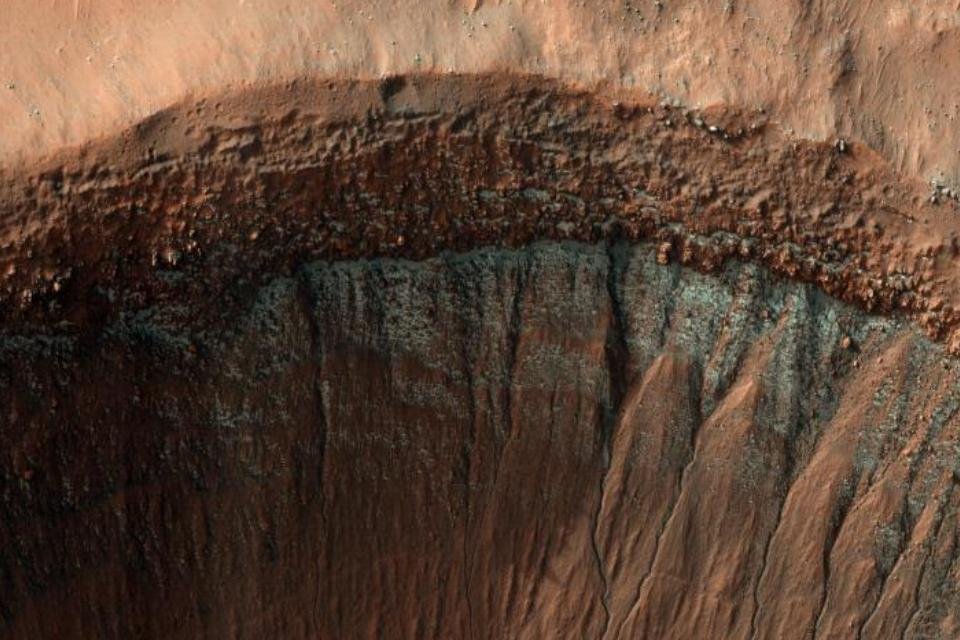
NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) has found an ice crater on Mars. The space agency’s enhanced image shows a layer of frozen carbon dioxide on the red planet’s southern surface, which appears as bright blue dots in the landscape.
Dry ice formations occur throughout the entire winter on Mars, which lasts about 4 months. In the polar regions, temperatures can reach -125 degrees Celsius, while in more extreme periods freezes that can extend to mid-latitudes.
However, some slopes closer to the equator face the poles, which makes them cooler due to less sunlight. So carbon dioxide stays frozen longer around the many valleys carved out by debris flows that cause the planet’s rough surface during the warmer months.
NASA probe
The MRO spacecraft was launched in 2005 to study the history of water on Mars. Its instruments photograph the Martian surface in detail, allowing it to perform analyzes on Earth’s minerals, groundwater and climate on the planet.
More recent studies are bringing in more information about our neighbor’s formation and evolution in the Solar System. Discoveries include processes responsible for the river network in the past and the dominance of ice that led to soil erosion and caused craters.
Also, newer missions like InSight and the Perseverance rover are expected to bring more details about the interior of Mars.
Source: Tec Mundo
I am Bret Jackson, a professional journalist and author for Gadget Onus, where I specialize in writing about the gaming industry. With over 6 years of experience in my field, I have built up an extensive portfolio that ranges from reviews to interviews with top figures within the industry. My work has been featured on various news sites, providing readers with insightful analysis regarding the current state of gaming culture.