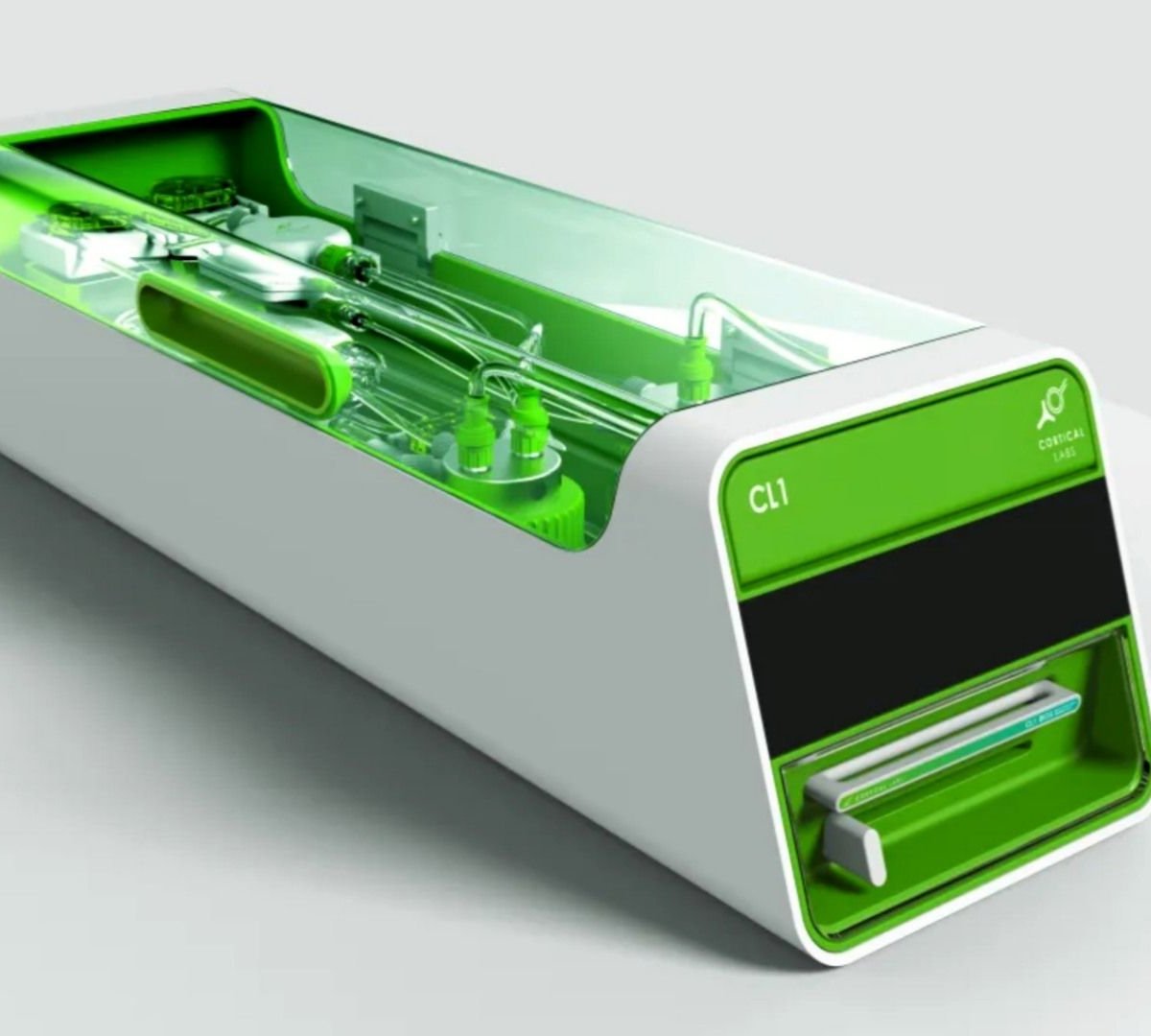
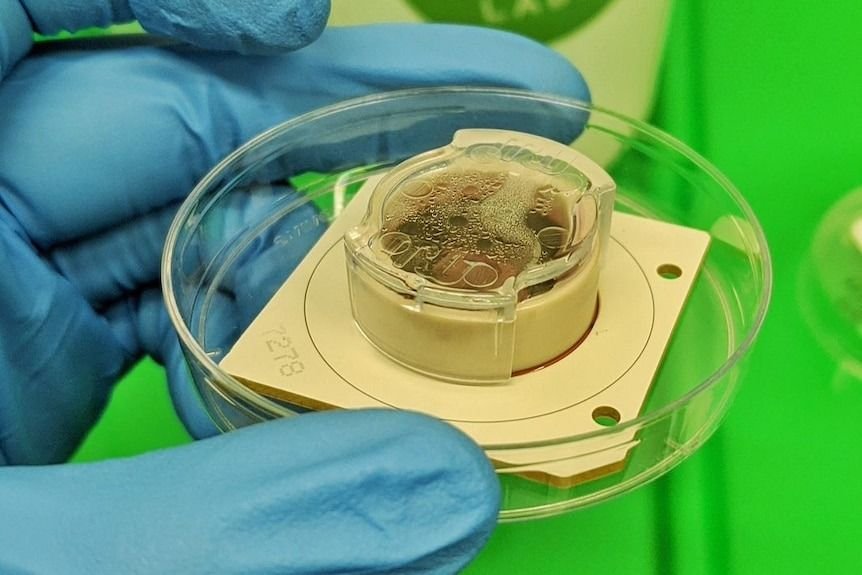
Australian initial cortical laboratories launched the world’s first biological computer during the Mobile World Congress in Spain (MCW) 2025. The device, which is a shoe box called CL1, uses a chip with neurons grown from stem cells to create biological artificial intelligence.
In rectangular format, CL1 is a small computer to learn. For this, this PC uses thousands of small brain -sized neurons from a silicone -related cheap.
Computer neurons are produced in the laboratory Blood cell is a technique that converts blood cells into stem cells and then converted into neurons. According to Brett Kagan, the scientific director of cortical laboratories, the process is not very different from what a doctor has done in routine exams.
The CL1, which combines biology and equipment through silicone, and the great secret of the approach is that neurons can learn with electrophiziological stimuli. By sending information from the chip, while these cells receive response through random information, the correct answers come with standard data and finally realizes what is right to neurons.
This system, known as Dishbrain, played Pong from such a stimulus. Although biological technology missed several balls, he was able to play the iconic table tennis game in 2022, but at that time he carried an impressive mile to the start of the CL1 launch.
Even the construction of CL1 is quite different from a domestic or professional use. This PC’s carcass was made to provide ideal living conditions especially for neurons.Because they demand cells that require free and continuous nutrient supply environment for their functioning and growth.
Creation of a biological artificial intelligence
The success of cortical laboratories aims not only the democratization of CL1, but also the expansion of less -known biological artificial intelligence or rather a synthetic biological intelligence. This is still a creeping area, but it consists of combining machine education and collection of human knowledge in the field of biology.
The idea of starting literallyCook the parts of the brain with neurons to create an artificial intelligence that resembles a real brain. In the end, the goal of imitating an Openai, Google and Microsoft, as the productive IAS, as Kagan points out, the brain is the only thing with productive intelligence ”with its own cells.
The researcher says that the aim of this artificial intelligence is not to compete with complex language models such as GPT or DALL-E. Currently, a PCS CL1’s processing capacity cannot compete with these technologies using huge data center accelerators.

With the expectations containing, Kagan bets that CL1 can be a turning point about energy consumption. Grandiose models consume more than 1,300 megawatt, while consuming more energy A cluster of 30 Cl1 should be pulled between 850 and 1,000 watts of the socket.
Therefore, the merger of equipment with these neurons can be an alternative way to minimize the wide energy consumption in which large technologies are spent. However, this type of technology will take a few good years until it matures and enters the market effectively.
Even if, Brett Kagan is the rapid learning of these structures, the biggest difference of using brain cells for technology.. “What can people, mice, cats and birds do? [que a IA não pode] It is to get rid of a small amount of data and to make complex decisions later, ”he says.
CL1 available for medical research
CL1 and AI are more than ideal for huge technology companies, researchers believe that computer neurons can help medical research. The aim is to put technology to understand the functioning of various diseases and even the preparation of drugs.
Scientists work in a series of cells with features to increase the functioning of certain organs in small neuron clusters baptized by cerebral organoids. Cortical Labs works jointly with the researcher in Stem cells from the University of Queensland Ernst Wolvetang.
Wolvengeg has been examining such cells with 3D organoids for years, while the start uses neurons on a simplified 2D plane. Even with skepticism about how this will work, the scientist points out that cortical manages to develop a software and analysis method to show how these neurons can really learn.

The idea of the researcher is to use his own 3D organoids with the power of the company’s 2D models. If this responds positively to the more complex cell group stimuli and starts to learn, there is a huge scientific possibility to explore.
One of the examples used Adding samples of neurodegenerative diseases to these organoids can explain how it affects memory and learning in humans.. Already Murdoch Children’s Research Institute Silvia Velasco stem cell researcher, trying to understand how the human cerebral cortex is formed.
To ethical questions
As always, there is a strong debate about the ethical decisions involved in processes containing cells and brains. As with embryonic, advanced versions of CL1 and Biological AI can create more understanding and even with some kind of consciousness.
For Velasco, it would be a missed opportunity not to investigate and not to investigate a system with the potential to improve destructive brain diseases. However, the researcher also states that it is important to evaluate and predict possible concerns that the use of these models may increase ”.
Kagan is currently minimizing risks and Science cannot answer these questions yet, given the first stage of the research..
Source: Tec Mundo
I’m Blaine Morgan, an experienced journalist and writer with over 8 years of experience in the tech industry. My expertise lies in writing about technology news and trends, covering everything from cutting-edge gadgets to emerging software developments. I’ve written for several leading publications including Gadget Onus where I am an author.