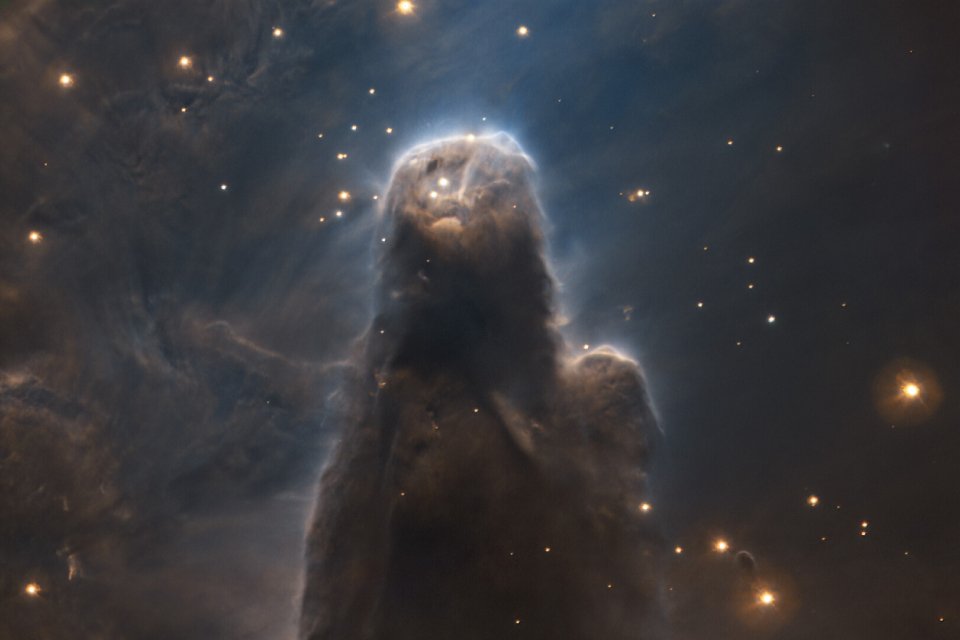
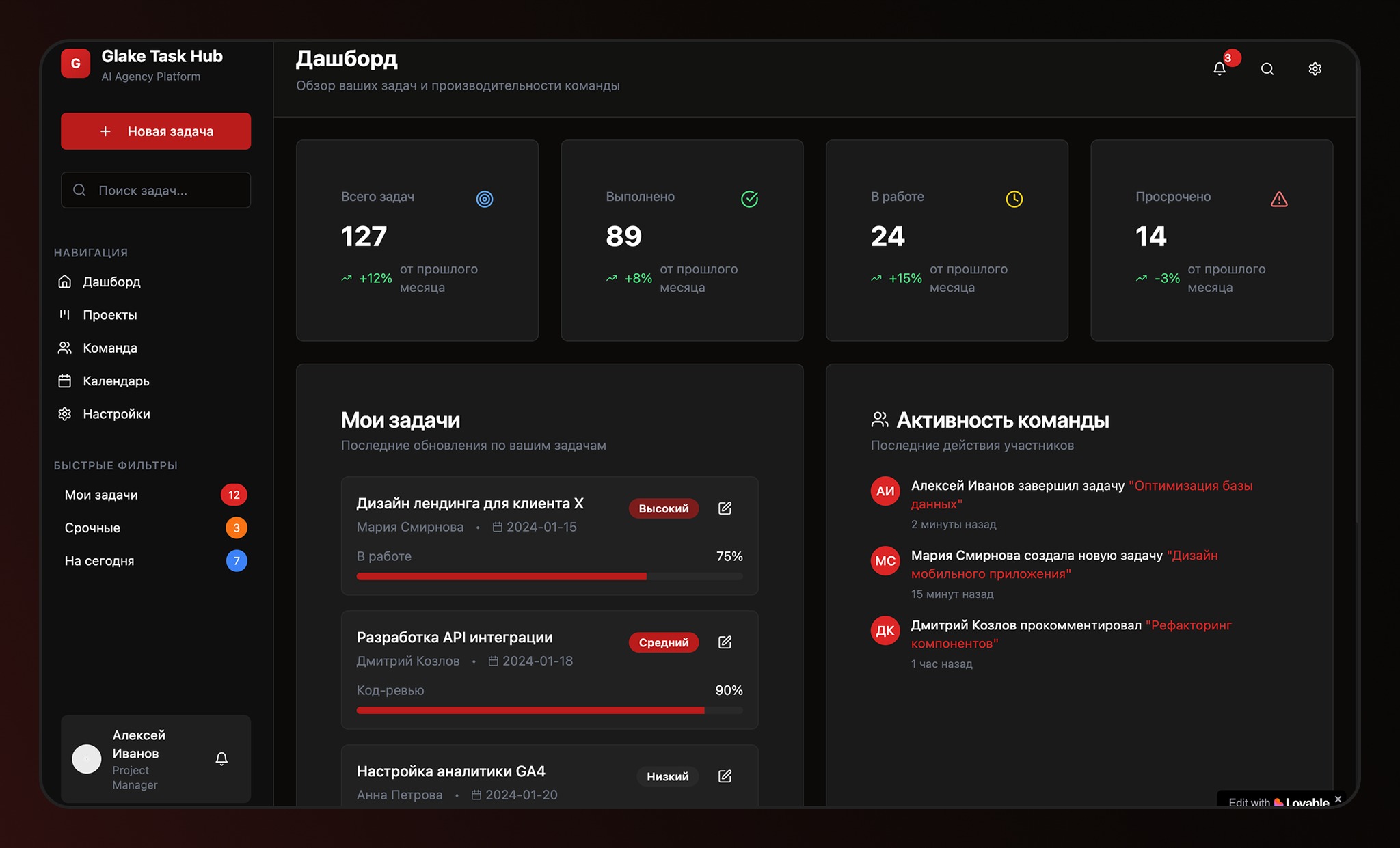
HE European Southern Observatory (ESO) photographed Cone Nebulaa “star factory” in the gas and dust column. The cosmic cloud is located relatively close to Earth, 2,500 light-years away, and is, along with Orion, part of the largest star forming region in the constellation Unicorn.
Saved by the Cone Nebula Very Large Telescope (VLT), from ESO. The star chamber is shaped like columns and develops precisely in giant clouds of molecular gas and cosmic dust. Such a structure occurs when newly formed, massive, bright blue stars emit stellar winds and intense ultraviolet radiation.
The action causes the ejected material to condense into large, dense, dark columns. In the picture, the filters show the final golden star formation resulting from the interactions of hydrogen molecules (blue) and sulfur (in warmer hues). Look!
The release of the image marks the 60th anniversary celebration of the world’s largest and most powerful telescope array located in Chile.
Throughout its history, the observatory has allowed for revolutionary astronomical discoveries such as the first capture of an exoplanet, the existence of a black hole in our galaxy, as well as proving that the Universe is expanding.
Source: Tec Mundo
I am Bret Jackson, a professional journalist and author for Gadget Onus, where I specialize in writing about the gaming industry. With over 6 years of experience in my field, I have built up an extensive portfolio that ranges from reviews to interviews with top figures within the industry. My work has been featured on various news sites, providing readers with insightful analysis regarding the current state of gaming culture.