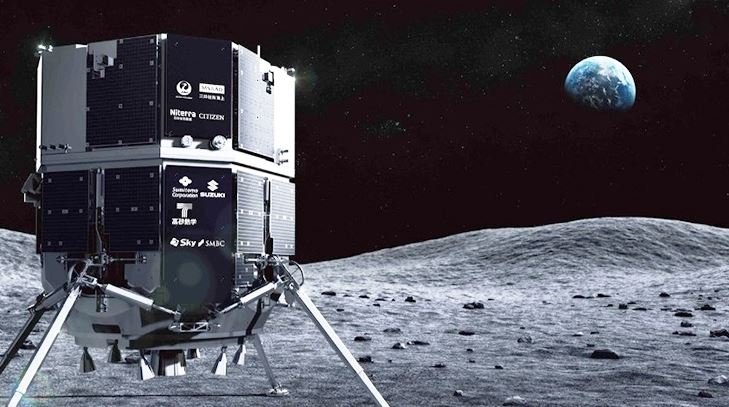
Last Tuesday (25), Japanese company ispace tried to land a spacecraft on the surface of the Moon and, As with 64% of other official moon landing attempts, the mission failed.. In total, 41 missions sent modules to attempt to land on the Moon, but only 15 were successful; that is, only 36% of all landings had a truly positive outcome.
According to the company, the lunar module HAKUTO-R M1 It appeared to be landing on the Moon’s surface as planned, but the ground crew lost contact after not receiving updates for five minutes during the event’s live stream.
Shortly after communication with the module was lost, ispace CEO Takeshi Hakamada said the team managed to communicate with the HAKUTO-R M1 until the end of the landing attempt, but lost contact before completing the mission. “Our engineers will continue to investigate the situation and then update with more information,” said Hakamada.
ispace’s mission is to land on the moon to explore the region to work with sending cargo to lunar soil, including NASA cargo.
Several missions landed on the moon
although we know Of the 41 known probes attempting to land on lunar soil, it’s not possible to pinpoint an exact number, as all failed missions to the former Soviet Union have not been made public. — some modules did not even reach the orbit of the Moon.
One of the biggest problems in space missions is landing precisely because, like launching a rocket, everything has to go smoothly for the mission to be successful. During landing, the landing crew must execute a complex series of commands with almost no margin for error. Additionally, there are different factors that can disrupt a landing, Like the moon’s unstable gravity, moon dust, and the rough terrain of the landing site.
“Of all the things we do in space, landing is one of the most challenging because time is so short. There’s very little room to try something again if it doesn’t go as planned,” said an engineer who worked on the landing crews. Robert Braun in an interview with Insider about various NASA missions to Mars.
The HAKUTO-R M1 module was launched into space with SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket on December 11, 2022, but managed to enter lunar orbit by the end of March. The Japanese company’s lawsuit comes just months after India tried and failed to land on the lunar surface.
Source: Tec Mundo
I’m Blaine Morgan, an experienced journalist and writer with over 8 years of experience in the tech industry. My expertise lies in writing about technology news and trends, covering everything from cutting-edge gadgets to emerging software developments. I’ve written for several leading publications including Gadget Onus where I am an author.