researchers led by Peter Zeidler ESA measured the radial velocity of the cluster and came to the same conclusion, that everything spirals inward.
Source: Lega Nerd
I am Bret Jackson, a professional journalist and author for Gadget Onus, where I specialize in writing about the gaming industry. With over 6 years of experience in my field, I have built up an extensive portfolio that ranges from reviews to interviews with top figures within the industry. My work has been featured on various news sites, providing readers with insightful analysis regarding the current state of gaming culture.