The Graphics Processing Unit, or GPU, is a key component found in many modern devices, designed to accelerate image and graphics processing.
Since its launch with Nvidia’s GeForce 256 in 1999, GPUs have revolutionized the world of computingIt allows computers and mobile devices to process complex graphics and parallel computations with high efficiency.
GPUs can process multiple data items simultaneously, rather than performing a single task at a time like older PCs. We make running programs and games faster and smoother.
Want to better understand how a GPU works, what the difference is between a GPU and a CPU, and how it compares to a graphics card? Read on to discover everything you need to know about this essential piece of modern technology!
GPU: What is it for?
The GPU has become a central element in many areas of modern technology. Although its popularity began with The improvements that graphics processing units bring to games and visual applicationsThe role of GPUs goes even further.
Leading GPU vendors NVIDIA and AMD are developing technologies that serve different needs and industries. The primary areas of use for GPUs can be listed as follows:
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI)
In enterprise and IT environments, the GPU is critical to supporting Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI), which allows you to use a complete desktop environment hosted in the cloud as if it were on your own PC.
This type of setup helps ensure that graphics-intensive applications like design, 3D modeling, and video editing software run smoothly, even when working remotely.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
GPUs are used to build and train neural networks, systems designed to learn and make decisions like the human brain. This includes everything from analyzing large volumes of data in financial services to research in the medical field.
High Performance Computing (HPC)
High Performance Computing (HPC) involves running highly complex and intensive tasks simultaneously on multiple computers.
GPUs help distribute these heavy tasks among different machinesIncreasing the efficiency and speed of data processing. This is necessary for scientific simulations, advanced research, and other applications that require a lot of processing power.
Blockchain
As we explained earlier, GPUs are particularly good at performing complex calculations quickly and efficiently, so these components have great potential for cryptocurrency mining.
In mining, GPUs help solve difficult mathematical problems to verify transactions and add new blocks to the blockchain. However, mining with GPUs in Brazil can be unprofitable due to high electricity costs and import taxes.
How does a GPU work?
The GPU is designed to perform intensive graphics processing tasks and complex mathematical calculations. To process images efficiently, Graphics Processing Unit works with vector graphicsIt consists of coordinates called vertices.
These vertices are connected to form polygons that make up the virtual scene. The GPU is responsible for applying textures and lighting to these polygons, adjusting the details to make the scene more realistic.
Once the entire scene has been calculated in the virtual space, the GPU converts this information into pixel data through a process called rasterization. The pixel data is then sent to the monitor, producing the final image we see.
The process is highly iterative (thousands of times per second!) and requires significant processing power to provide a smooth visual experience.
Besides, The GPU has its own fast access memory known as VRAM (Video RAM). This memory stores the code and data required for graphics processing, allowing the GPU to quickly access and manipulate this information as it performs its tasks.
GPU in the cloud
Cloud GPU technology is revolutionizing the way businesses access advanced computing power. Instead of investing heavily in purchasing and maintaining hardware that can quickly become obsolete as new models are released each year, companies can rent GPUs through cloud services.
Cloud providers offer the advantage of a “pay-as-you-go” model companies access powerful GPUs only when neededwithout fixed purchasing costs and constant updates.
This means companies can focus more on their core operations and manufacturing rather than worrying about keeping up with the rapid technological development of GPUs.
How do I know what is using my GPU?
Node Windows, Task Manager It is a useful tool to check GPU usage:
- When opening the Task Manager (Ctrl + Shift + Esc), go to the “Performance” tab;
- Select “GPU” to see the current graphics processing unit usage;
- You can monitor which applications are using the GPU at what percentage by adding the “GPU Usage” column in the “Processes” tab.
for its users MacOS, Activity Monitor offers a similar appearance.
- Access the “Window” tab;
- Select “GPU History” to view real-time GPU workload and determine which processes are using your resources.
Another option is to use dedicated software like MSI Afterburner or GPU-Z that provides detailed information about GPU performance.
What is the difference between CPU and GPU?
THE The CPU can be compared to the brain of the computer.Responsible for executing software instructions and general tasks such as running programs and making decisions based on commands.
CPUs have fewer cores that work sequentially, processing one task at a time in a linear order. This makes them ideal for performing complex and diverse operations, such as running applications and managing the operating system.
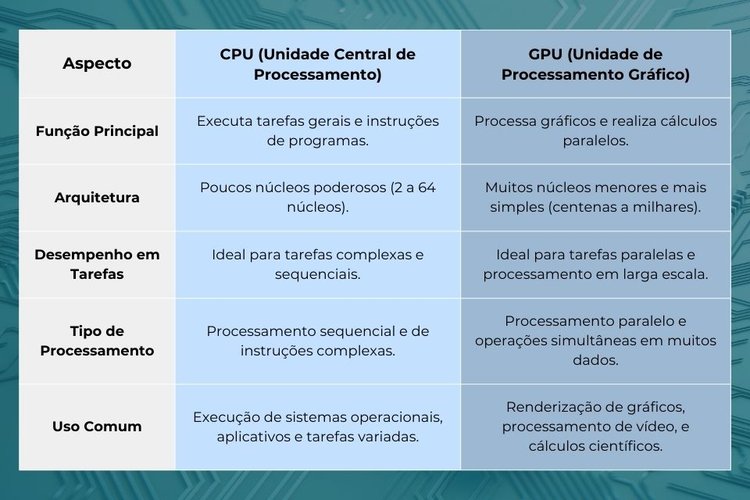
On the other hand, GPU specializes in processing large amounts of data simultaneously. GPUs, with hundreds or even thousands of cores, are designed to perform parallel computations that are extremely efficient for tasks such as rendering high-resolution graphics, games, and machine learning applications.
Both of them work together to deliver balanced and optimized computer performance and leverage their expertise to ensure the system runs effectively.
What is the difference between a GPU and a graphics card?
The terms GPU and graphics card may sound similar, but they refer to different parts and functions in your device. The GPU is the chip responsible for processing graphics and images.
It performs the complex calculations required to create the images and videos we see on the screen. We could even say that the GPU is the “chef” and the graphics card is the “kitchen” where it works!
By definition, a video card is a hardware component that includes elements such as a GPU, power systems, display output connectors, and video memory (VRAM).
Where is the GPU in a PC?
The GPU is usually located in one of two locations in the computer:
- Dedicated graphics card (onboard GPU): If you have a dedicated graphics card, the GPU is mounted on an expansion card that fits into a specific slot on the motherboard, known as a PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) slot. This card is visible and is a separate part from the rest of the computer;
- Integrated GPU (onboard): The GPU is integrated directly into the processor (CPU) or motherboard, unless you have a dedicated graphics card. In this case, the GPU shares resources with the CPU and is not visible as a separate part, as it is part of the processor chip or motherboard itself.
Integrated GPUs are commonly used in laptops, where power and battery savings are important factors in device performance and cost.
Understanding the difference between a GPU and a graphics card, as well as their importance in different contexts like the cloud and compared to a CPU, will help you make more informed decisions about which hardware to use for your specific needs.
If you are considering investing in a graphics card and want to learn more about it What to consider when purchasingDon’t forget to check out the TecMundo graphics card Price Guide!
Source: Tec Mundo
I am a passionate and hardworking journalist with an eye for detail. I specialize in the field of news reporting, and have been writing for Gadget Onus, a renowned online news site, since 2019. As the author of their Hot News section, I’m proud to be at the forefront of today’s headlines and current affairs.