If you ask random people what artificial intelligence is, the answers will be different. You might think that these are humanoid robots, like those from movies, others that they are chat bots with whom you can talk, and thirdly, that they are something mysterious or even dangerous.
But we use artificial intelligence every day, without even thinking about it:
- our social media feed feeds us a publication
- The camera on your phone recognizes your face
- the translator translates the text almost instantly
- the voice assistant turns on music according to our decision
- The navigator is planning a route, behind a traffic jam
- a filter is installed in the mail, where is spam, and where is important mail
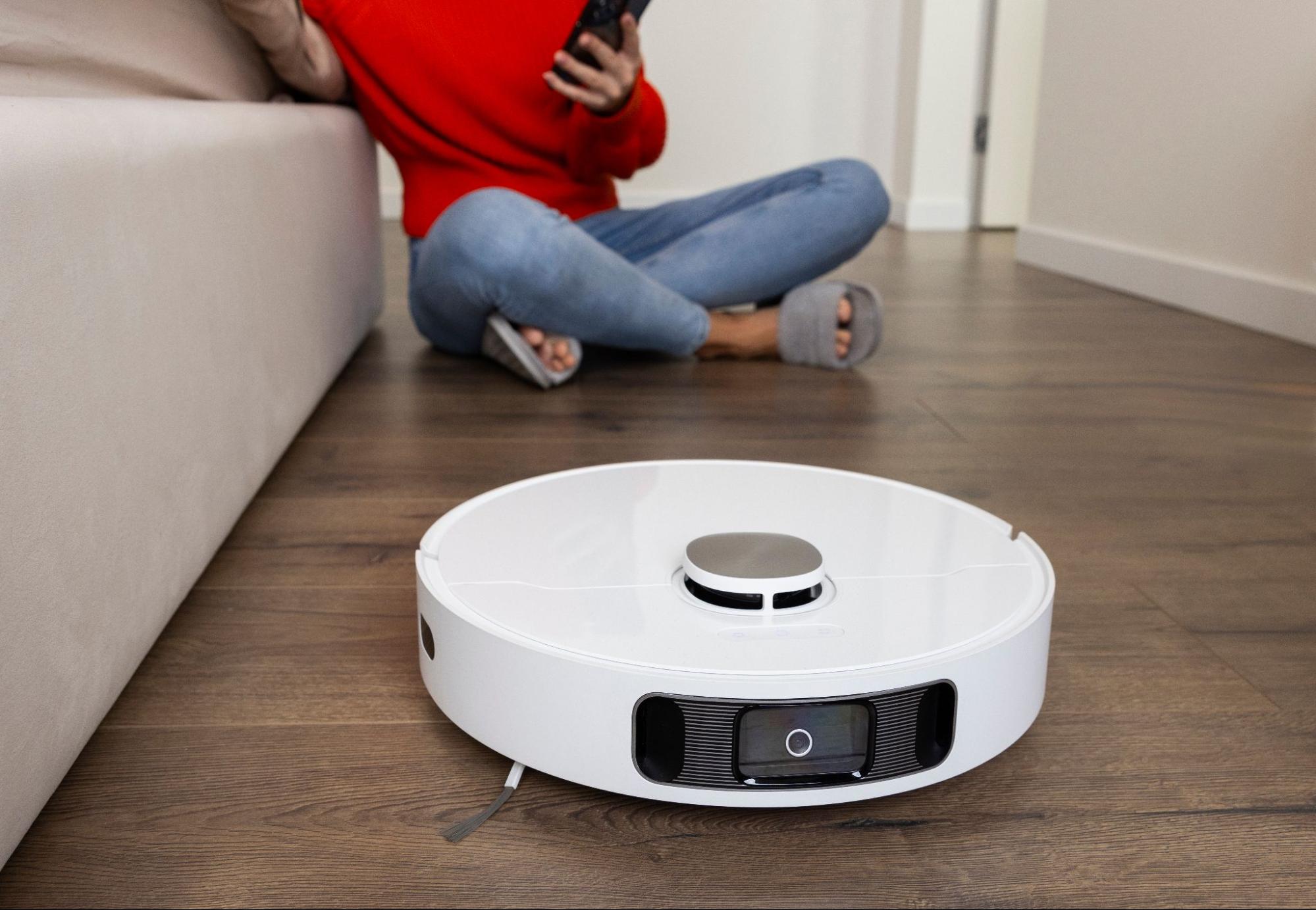
- robot vacuum cleaner cleans apartment according to schedule
- chess program plays chess with us
- The bank’s scoring system decides whether to approve the loan.
The examples listed do indeed relate to AI. But there are also such concepts as machine learning and neural networks. Often all three concepts are used interchangeably. Now we will take a deeper look at what they mean.
To do this, we present three nested dolls:
- The biggest nesting doll is artificial intelligence
- There is a smaller nesting doll inside it – this is machine learning
- and the smallest one is neural networks.
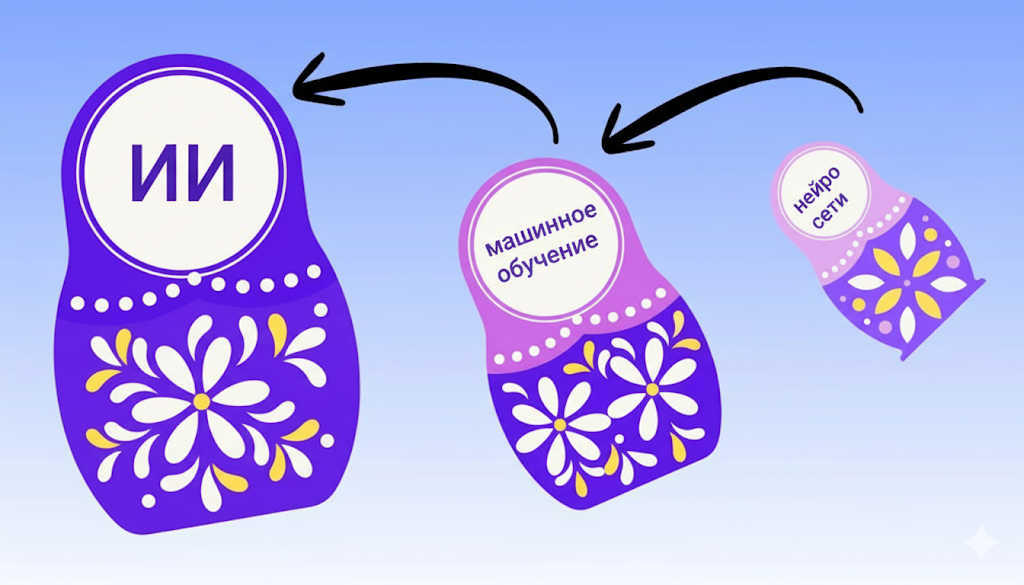
In this case, the nesting dolls symbolize the nesting of concepts, the fact that each previous concept is broader, follows further. Let’s talk in more detail about each of them.
What is artificial intelligence

This is the field of science that deals with the creation of artificial beings. They can imitate the actions of living beings, their thinking process, and sometimes even their appearance. At the same time, the created mechanism cannot have anything living inside it, the main thing is that it looks reasonable and copes. with the assigned tasks.
For example, in 1997, IBM’s Deep Blue chess supercomputer beat world champion Garry Kasparov, playing according to standard tournament rules. Externally, Deep Blue looked like a big one with electronics and weighed about 1.4 tons. Inside this cabinet are 32 processors that could calculate about 200 million chess positions per second.
Deep Blue was already artificial intelligence, but did not yet use machine learning or neural networks, which we will talk about later. To “teach” a computer game of chess, the developers manually input knowledge about chess games into it. And then, during the game, Deep Blue quickly went through the options and found the best solutions. At the same time, he did not study, did not analyze his mistakes, did not improve the game, but simply acted according to the rules.
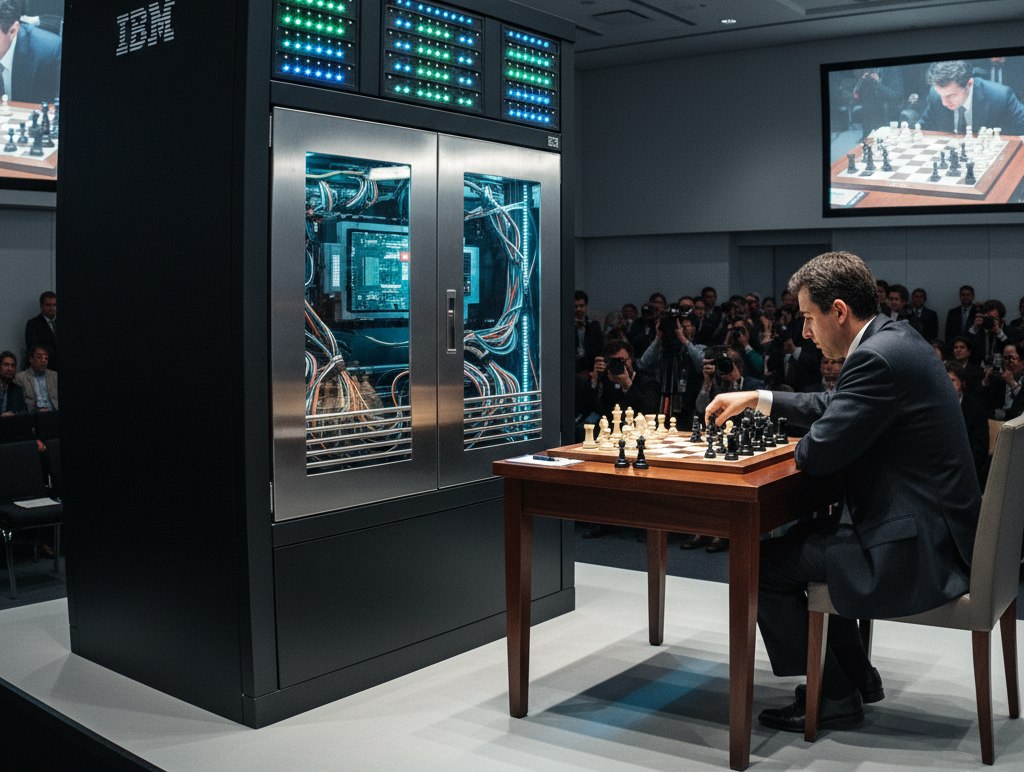

This is how Gemini depicted the match between Kasparov and Deep Blue. In fact, the supercomputer looked like this; the photo can be seen in the archival IBM publication.
The machine’s victory over the strongest chess player on the planet was a big event: media outlets all over the world wrote about it, there were news programs that were shown live on air. But before this, it was believed that chess was the pinnacle of human intelligence, and it would not be possible to beat a computer for a long time. best player.
As a result, Deep Blue not only made a splash, but also drew attention to the development of computing technology in many industries. Similar methods and current interpretations in financial modeling, medical diagnostics, medical care.
Other examples of AI, even before the use of machine learning and neural networks:
- ELIZA – a program created at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology from 1964 to 1967. She simulated a conversation between a therapist and a patient, using predetermined response patterns.
- MITSIN is an expert system created by Stanford University in the mid-1970s. She left it to doctors to diagnose the blood infection and prescribe antibiotics for treatment.
So, AI is a broad concept. It flies in the face of many approaches and methods that help artificial systems look, act, or think. as a person.
What is machine learning
The term “machine learning” is more accurately translated as “teaching machines.” This section within AI deals with the creation of special algorithms. These algorithms are like step-by-step instructions for computer systems: they explain the system how to learn from examples in order to then solve various problems. A system trained in this way is usually called a model.
With machine learning, developers do not prescribe strict rules, but give the system many examples from which it learns to identify patterns. Sometimes they suggest a system that you need to pay attention to.
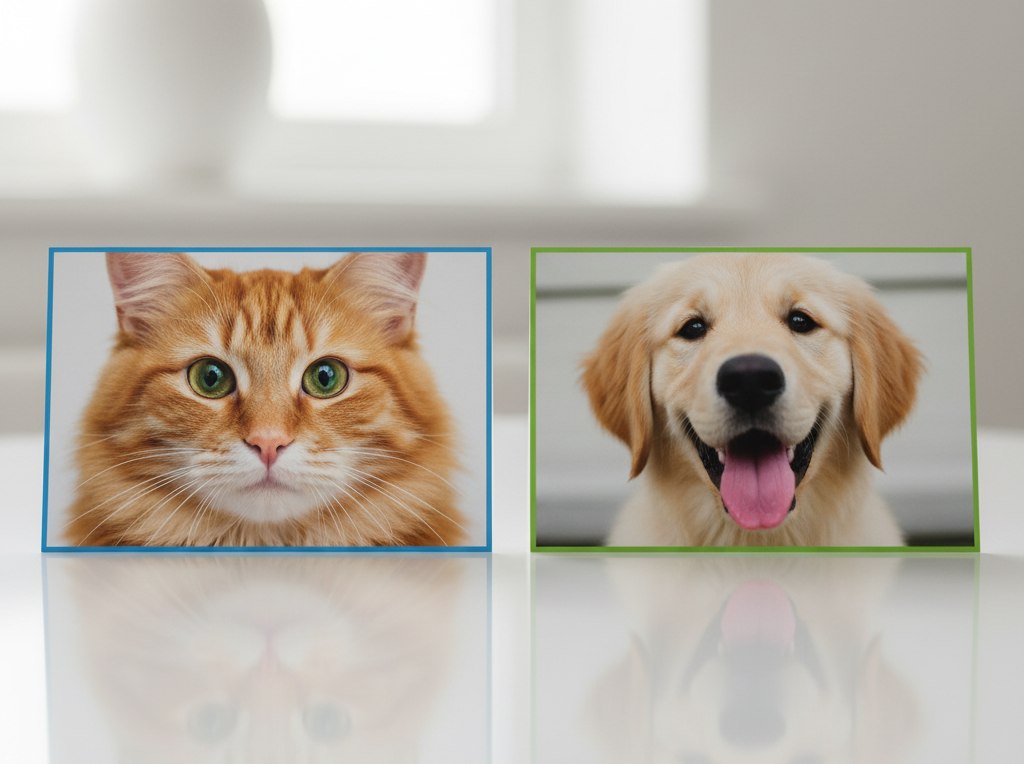
Let’s say the developers wanted the model to distinguish cats from dogs. They provide the system with a large number of images, but at the same time mark where cats are and where dogs are, and also indicate what details to pay attention to: the shape of the ears, the shape of the muzzle, the proportions of the body. With this data, the system must find and make changes to subsequently distinguish between animals on its own.
For example, in 2001, a computer program for filtering spam mail, SpamAssassin, was launched. In addition to other tools, this program uses Bayesian filtering, which is a machine learning method. Thanks to this, the user did not manually write down rules like “if the letter contains the word “winning”, then it is spam.” Instead, it showed examples of good and bad email filters. The model itself analyzed what suspicious words and phrases looked like.
Other examples of AI using classical machine learning:
- Netflix Recommendation System is Netflix’s help algorithm that tells users what movies to watch.
- Amazon Product Recommendations — develop an Amazon algorithm that shows customers suitable products.
Both projects were initially based on classical machine learning, but now also include neural networks.
The peculiarity of machine learning is that the model can be improved based on new data. And the more quality data she receives, the more accurate the results will be.
What is a neural network

Artificial neural networks, or neural networks for short, are a class of machine learning algorithms inspired by the principles of the human brain, its essence, its structure.
A neural network consists of periodic visits to artificial neurons. But these are not the same neurons as in the human brain, mathematical models. Each artificial neuron receives data, performs mathematical calculations and produces the following result. neuron or cook immediately.
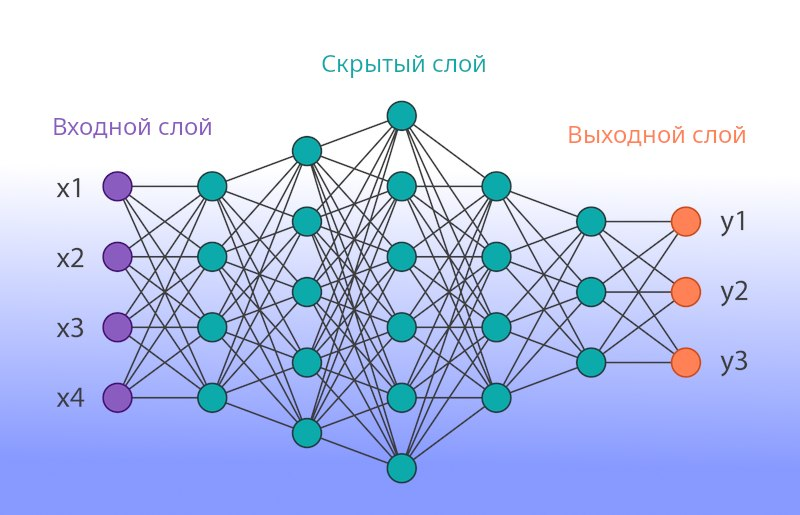
The neurons in the network are organized in the following order:
- input layer receives information
- hidden layers process it
- the output layer produces the result
In 2012, the image database for training algorithms in the computer competition ImageNet conducted an annual survey, in which the AlexNet algorithm won, and by a large margin. AlexNet was a deep convolutional neural network, because, as we remember, there are connections of a family of different neural networks. And it was the beginning of this victory that marked the achievements of science in the field of neural networks.
Other examples of AI using neural networks:
- Generative Pretrained Transformer or ChatGPT for short, is a large language model that in 2025 will be able to translate texts, read data from images, restrict images, and search the Internet in 2025 by any user using text and voice.
- Alice is a virtual voice assistant from Yandex. She can maintain a coherent dialogue with the user, search the Internet, and control devices in smart mode. home, set alarms and timers, build routes in the navigator, order a taxi and even play games with the user.
The main strength of neural networks is that they are self-learning. They are also good at working with unstructured data: pictures, sounds, text. Traditional machine learning algorithms did not cope well with this, but neural networks learned to recognize faces and handwriting, translate texts, and create images or videos based on descriptions.
A simple scheme that allows you to ignore the difference once and for all
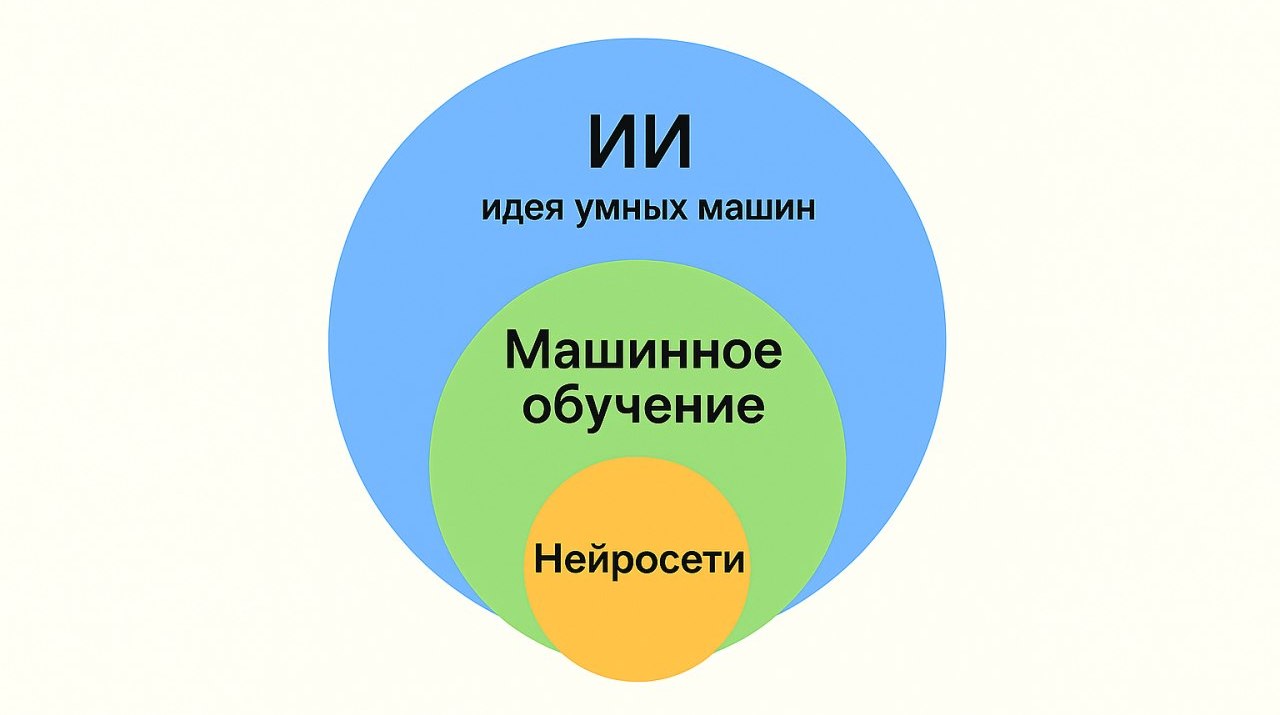
Remember this:
- AI is the idea of smart machines in general, in all variations and manifestations, using all possible methods.
- machine learning – algorithms, ability to work from personal experience
- neural networks – department of machine learning, algorithms inspired by the work of the brain
In short: all machine learning is AI, but not all AI is machine learning. And it’s the same with neural networks: any neural network is AI, but not every AI is a neural network.
In this article I will explain how to train a neural network…
4
1
1
Source: Iphones RU
I am a professional journalist and content creator with extensive experience writing for news websites. I currently work as an author at Gadget Onus, where I specialize in covering hot news topics. My written pieces have been published on some of the biggest media outlets around the world, including The Guardian and BBC News.











