Although the theory of spontaneous generation has been rejected since the 17th century, explaining how life emerged from nonliving remains one of the most difficult problems of modern science. Maybe that’s why there have never been so many Scientific theories that suggest answers based on chemistry, physics, astrobiology, biochemistry, and other propositions.
Although science itself does not yet have a definitive answer, some currently accepted hypotheses Give us an insight into how life arose on planet Earth. Find out what they are below.
Discover 7 theories about the origin of life on Earth
1. Abiogenesis: Life on Earth began with lightning
Although the idea of a non-biological origin of life has been largely rejected by modern science, a 1953 experiment by Stanley Miller and Harold Urey showed that under certain conditions, Even in a sterile environment, complex organic molecules can be formed from simple molecules.
In the study currently discussed, The glow of life was triggered by a spark of electricity, produced amino acids and sugars in an atmosphere inside a glass ball containing water, methane, ammonia and hydrogen.
2. Panspermia: Are we all Martians?

“Panspermia”, proposed by Anaxagoras in the 5th century BC, suggests that life did not begin directly here on Earth, but that “seeds” in the form of microorganisms came from space. hitchhiking on rocks regularly thrown off Mars by cosmic impacts.
Others claim that comets from other star systems may have brought life to Earth. But even if this hypothesis is one day confirmed, the doubt will change to: What is the origin of life brought by space objects to our planet?
3. Hydrothermal vents: Life on Earth emerged from deep waters

A 2008 study published in the journal Nature suggested that hydrothermal vents, naturally occurring structures at the bottom of the oceans, may be the origin of life. According to scientists, Water heated to extreme temperatures leaking from the interior of the Earth’s crust may have brought to Earth the energy and chemicals necessary for the formation of the first life forms..
Interestingly, the theory of the origin of life in hydrothermal vents has not yet been refuted but continues to be investigated, a very difficult and expensive process, as it requires the use of special ships equipped with ROVs (remotely operated vehicles). manned submarines.
4. The RNA world led to the emergence of life on Earth
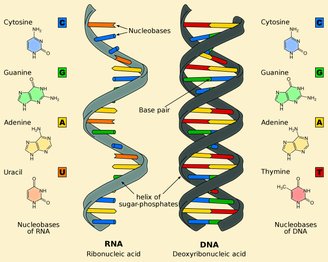
Based on Charles Darwin’s proposition that evolution is “descent with modification”, scientists at the Salk Institute in the USA have recently provided new information about the origin of life. The hypothesis is: There was an ‘RNA world’ even before cells, proteins and DNA existedwhere vital components evolve on a simpler scale.
Although this theory has not yet been disproved, it continues to be tested and researched, but even if confirmed, it would turn the question of the origin of life into RNA.
5. Icy world: Life may have emerged in a frozen ocean

The theory that advocates the formation of life under a sheet of ice that covered the Earth’s oceans three billion years ago suggests that ice, in addition to increasing the synthesis of some important molecules, may have protected some fragile organic compounds from ultraviolet light and cosmic influences.
Although still debated, the glaciation theory has been challenged by some recent research. such as the discovery of microorganisms in rocks more than three billion years old (pre-glacial periods) and the hypothesis of hydrothermal vents remaining active during glaciation in the deep oceans.
6. Lipid Bubbles: A Simple and Oily Start
The theory of spontaneous lipid bubble formation, also known as the protocell hypothesis, suggests that in prebiotic aquatic environments such as Earth’s early oceans, these oil molecules suddenly began to come together and form bubbles.
The organic molecules encapsulated in them began to produce complex chemical reactions. Over time, these complex molecules gave rise to the first cells. The theory continues to be tested, but it does not explain, for example, how the first lipids appeared on Earth.
7. LUCA: The last universal ancestor
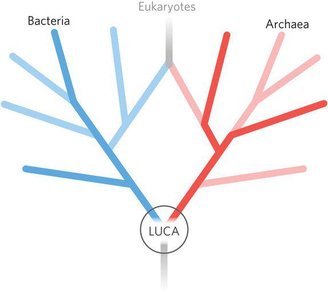
LUCA, abbreviation for “last universal common ancestor” In English, LUCA, a microbe that lived four billion years ago, did not breathe air, produced its own food, and lived in ocean depths rich in iron and sulfur, is a complementary theory to the theory of hydrothermal vents.
Metabolizing hydrogen, carbon dioxide and nitrogen, LUCA converted these elements into ammonia and became the common ancestor of all life forms on our planet, which became increasingly diverse over billions of years. But some questions are still unanswered: How did LUCA come about? Where did he really live? And most importantly, how did it multiply?
Did you like the content? So stay updated with more topics like this on TecMundo and seize the opportunity to understand the role of gravitational waves in the origin of life.
Source: Tec Mundo
I’m Blaine Morgan, an experienced journalist and writer with over 8 years of experience in the tech industry. My expertise lies in writing about technology news and trends, covering everything from cutting-edge gadgets to emerging software developments. I’ve written for several leading publications including Gadget Onus where I am an author.












