Does the charger waste energy when left plugged in? This is a doubt I’ve had as well, and it’s compounded when I find my cell phone charger or other devices plugged in, even when I’m not using it. After all, who has never done this out of practicality or forgetfulness?
The answer is directly: Yes, the charger in the socket consumes energy.even if you are not charging any device.
This phenomenon, known as phantom consumption, may seem insignificant at first glance, but when added to other devices left in standby mode, it can affect your electricity bill over time.
So how much exactly does a charger consume? Does this really make a difference in your pocket? Are there any other problems when leaving the charger connected all the time?
We’ll explore these and other questions throughout this article to help you understand how small habits can affect your energy consumption and even the safety of your home.
What is imaginary consumption?
Phantom consumption or phantom power refers to the energy consumed by devices that remain plugged in even when not in use.
This is also the case with devices such as televisions in standby mode, monitors that have been turned off, forgotten lamps and, of course, mobile phone chargers that remain plugged in for next use.
If the charger is plugged in, continues to consume energy because its internal transformer remains active. The part is responsible for converting the high voltage of Brazilian outlets (127V or 220V) into a lower, more stable voltage (usually 5V or 9V) that is safe for charging smartphone batteries, for example.
This conversion process does not stop completely even if there is nothing connected to the charger. Although more modern models are designed to minimize this waiting cost, it still exists.
Charger phantom consumption may seem insignificant on its own, but when added to other devices, Can represent up to 10% of your monthly electricity bill According to the Spanish Consumers and Users Organization.
Therefore, understanding how this happens and making small changes can help you avoid unnecessary expenses and even contribute to sustainability at home and work.
How much energy does a charger consume when plugged in?
Knowing how much the charger at the outlet affects your electric bill may present two surprises. The first is to discover that spending actually exists and then stumble upon an almost distinct value. I said almost!
Charger constantly plugged in Consumes approximately 0.26 watts (W) without mobile phone connected. Calculating this monthly consumption is easier than it seems. To look!
- Identify the power of the charger, usually written on the accessory and expressed in watts (W);
- Multiply by the number of hours it remained unused;
- Convert the value to kilowatt hours (kWh) by dividing it by 1000;
- Calculate the monthly expense by multiplying the daily amount by 30 days;
- Multiply the amount stated on your electricity bill by the cost per kWh.
For example, if a charger consumes an average of 0.26 W and is on for 24 hours, the calculation will be as follows:
0.26 W x 24 hours = 6.24 Wh (watt-hours).
6.24 Wh ÷ 1000 = 0.00624 kWh/day.
0.00624 kWh x 30 days = 0.1872 kWh per month.
0.1872 kWh x 0.65715 R$ = 0.12 R$ per month.
NOTES: It is important to remember that there are many factors that change the results of this calculation, such as the cost of the energy tariff determined by the company serving your region, the power of the charger in standby mode and the time it remains connected. , but was not used.
In the table below, you can see the different periods during off-peak hours (22:00 – 17:00), intermediate hours (17:00 – 18:00 and 21:00 – 22:00) and peak hours (18:00 – 21:00). It is possible to compare wage values. .
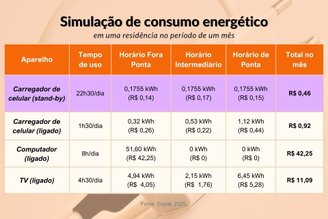
What may seem trivial can add up to a heavy burden over time, especially in homes with multiple people or workplaces where many chargers and devices remain connected in standby mode.
The financial impact can be negligible if a single charger is used. Something like R$1.47 per year. However, getting into the habit of unplugging the charger when not in use not only saves energy, but also helps extend the lifespan of the equipment and prevent waste.
Can you leave the charger plugged directly into the wall socket?
For starters, licensed chargers from trusted brands are designed with protective circuits and can theoretically stay plugged in without any problems. Even though they’re still safe The general recommendation is to avoid this habit.
The practice of leaving the charger plugged in can pose safety risks that go far beyond the electric bill. According to the Brazilian Association for Awareness of the Hazards of Electricity (Abracopel), accidents involving chargers are more common than thought.
For example, in 2021, 20 cases of electrical accidents related to chargers were recorded in Brazil, It resulted in 16 confirmed deaths. In 2023, loaders were responsible for 14 fires, 5 of which were fatal.
The figures show that the risk is real, especially in certain situations such as lightning strikes, electrical grid overload or the use of fake chargers.
Additionally, household factors such as damaged cables, children or animals that may bite the cables, or even accidental drops can turn the charger into a potential hazard.
So it’s time to say goodbye to another bad habit and put your charger aside after use, okay?
What’s the problem with leaving the charger plugged in?
We already know that one of the problems with leaving the charger plugged in is that it wastes energy. The list of losses includes 3 more consequences that are more serious than you might imagine. Check this out!
1) Electrical accident risks
According to Abracopel, plug-in chargers can cause problems fires, shocks and even explosionsEspecially in cases of electrical overload such as storms.

2) Damage to the charger and device
Even if the charger is not used, it remains powered as long as it is connected to the outlet. This can accelerate internal wear of components, shortening their lifespan.
In addition, carelessness such as pulling the cable too hard, stepping on the charger, or leaving it exposed may cause damage that will negatively affect the operation of the device and increase the risk of accidents.
3) Unnecessary energy consumption
Although energy consumption is minimal when added to other backup devices (less than R$2 per year for a single charger), the impact can be up to 10% of a month’s electricity bill.
What draws energy even when turned off?
Invisible consumption, known as phantom consumption, occurs due to some devices remaining on the device. connected to the electrical grid to perform standby functionssuch as updates, maintenance of configurations or making them ready for immediate use.
Examples of devices that consume energy when turned off:
- Televisions and monitors;
- Plug-in chargers;
- Internet and cable TV equipment;
- Microwaves with digital clocks;
- Programmable coffee machines;
- Refrigerators;
- Computers and game consoles.
How do I know what’s draining my energy?
Seemingly harmless devices, especially those left on or in standby, may be responsible for high consumption. There are several ways to find out which devices affect your electric bill.
First, Analyze your energy bill to understand consumption patterns. Observe kWh values and monthly fluctuations. If the consumption is higher than expected, it is a sign that there may be devices that consume more than they should.
Portable electricity meters are excellent tools for determining the consumption of individual appliances. Simply connect the device to the meter and outlet to check how much energy it consumes in real time, both on and in standby mode.
A simpler way to identify energy villains unplug unused devices and keep track of the electricity bill in the following months. In this way, you can check whether there is a decrease in consumption.
The main suspects of high energy consumption are air conditioning, electric showers and older appliances such as refrigerators, freezers and TVs.
If you still have doubts about excessive consumption, It is worth consulting an electrician or a specialist technician. They can detect overloads and energy losses in the electrical system and suggest solutions.
Preventing imaginary consumption: tips for saving energy
- Unplug unused devices such as chargers and secondary devices;
- Use row filtersequipment with switches that allow multiple devices to be turned off simultaneously, reducing phantom consumption;
- Invest in efficient devices designed to consume less energy in standby mode;
- Check your energy consumption every month to understand which changes in your routine are creating more energy unnecessarily.
Small actions can add up to the much-desired savings on your electricity bill and make a difference at the end of the month.
Did you like the content? Share on your social networks and keep browsing TecMundo to get the best tips and news about technology!
Source: Tec Mundo
I am a passionate and hardworking journalist with an eye for detail. I specialize in the field of news reporting, and have been writing for Gadget Onus, a renowned online news site, since 2019. As the author of their Hot News section, I’m proud to be at the forefront of today’s headlines and current affairs.