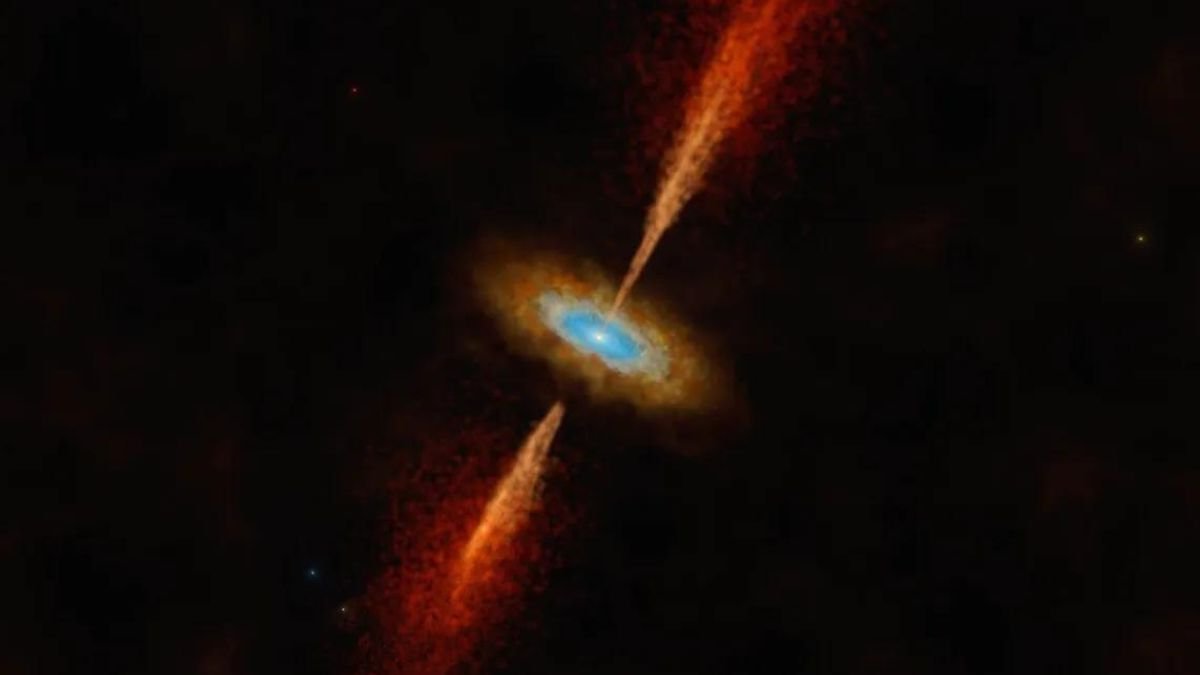
Researchers found that First example of a disk orbiting a star outside the Milky Way. This structure is almost identical to those found around young stars in our galaxy and may suggest that the formation of celestial bodies is similar at different points in the universe.
The star in question is located in the Large Magellanic Cloud, approximately 160 thousand light-years away from Earth. The system called HH 1177 is surrounded by a large gas cloud.
The observation was made by the Atacama Large Millimeter Array (ALMA), a radio telescope with more than 60 antennas deployed in the Chilean desert in 2011. This project is the largest project ever undertaken in terrestrial astronomy, capable of producing high-resolution images..
The discovery could impact the way scientists understand the formation of planets and stars, as it suggests similarities between distant galaxies. This is what the project’s lead researcher, Anna McLeod, from Durham University, says.
“When I first saw evidence of a rotating structure in the ALMA data, I couldn’t believe that we had detected the first extragalactic accretion disk. It was a special moment. We know that disks are vital to the formation of stars and planets in the Universe. “Here we see direct evidence of this in another galaxy for the first time,” he said. added.
Accretion Disks
Since matter cannot fall directly onto a star, it is common for it to cluster and “planate” around the celestial body. Therefore, large disks of dispersed material are formed, spinning faster as they approach the center. Disks known as accretion disks often form on young stars, black holes, or neutron stars..
Gas at the center of the accretion disk (closest to the central object) moves faster than the material around the disk, and it is this change in speed that draws attention to the existence of this phenomenon.
“The frequency of light changes depending on how quickly the gas emitting the light approaches or moves away from us,” said researcher Jonathan Henshaw from Liverpool John Moores University.
This is the same phenomenon that occurs when an ambulance siren changes in pitch and the frequency of the sound decreases from high to low as it passes by. In traditional physics, we call this the Doppler effect.. In astronomy, it is known as “redshift” or “blueshift”, depending on whether the observed object is approaching or moving away from the Earth.
Is there anything you want to ask? Tell us on our social networks and get the opportunity to share the article with your friends who love astronomy.
Source: Tec Mundo
I’m Blaine Morgan, an experienced journalist and writer with over 8 years of experience in the tech industry. My expertise lies in writing about technology news and trends, covering everything from cutting-edge gadgets to emerging software developments. I’ve written for several leading publications including Gadget Onus where I am an author.