The Big Bang theory is a widely accepted scientific theory when it comes to the origin and development of the universe. According to this theory, The universe began as an infinitely small, dense, hot singularity about 13.8 billion years ago.. In a fraction of a second, this singularity expanded rapidly, giving rise to dimensions of matter, energy, space, and time.
Some people still have some doubts about the subject, so TecMundo has put together five fascinating facts about the Big Bang theory. Check out:
1 – For the first time a Catholic priest thought
Albert Einstein in 1915 revolutionized the world of physics by publishing his general theory of relativity. Initially, this theory argued that the universe is expanding or contracting naturally. However, both Einstein and most astronomers and physicists at the time believed that the universe was static. That’s why Einstein added additional terms to his equations to balance things out.
Years later, Edwin Hubble made an important discovery when he observed galaxies moving away from us. As astronomers continue to debate the implications of this observation, Belgian physicist and Catholic priest Georges Lemaître was the first to accept the results of Einstein and Hubble for what they really are, arguing that we once lived in a much smaller, hotter, and expanding universe. busier than it is today. Lemaître named this point of departure. “primitive atom”.
The revolutionary ideas of Einstein and Lemaître changed our understanding of the universe forever. We now know that we live in an ever-expanding universe that started from an incredibly dense state. This cosmic discovery has led us to rethink our ideas about the origin and evolution of the universe. and opened the door to new research and surprising discoveries.
2 – Theory was mistakenly confirmed

Georges Lemaître’s idea met with considerable skepticism among physicists because it resembled the Genesis story. Despite doubts, other attempts to explain Edwin Hubble’s observations have failed under observational scrutiny. The “Big Bang” theory, while intriguing, was considered illogical by many.
On a fortuitous flashback in 1964, two brilliant Bell Labs radio engineers, Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson, stumbled upon a startling discovery. While testing a new microwave receiver, they found an incessant background hiss that persisted despite all efforts to eliminate it, including wiping pigeon droppings from equipment.
Desperate for an explanation, they chanced upon a team of theoretical physicists seeking funding for a similar project.
Theoretical physicists have revealed that originates from cosmic microwave background radiation – a remnant of the universe’s transition from a hot, dense plasma to a slightly cooler neutral gas. This remarkable discovery became the cornerstone of our understanding of the Big Bang theory.
3 – It is not the theory of creation.

The Big Bang Theory Is Not The Theory of Creation theory of the history of the universe. It would be fair to say that our entire observable universe was once compressed into a peach-sized volume with a temperature of over 1 trillion degrees Celsius.
However, deep within this theory lies an uncanny void – questions that remain unanswered, mysteries that remain. The origin of the universe and whether such research is meaningful is beyond our current understanding.
In essence, the birth of the universe as its “starting point” is shrouded in uncertainty. stay together information that only goes back to what happened later.
4 – Cosmic background radiation
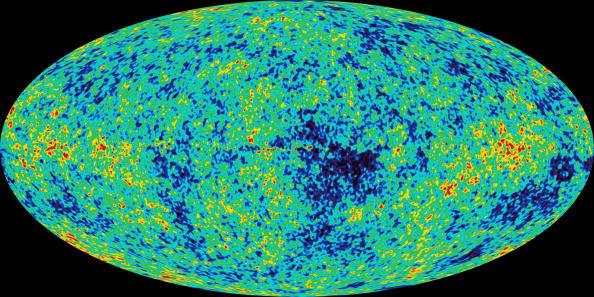
A cosmic background radiation (CMB) is a fundamental discovery that solidifies the Big Bang theory as an unrivaled explanation for all observed data. In addition to its groundbreaking results, the CMB serves as a fascinating portal to our distant past.
In the early stages of our universe, when it existed in a very small fraction of its current size, temperatures rose above 10,000 Kelvin (over 17,000 degrees Fahrenheit), covering the cosmos in a plasma state.
As the universe expanded and cooled, plasma turned into a neutral gas, marking the formation of the first atoms. This transformative event triggered an enormous release of radiation that continues to this day as the cosmic microwave background.
5 – Big explosion of space

Likewise, the Big Bang, one of the most extraordinary events in cosmic history, challenges our understanding. It was not an explosion in space, as is commonly imagined, but an explosion in space itself.. The Big Bang happened simultaneously for everything in the universe. It didn’t happen at a specific place in space, but at a specific moment in time.
Although intuitively difficult to understand, this is precisely why we rely on mathematics – to help us navigate and understand concepts that push the boundaries of our ordinary thinking.
Source: Tec Mundo
I’m Blaine Morgan, an experienced journalist and writer with over 8 years of experience in the tech industry. My expertise lies in writing about technology news and trends, covering everything from cutting-edge gadgets to emerging software developments. I’ve written for several leading publications including Gadget Onus where I am an author.