Supermassive black holes, considered the most impressive objects in the universe, Hundreds of thousands to billions of times heavier than the mass of our sun. As we learned in high school, gravity is so strong that nothing, not even light, can escape its pull.
These monsters, hard to imagine given their size and density, can now be assimilated and compared in a new animation released by NASA on its website earlier this month.
i watched it helps to understand the meaning of the term “super” This precedes supermassives at the center of most large galaxies, including our beloved Milky Way.
Which supermassive black holes appear in the NASA video?
There are some supermassive black holes in NASA’s “parade” of supermas, such as Cygnus A, 780 million light-years from Earth, or the “small” black hole at the center of the dwarf galaxy J1601+3113. There was no shortage Sagittarius A*, “our” pet supermassive black hole, “sitting” quietly at the center of the galaxy we live in.
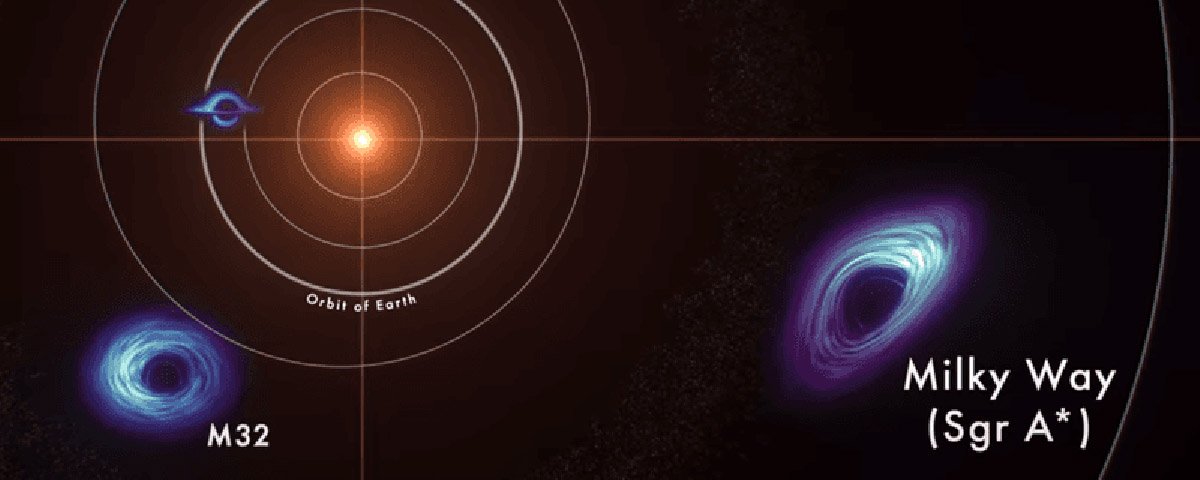
NASA presents two black holes in its “near-Earth supermassive” matter, both located inside the galaxy NGC 7727. But the masses are quite different: one is only 6 million solar masses and the other is more bodied, weighing 150 million suns.
separated by only 1,600 light-years today, The couple will merge in 250 million years. Anyone alive will see incredible gravitational waves.
Two NASA champions?
Finally, two supermassives emerge that certainly combine the super prefix with eligibility, even if they aren’t the best on the list. The first is M87Famous for being the first object of its kind to be directly captured by an international team of scientists in the Event Horizon Telescope project in April 2019.
A media darling, M87 was recently spotted showing off its powerful astrophysical jet to the GMVA, ALMA, and GLT telescopes.
But when it comes to size, nothing compares to TON 618, which today is considered not only the heaviest supermassive black hole but also the heaviest object in the Universe. To be able to hold within itself a mass of about 60 billion times that of the Sun. The good news is that this animal lives so far away: Its light is estimated to be 10.8 billion years old, which is a relief when you consider it being pulled together by relentless gravity.
Source: Tec Mundo
I’m Blaine Morgan, an experienced journalist and writer with over 8 years of experience in the tech industry. My expertise lies in writing about technology news and trends, covering everything from cutting-edge gadgets to emerging software developments. I’ve written for several leading publications including Gadget Onus where I am an author.