The hands on the cosmic clock are constantly moving towards the end of time. With each passing second, the motion of every atom and particle in existence is leading us towards the final reaches of the Universe.
One possible scenario for how our universe could end is hidden in clues contained in the fundamental laws of nature that govern heat, energy, and time: Laws of Thermodynamics.
This set of laws shows that one day, The entire Universe will enter a death of heat, a dull, motionless and barren end..So how do you come to this idea?
Heat death of the universe
The hypothesis of the thermal death of the Universe emerged in the 19th century, at the height of the development of thermodynamics, when scientists such as Lord Kelvin and Rudolf Clausius began to understand the profound implications of the Laws of Thermodynamics not only for closed systems, but for the Universe as a whole.
Lord Kelvin was one of the first to suggest, in 1852, that the Universe might be moving towards a final state of thermal equilibrium, in which all energy would be distributed equally and there would be no more useful work to be done. This idea, known as “heat death,” has brought a new and alarming perspective to the fate of the Cosmos..
To understand how these laws signal the end of the Universe, we must first understand what these laws are and how they govern the behavior of energy in all systems.
The laws of thermodynamics and the end of the universe
The First Law of Thermodynamics is a consequence of the law of conservation of energy and determines that, physically, the change in the internal energy of a thermodynamic system is equivalent to the difference between the amount of heat absorbed by the system and the work done by it.
This expression has one meaning Energy in an isolated system can neither be created nor destroyed, but can only be converted from one form to another..
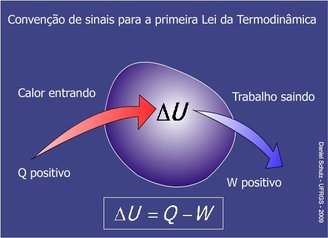
In cosmic terms, this means that the total amount of energy in the Universe is fixed, and although energy cannot be destroyed, its usefulness can change. For example, energy can be converted into heat, which radiates out and becomes less available to do useful work.
The Second Law of Thermodynamics is the main key to understanding the fate of the Universe. It establishes that in an isolated system, entropy, which can be understood as a measure of the degree of disorder or distribution of energy, tends to increase with time. In other words, natural systems evolve toward states of greater disorder and less ability to do useful work..

The meaning of this law is profound: as time progresses, the entropy of the entire Universe is constantly increasing. Stars burn their nuclear fuel and convert useful energy into heat that is radiated into space.
Eventually this process will lead to a state where all energy is distributed equally and the Universe reaches thermal equilibrium. At this point, There will no longer be energy exchanges that power the stars, planets, any movement or life..
Finally, the Third Law of Thermodynamics states that as the temperature of a system approaches absolute zero (-273.15 °C), the entropy of the system tends to reach a constant minimum value. Although absolute zero is theoretically unattainable, this law gives us some idea of the limits of thermodynamics.

Applied to the entire Universe, it suggests that as the cosmos approaches thermal death, the temperature will approach absolute zero, but never quite reach it. In this final state, the Universe will be a vast, cold void where entropy is at its maximum and nothing more can happen.
In short, the heat death of the Universe emerges as an inevitable consequence of these laws.
In this scenario, all stars will have extinguished, all black holes will have evaporated (via the process of Hawking radiation), and all matter will have dispersed. There will be no more temperature differences and therefore no thermodynamic processes will occur.

In this cold, dark, and stagnant Universe, all energy would be available, but it would be of no use, unable to do any work or sustain any form of life. This latter situation would be the natural result of the constant and powerful action of the Laws of Thermodynamics over trillions of years.
The idea of the heat death of the universe is a sobering reminder of the inexorable power of the laws of nature, which confronts us with the fact that no matter how advanced the universe and its activities may be, the fate of everything we know is silence and stillness.
But it’s better than regretting a distant ending It is to appreciate the brief, bright flame of existence that exists in the vast ocean of cosmic time..
Source: Tec Mundo
I’m Blaine Morgan, an experienced journalist and writer with over 8 years of experience in the tech industry. My expertise lies in writing about technology news and trends, covering everything from cutting-edge gadgets to emerging software developments. I’ve written for several leading publications including Gadget Onus where I am an author.












