While we all know it as 4G, some phones may recognize this network by the name LTEincluding some variants such as LTE-A and LTE-A Pro. But what is the real difference between 5G against. LTE? To begin with, for the fifth generation network, you will need to buy a new phone that supports this technology, which is already available in major cities around the world.
You will be interested:
- 5G vs. 4G: what are the new generation improvements
- What is 5G fixed wireless access?
- US 5G coverage maps
In short, “G.” represents generationThus, 5G is a collective term for the fifth generation of mobile network technologies. LTE is an acronym for Long Term Evolution (Long Term Evolution).Long term evolution) and in fact it is 4G technology. The new 5G will not automatically replace 4G, so we will see both technologies coexist in the short to medium term.
What benefits does 5G offer?
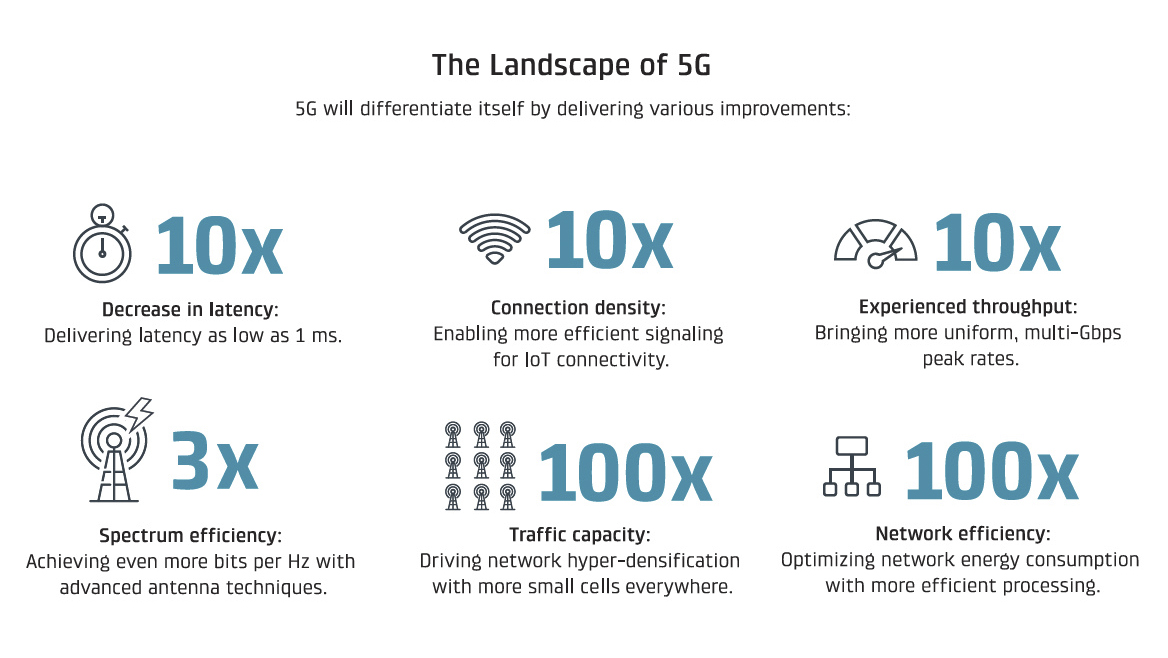
“The main advantage of 5G over 4G LTE is faster speeds, mainly because more spectrum will be available for 5G and more advanced radio technologies will be used. It will also provide much lower latency than 4G, enabling new applications to be built in the Internet of Things (IoT) space,” he explains. Digital Trends Els Baert, director of marketing and communications at NetComm.
5G will allow downloading and uploading data much faster than previous technologies; The theoretical maximum speed is extremely high: 1 to 10 Gbps and 1 millisecond latency, but in reality we can expect the minimum average download speed to be 50 Mbps and 10 ms latency compared to current average 4G speeds from 15 Mbps /s up to 50 ms. This will depend on network coverage, the number of people connected, and the device you are using.
Since 5G is an umbrella term covering many different technologies, it’s hard to surgically separate everything, and there are some overlaps. The faster speeds that really set 5G apart from any of the 4G LTE options require high-frequency millimeter wave (millimeter wave) bands.
They have very high bandwidth, making them ideal for keeping everyone connected in high-traffic areas such as stadiums. The efficiency of this operation depends on a large number of MIMO (multiple inputs and multiple outputs) and beamforming.
While 4G base stations typically have 12 antennas for transmitting and receiving data, due to the high level of MIMO, 5G base stations can support up to 100 antennas. An important feature of these higher millimeter-wave frequencies is that they are much easier to jam, and multiple antennas can cause more interference.
Beamforming is used to determine the best path for each connected user, helping to reduce interference and increasing the chance that easily blocked signals reach the recipient.
While 4G LTE uses a relatively small number of repeaters spaced a few kilometers apart, 5G will require several small cells located much closer together. These mini 5G base stations can be placed on street lights or on the sides of buildings every few hundred meters in urban areas. Logistically, building such a network would be a complex, expensive, and time-consuming task.
What about 4G LTE-A?
The fact that 5G is starting to take off does not mean that the 4G network has ended or stopped developing. The latest 4G technology to be developed is LTE-A (Long Term Evolution Advanced), which promises a maximum speed of 1 Gbps, although a more realistic average is likely to be comparable to the lower bound of 5G. There is also LTE-Advanced Pro, which is even faster.
Unfortunately, AT&T has chosen to name some of its 4G technologies 5GE (5G Evolution) and put 5GE logos on phones that don’t actually support 5G. This brings us to an important distinction: while 4G LTE, LTE-A, and LTE-A Pro will work with phones you own right now, true 5G will require you to buy a new phone with the right hardware.
Why should you care?
If you think you need at least 25Mbps to enjoy 4K, or better yet the 50Mbps that LTE already offers in some places, then you might be wondering why you need even more speed. The truth is, if you have good LTE coverage right now, you won’t see much immediate benefit from switching to a 5G phone.
“The most important thing for the average phone owner is to have a quality connection with a decent speed. In the end, it’s not about the technology, but about the service provided. For many end users, this can be achieved with 4G LTE. The most advanced users will need the faster speeds and lower latency that 5G can provide,” Baert said.
The future of 5G may lie in self-driving cars, wireless virtual reality games, and remote-controlled robots. There will no doubt be many more applications for this technology, but it will take time for 5G to bring tangible benefits to most.
While major manufacturers already offer 5G support, if you’re unlucky enough to live in an area that has 5G coverage, you won’t notice much of a difference in your daily life. In the long run, there is no doubt that you will need a 5G capable phone. At this point it will depend on your budget and how long you intend to keep your device.
Ultimately, 5G networks will complement 4G and LTE coverage, and they will work together to provide fast connectivity wherever we are.
Source: Digital Trends













