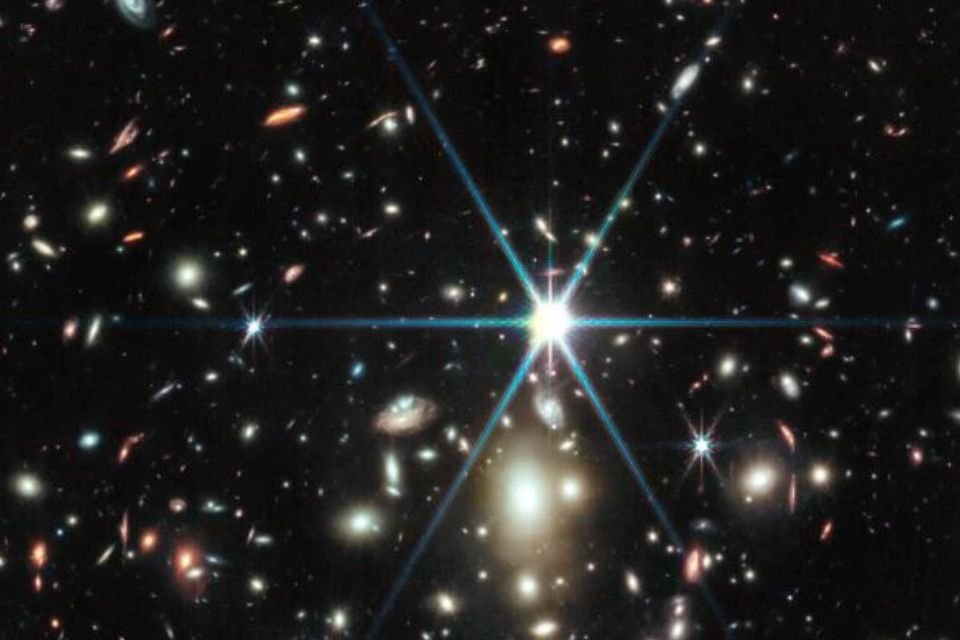
Recently, the United States National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) released a new image captured by the James Webb Space Telescope in collaboration with the Hubble telescope. This is about a Photograph of Earendel, the farthest star in the universe, located in the Sunrise Arc galaxy about 13 billion years from Earth.
The cosmic object was first observed in 2022, when the Hubble Space Telescope broke the record for observing the most distant star to date. Earendel is twice as hot and about a million times brighter than our Sun.; The object appeared only 900 million years after the Big Bang.
Because it is so far away, the star’s light is distorted by the redshift phenomenon. The problem is that Hubble isn’t that strong at detecting infrared signals, so infrared instruments on the James Webb Space Telescope can give more answers about the star.
What is redshift?
Redshift or Portuguese redshift is the measure of red light in distant space objects such as galaxies. The further away in space, the more “stretched” the light and redshifted. This is why the infrared instruments in the James Webb Telescope are so powerful and can capture images of cosmic objects billions of light-years from Earth.
“Observing and confirming the star’s distance is just the beginning. This is where NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope comes into play. Webb’s early observations of Earendel provided information about the star’s type and even the galaxy surrounding it. Future analysis of spectroscopic observations of Earendel and its host galaxy, the Sunrise Arc, could also reveal information about luminosity, temperature, and composition.”
Hubble, James Webb and the Farthest Star
The scientists explain that despite the power of both telescopes, Earendel can only be seen due to the gravitational lensing effect created by the WHL0137-08 galaxy cluster. The cluster is between the Earth and the star and thus acts as a magnifying glass that distorts space-time. — as if WHL0137-08 works like a cosmic magnifying glass for Earendel’s observation.
Astronomers also suggest that Earendel may have a companion cosmic object in the same region. Most likely, the companion star is cooler and redder. The data also suggest star forming regions and older clusters, some of which are “as small as 10 light-years”. In any case, scientists plan to continue studying Webb’s observations to better understand the cluster and star.
“The research team is cautiously hopeful that this may be a step towards the eventual detection of one of the first generation stars that is composed solely of the raw components of the universe (hydrogen and helium) created in the big bang,” the statement said.
Did you like the content? So keep a close eye on more topics like this here Discover how colorful the images from the TecMundo and James Webb telescope are.
Source: Tec Mundo
I’m Blaine Morgan, an experienced journalist and writer with over 8 years of experience in the tech industry. My expertise lies in writing about technology news and trends, covering everything from cutting-edge gadgets to emerging software developments. I’ve written for several leading publications including Gadget Onus where I am an author.