Every Saturday, TecMundo and #AstroMiniBR brings together five relevant and entertaining astronomical curiosities produced by the world’s collaborators. profile on twitter to spread the knowledge of this science, which is the oldest!
#1: An astronomical crustacean
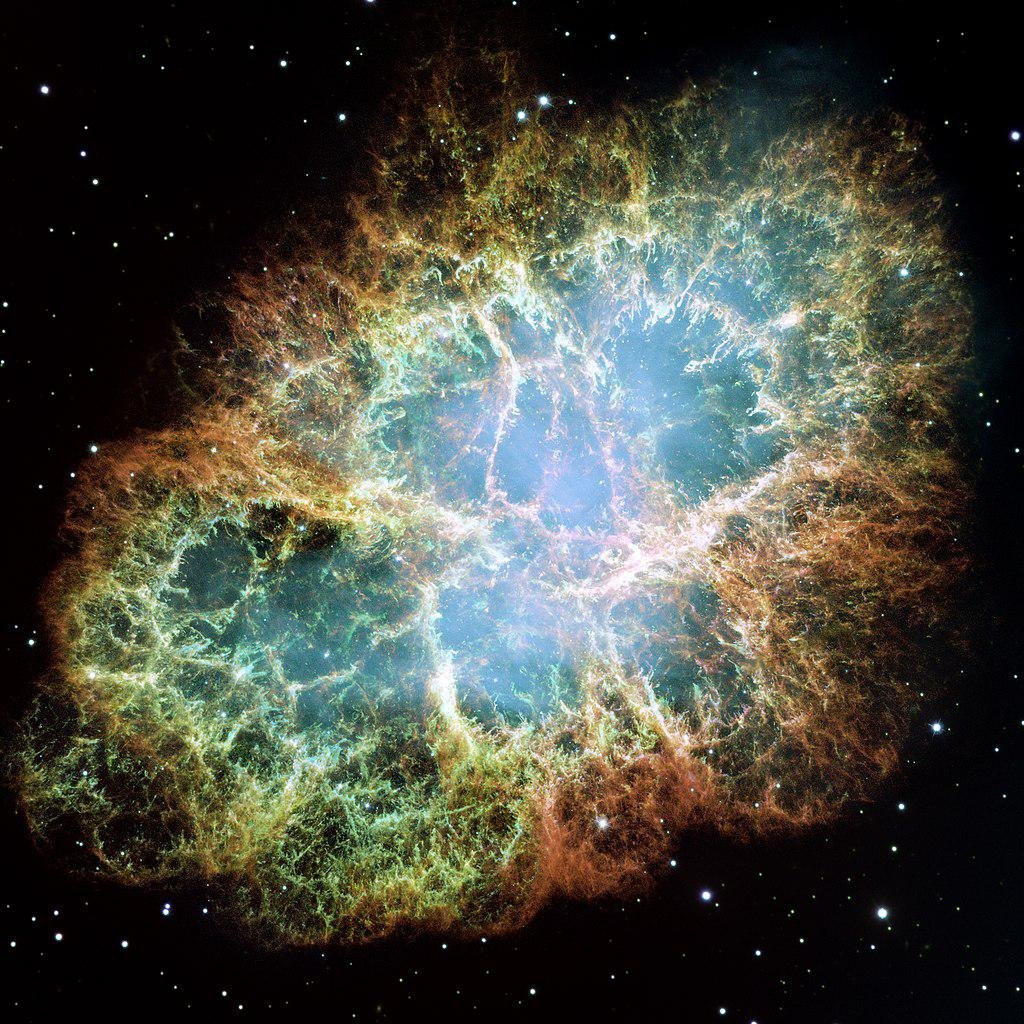
The Crab Nebula by the Hubble Space Telescope, which turns 32 today! ??
The nebula is the result of a supernova (explosion of a star) observed in 1054! #AstroMiniBR #Hubble32 pic.twitter.com/kwnrGXwQ7n
— Giovanna Liberato (@liberato_gio) 24 April 2022
About a thousand years ago, in the year 1054, the sky over China received a light unlike anything commonly seen in the night sky at the time. Chinese astronomers called it a “guest star”, visible even during the day for almost a month.
This light was actually an explosion. supernova causing Crab Nebula, a six-light-year-wide remnant of this catastrophic cosmic event. The Crab Nebula lies 6,500 light-years from Earth and is easily visible with a small telescope.
The remnant of this powerful light was rediscovered in 1731 and observed by Charles Messier, who was later inspired to create a catalog of celestial bodies. The color of the image presented above tells us about the chemical composition of the nebula: the orange filaments represent structures of plasma and star gas, mainly composed of hydrogen; blue hues in the outer strands represent oxygen; and green represents ionized sulfur.
All these elements were ejected so violently during the supernova explosion that remained a dying star with a tiny neutron star at its center spinning at about 30 times per second!
#2: Myopia of the Hubble Space Telescope
There was a flaw in the images when Hubble was released. A space mission was required to solve the problem. #Hubble32 #AstroMiniBR pic.twitter.com/Ucfn10r9BA
— Thiago S Gonçalves (@thiagosgbr) 24 April 2022
When the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) was launched in 1990, a golden age in astronomy began. The telescope opened the windows of the Universe for humanity and made possible an unprecedented understanding of the Cosmos. However, not all stages of this journey blossomed in this 32 years of activity of HST.
Shortly after it was launched into Earth orbit, scientists discovered that its main mirror was incorrectly grounded, causing spherical aberration that greatly compromised the telescope’s capabilities.
A maintenance task in 1993 solved the problem by correcting the optics and adjusting the desired quality. Since then, a total of five space missions have made repairs, upgrades, and replacements of telescope systems and parts, including many of their main vehicles. The last one happened in 2009, significantly extending the life of the telescope, which is expected to last another ten or twenty years.
#3: An empty place in the middle of the galaxy?
Cosmic fireflies!
This time-lapse shows stars orbiting a seemingly empty region in space for 20 years…
In fact, they orbit the supermassive black hole at the heart of the Milky Way!#AstroMiniBR
(c) ESOpic.twitter.com/hdrJ1fCSpZ
— Nicolas Oliveira (@nicooliveira_) April 28, 2022
These black holes are one of the most impressive and powerful celestial bodies we know of in the Universe. However, we rarely get the opportunity to see it in action, because we can only observe its indirect effects.
The video above showcases the awesome gravitational force from the central supermassive black hole hosted at the center of our galaxy! The European Southern Observatory’s (ESO) Very Large Telescope (VLT) in the Chilean desert observes the supermassive black hole at the center of our galaxy and the stars orbiting it.
Using observations from the past 20 years, ESO has compiled observations of S2 stars orbiting the massive hole with the mass of four million suns! At their closest, some stars came within 20 billion kilometers of the black hole and were moving at more than 25 million kilometers per hour, which is about 3% of the speed of light!
#4: How bright is a supernova?
Meanwhile, in the galaxy NGC 4647, in the direction of the Virgo constellation, a star brighter than the entire galaxy explodes violently. Supernova SN2022hrs is the centrally marked spot that we view with the robotic telescope 0.4m from the centre. @LCO_Global #AstroMiniBR pic.twitter.com/aYw6nTQK67
— The Deep Sky Project (@CeuProfundo) April 26, 2022
NGC 4647 is the name given to an intermediate spiral galaxy located in the constellation Virgo, about 63 million light-years from Earth. Discovered in 1784, NGC 4647 is part of a pair of interacting galaxies known as Arp 116. NGC 4647 presents the typical features of a spiral galaxy and is not surprising in principle, it will go unnoticed even by astronomy enthusiasts. Happy to be able to present a relatively rare image recently: The luminosity of a type Ia supernova, one of the most energetic and violent events in the universe, is comparable to the total luminosity of the host galaxy itself!
#5: How are galaxies formed?
Simulation of spiral galaxy formation with TNG50 – (c) Team Illustris
Galaxies grow according to the hierarchical model: smaller galaxies form first, and several merge together¹. They also accumulate gases from cosmic rays.#AstroMiniBR pic.twitter.com/g71n0590zg
— Ana Carolina Posses (@astroposses) 23 April 2022
Tracing the formation and evolution of a single galaxy (or a planet or star) is not possible due to the large difference between our lifetimes and the ‘lifespan’ of galactic objects. However, observing a sufficiently large number of celestial bodies at different evolutionary stages and adding to the known laws of physics allows for the construction of theoretical models that cover much of the puzzle of cosmic history. For this, simulations like the simulations presented in the video above where IllustrisTNG “evolves” a galaxy are essential to helping astronomers derive and test scientific hypotheses!
Source: Tec Mundo
I am Bret Jackson, a professional journalist and author for Gadget Onus, where I specialize in writing about the gaming industry. With over 6 years of experience in my field, I have built up an extensive portfolio that ranges from reviews to interviews with top figures within the industry. My work has been featured on various news sites, providing readers with insightful analysis regarding the current state of gaming culture.