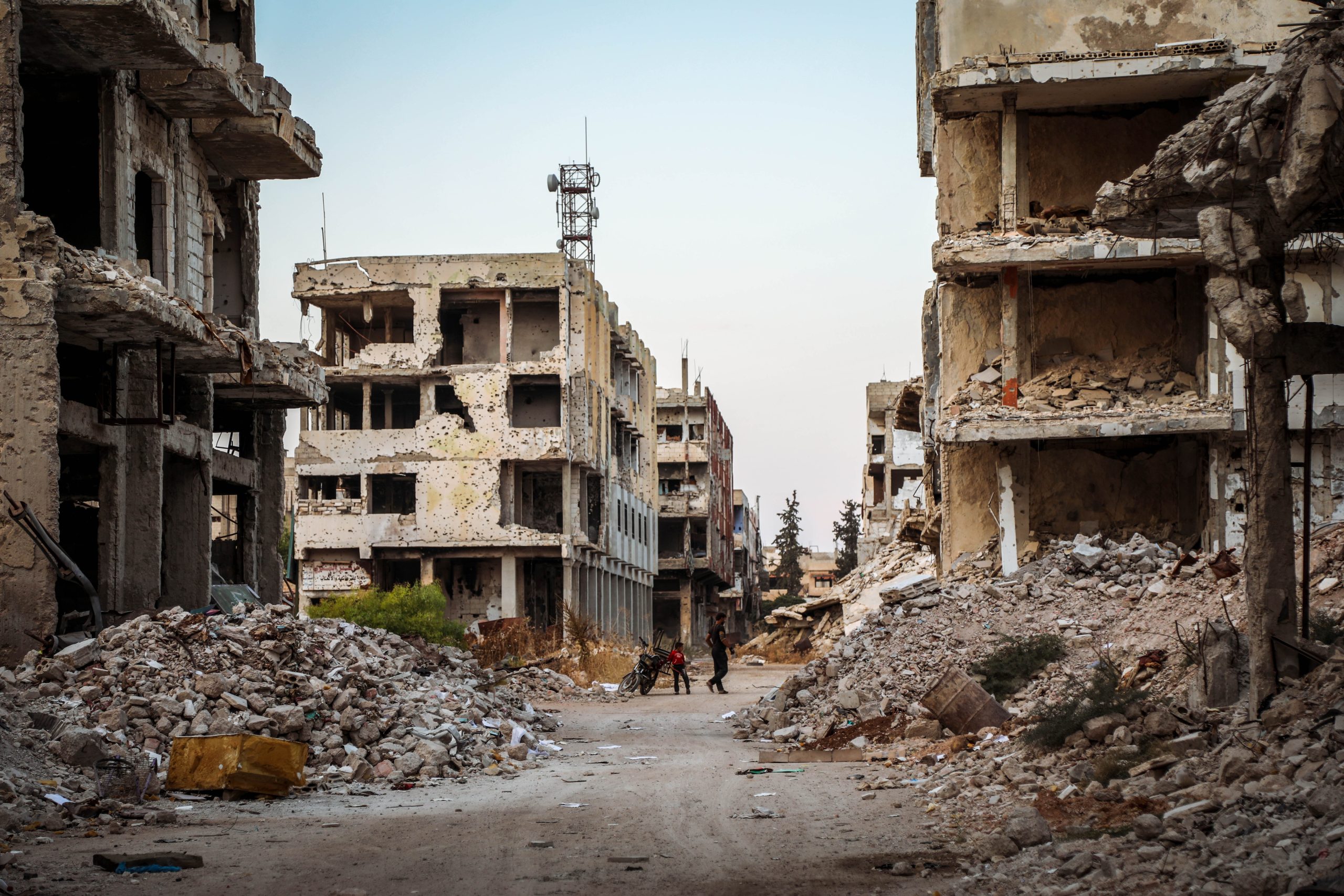
February 6, 7.8 magnitude earthquake shook Southeast Turkey and northern Syria, leaving thousands dead. This is not the first major earthquake in Turkey, although it was particularly strong. You might think that this is pure coincidence. It is still impossible to predict earthquakes. However, there is an explanation why this earthquake was so strong.
This is in error size in which the earthquake occurred in Turkey. There are doubts between East Anatolia or Dead Sea Fault, but most indications point to what happened in the first case. It’s a failure 700 kilometers longtherefore, it offers an ideal scenario for the occurrence of large earthquakes.
In fact, this is usually a common factor in all areas where strong earthquakes occur. This is not the only requirement, but it can help you get an idea of the strength of future shocks and at the same time conscientiously prepare the buildings. So while it’s impossible to know when a disaster is coming, you can try to minimize it as much as possible. But what does the size of the flaws have to do with all this?
Before we begin: these are not degrees
After the earthquake in Turkey, we again hear about the degrees on the Richter scale to indicate its strength. This is something that is technically incorrect and not bad to remember.
To start, We must not confuse magnitude with intensity.. The Richter scale, now out of use, took into account the strength of the earthquake. This was quantified by analyzing their destruction level. For example, if whole buildings fall or only racks vibrate. Instead, the value refers to energy released during an earthquake. It has to do with his level of destruction, of course, but it’s not the same.
In the case of the earthquake in Turkey, it is incorrect to say that it was a magnitude of 7.8 on the Richter scale. It is appropriate to refer to the fact that this was an earthquake value 7.8.
</p>
<p>“data-medium-file=”https://i0.wp.com/imgs.hipertextual.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/jens-aber-fClNK-MIz_E-unsplash-scaled.jpg?fit= 800% 2C400&quality=55&strip=all&ssl=1″ data-large-file=”https://i0.wp.com/imgs.hipertextual.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/jens-aber-fClNK-MIz_E -unsplash-scaled.jpg?fit=780%2C390&quality=55&strip=all&ssl=1″ decoding=”async” width=”780″ height=”390″ alt=”Earthquakes in Japan, Pluto” class=”wp-image- 1374677 perfmatters-lazy” data-recalc-dims=”1″ data-src=”https://i0.wp.com/imgs.hipertextual.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/jens-aber-fClNK – MIz_E-unsplash-1500×750.jpg?resize=780%2C390&quality=55&strip=all&ssl=1″ data-srcset=”https://i0.wp.com/imgs.hipertextual.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/ 02 /jens-aber-fClNK-MIz_E-unsplash-scaled.jpg?resize=1500%2C750&quality=55&strip=all&ssl=1 1500w, https://i0.wp.com/imgs.hipertextual.com/wp-content/ uploads/ 2022/02/jens-aber-fClNK-MIz_E-unsplash-scaled.jpg?resize=800%2C400&quality=55&strip=all&ssl=1 800 W, https://i0 .wp.com/imgs.hip ertextual.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/jens-aber-fClNK-MIz_E-unsplash-scaled.jpg?resize=768%2C384&quality=55&strip=all&ssl=1768w, https: //i0.wp.com/ imgs.hipertextual.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/jens-aber-fClNK-MIz_E-unsplash-scaled.jpg?resize=1536%2C768&quality=55&strip=all&ssl=1 1536w , https://i0.wp .com/imgs.hipertextual.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/jens-aber-fClNK-MIz_E-unsplash-scaled.jpg?resize=2048%2C1024&quality=55&strip=all&ssl =1 2048w, https:///i0.wp.com/imgs.hipertextual.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/jens-aber-fClNK-MIz_E-unsplash-scaled.jpg?resize=1200%2C600&quality =55&strip=all&ssl=1 1200 W, https://i0.wp.com/imgs.hipertextual.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/jens-aber-fClNK-MIz_E-unsplash-scaled.jpg?resize =1568%2C784&quality=55&strip=all&ssl=1 1568w, https://i0.wp.com/imgs.hipertextual.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/jens-aber-fClNK-MIz_E-unsplash-scaled. jpg?resize=400%2C200&quality=55&strip=all&ssl=1400w, https://i0.wp.com/imgs.hipertextual.co m/wp-content/uploads/2022 /02/jens-aber-fClNK-MIz_E-unsplash-scaled.jpg?w=2340&quality=55&strip=all&ssl=1 2340w” data-sizes=”(max-width: 780px) 100vw , 780px”><noscript><img data-attachment-id=) Jens Aber (Unsplash)
Jens Aber (Unsplash)What are faults and how do they relate to the earthquake in Turkey?
A rift is a structure in the ground where rocks have slipped through. the edges of the two blocks. In the case of lithospheric plates that make up solid top layer of the earthwhen the edges between one and the other rub against each other, tension builds up, which can finally be suddenly released. This is what causes earthquakes.
For this reason, although they cannot be predicted, it is known what the hotspots of this type of shaking are: faults where the edges of these lithospheric plates converge. Now it’s not the same small flaw than a much longer one.
The larger it is, the greater the stresses can arise due to friction between plates and the more energy that is released along with them. For example, there was the strongest earthquake ever recorded in history. in Chile, 1960. It reached an alarming magnitude of 9.5 because it occurred on a 1,000-kilometer fault.
When Earthquake in Turkey and Syriaits epicenter fell on the point of collision Anatolian, Arabic and African plates. There is an East Anatolian fault with a length 700 kilometers. Therefore, there is a sufficiently large extent to cause strong shocks.
This does not mean that any earthquake at this moment should be so strong. In fact, as explained in Talk Jenny Jenkinsprofessor of earth sciences at Durham University, received only three earthquakes of magnitude greater than 6 within 250 km of this location since 1970
Unfortunately, this time the earthquake in Turkey and Syria reached numbers that will go down in history. This is sad news, to which, unfortunately, science still has many answers to find.
Source: Hiper Textual