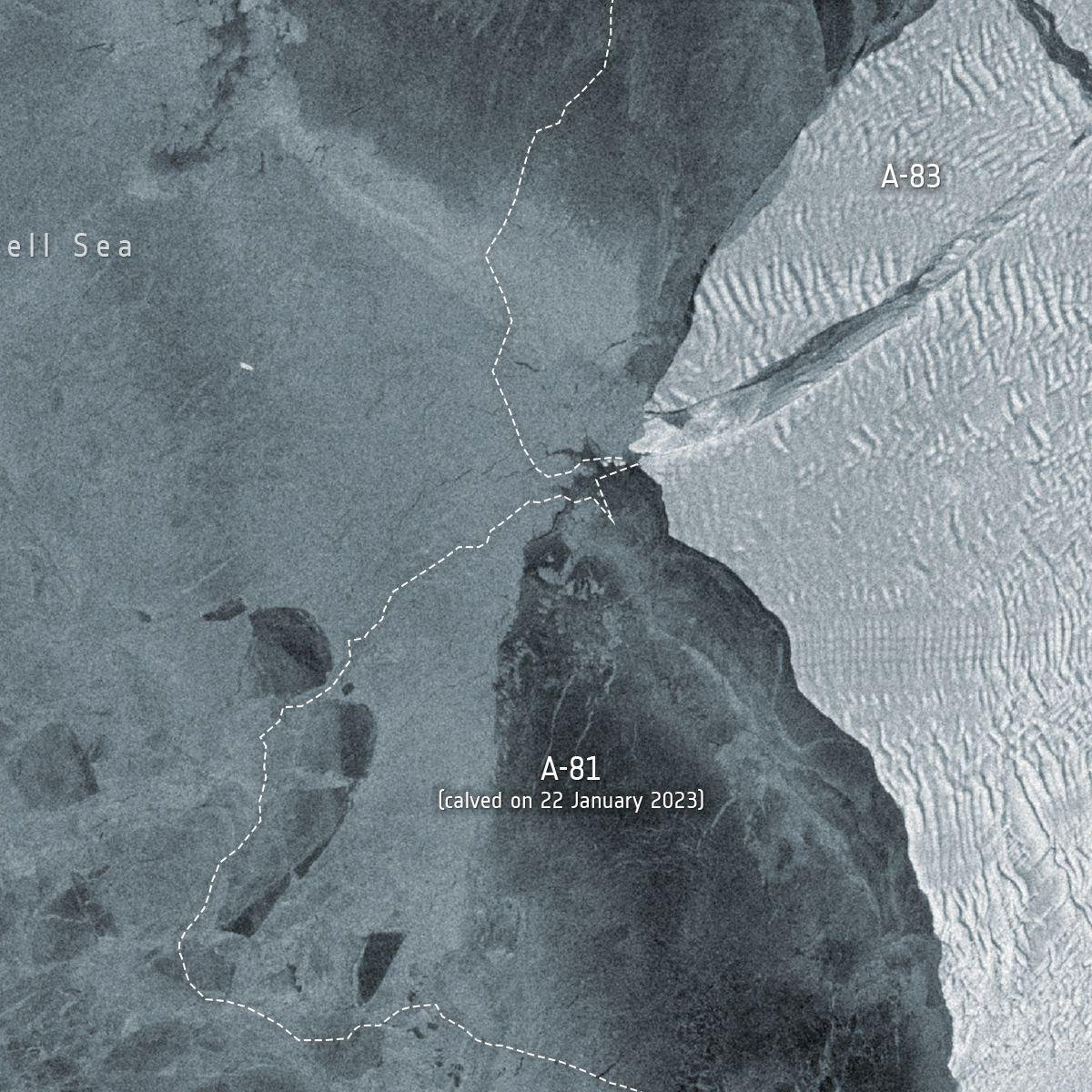
A massive iceberg, 380 square kilometers long, recently broke away from the Brunt Shelf, a vast, ancient Antarctic glacier located on the eastern shore of the Weddell Sea. The phenomenon called “iceberg calving” (calving in English) occurs when blocks of ice break away from the main glacier and begin to float freely in the ocean.
Although calving is a natural part of the life cycle of glaciers and ice shelves in general, Here, in addition to the magnitude, the frequency of occurrence is also alarming. This event, which covers the A-83 section of the platform, is the third largest organization held in the region in the last four years.
The first major event occurred in 2021, when subsection A-74 (these numbers are assigned by the US National Ice Center) broke away from the original ice sheet. But in January 2023, an even larger iceberg broke away from Brunt: A-81.
Why does the iceberg break away from the main glacier?
These events are observed by satellites such as ESA’s Copernicus Sentinel-1 and NASA’s Landsat 8, which provide radar images and thermal data respectively. allows scientists to monitor the structural integrity of ice shelves in real time. This even occurs during the Antarctic Night, when the Sun disappears for six months.
In their routine work, glaciologists evaluate the effects of rising atmospheric and ocean temperatures on ice dynamics, such as calvings like that of A-83. McDonald’s is caused by the weakening of ice waves, seabed heights of up to 10 metres, acting as a “lock” for the platform.
This was due to the “Halloween Crack”, a massive crack that opened in the Brunt Ice Shelf in October 2016. The huge crack, 200 km long and 50 meters wide, allows part of the ice shelf to pass over the McDonald ice locks and float freely.
What are the consequences of the separation of iceberg A-83?

The frequent departure of icebergs from Antarctica, a clear indicator of rising global temperatures, raises concerns about the loss of continental ice and its possible effects on the planet.
In addition to releasing freshwater into the oceans, it raises global sea levels. loss of polar ice means less ice to reflect solar radiationThis causes ocean water to warm, thus increasing the planet’s temperatures.
This is why monitoring polar ice sheets is so important in developing adaptation and mitigation strategies. Although iceberg calvings are routine, each calving provides valuable indicators about the behavior of the “shock absorbers” that keep ice sheets out of the oceans.
What awaits us in the future? Stay up to date with more news like this here at Science at TecMundo. To the next one!
Source: Tec Mundo
I’m Blaine Morgan, an experienced journalist and writer with over 8 years of experience in the tech industry. My expertise lies in writing about technology news and trends, covering everything from cutting-edge gadgets to emerging software developments. I’ve written for several leading publications including Gadget Onus where I am an author.