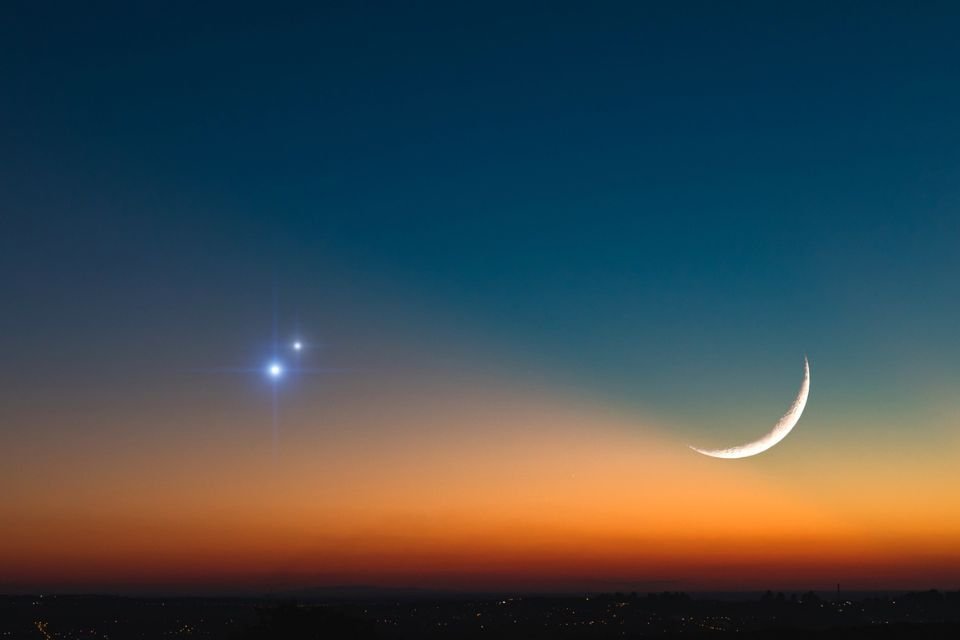
planet venus returned to the morning sky, is at inferior conjunction (aligned between the Earth and the Sun) after several months, meaning it is not visible to the naked eye. But its return was triumphant: in the early hours of this Monday (11), the planet was in conjunction with the thin, waning Moon, illuminated by 12%, and was visible as a “lighthouse” about two to three hours before the sun. visible.
The good news is that this phenomenon, which can be easily seen with the naked eye or binoculars, will repeat throughout September. when the so-called “morning star” can be admired in its entirety at the end of the morning. It will be at a very low position relative to the eastern horizon in the direction where the Sun rises.
The conjunction of the Moon and Venus means that the two celestial objects appear seemingly close together in the sky because they are observed in the same region of the celestial sphere. Venus will continue to be visible around 4:30 a.m. and will rise higher. until it reaches its brightest point on September 19, when it will be magnitude -4.8.It is 23 times brighter than Sirius, which is known to be the brightest in the sky.
How to observe the planet Venus?
By the end of September, Venus will become increasingly brighter, but will decrease in size. At the beginning of the month, only 12% of the planet was illuminated. but on September 26, this number will reach 36%. However, since it will be 27 million kilometers away from Earth, it will appear one-third smaller than at the beginning of the month.
The night of September 14th to September 15th will mark the change of the lunar phase from waning to new, and is the best time of the month to observe galaxies and star clusters, as the Full Moon dwarfs fainter objects. A clue to tell if you are observing a planet or a star is to observe whether the object blinks or not. If they are not blinking, they are planets. Two more will be visible in September: Saturn and Jupiter.
Venus will be visible to the naked eye, but a 10×50 binocular can provide a field of view of 6-7°, which is typical of high magnification telescopes that focus on only a small portion of the sky that includes the planet under study. During observation, Venus will appear pale yellow. If you’re using an astronomical app, simply point your device at the part of the sky where the target is located to identify it.
Stay informed about upcoming astronomical events on TecMundo. If you want, take the opportunity to discover which are the best applications to always know which month it is.
Source: Tec Mundo
I’m Blaine Morgan, an experienced journalist and writer with over 8 years of experience in the tech industry. My expertise lies in writing about technology news and trends, covering everything from cutting-edge gadgets to emerging software developments. I’ve written for several leading publications including Gadget Onus where I am an author.